Embed presentation
Downloaded 84 times



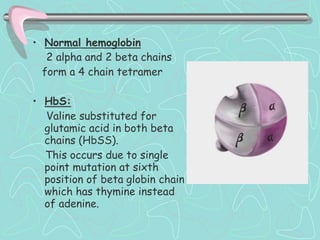
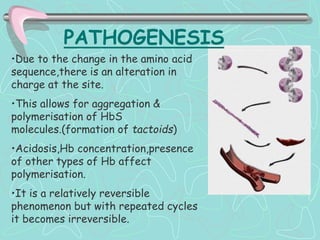



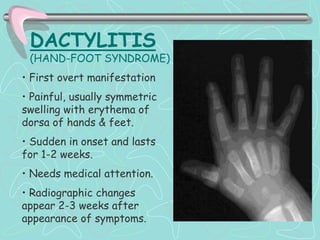

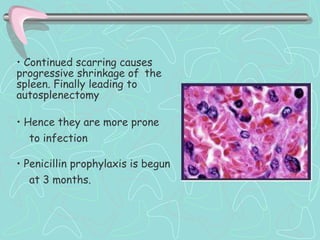

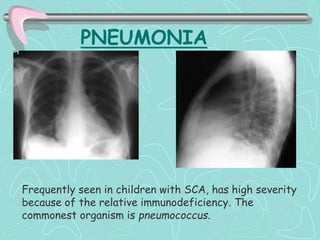




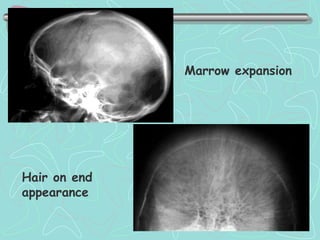

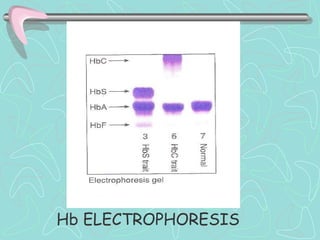
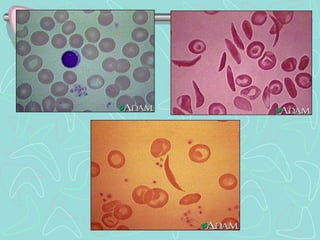















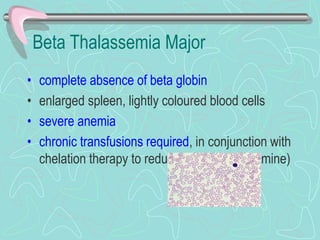

Hemoglobinopathies are inherited abnormalities of hemoglobin synthesis characterized by structurally abnormal hemoglobin variants. Sickle cell anemia is the prototype hemoglobinopathy caused by a single point mutation that results in production of abnormal hemoglobin S. This leads to polymerization of hemoglobin S molecules under conditions of low oxygen, causing distortion of red blood cells into a sickle shape and various complications. Other hemoglobinopathies include Hemoglobin C, E, and D disease, which typically have milder phenotypes.







































