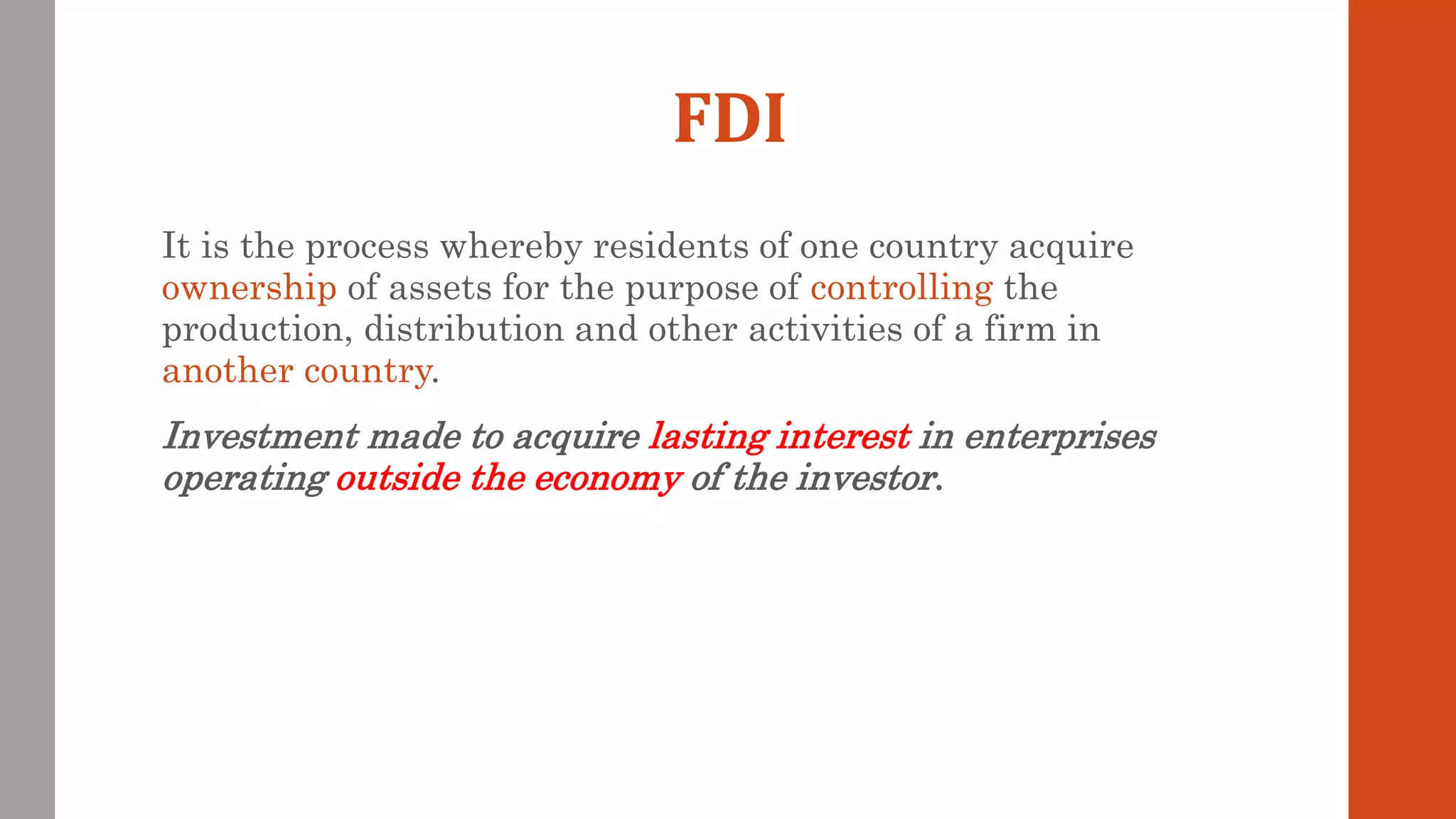
This document summarizes the types and motivations of foreign direct investment. It discusses inward and outward foreign direct investment, and the factors that encourage and restrict them. It also describes different types of foreign direct investments like greenfield investments, mergers and acquisitions, horizontal and vertical foreign direct investments. Finally, it outlines the main motivations for foreign direct investment, including resource seeking, market seeking, efficiency seeking and strategic asset seeking.