Embed presentation
Downloaded 299 times



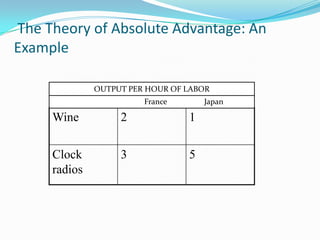



Adam Smith first proposed the theory of absolute advantage in his 1776 publication "An Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Nations" as a rebuttal to mercantilism. The theory argues that countries should specialize in and export goods they can produce at a lower relative cost than other nations, and import goods that other nations can produce at a lower cost, resulting in more global production and wealth overall. An example shows that France has an absolute advantage in wine production while Japan has an advantage in clock and radio production based on their differing labor outputs.





