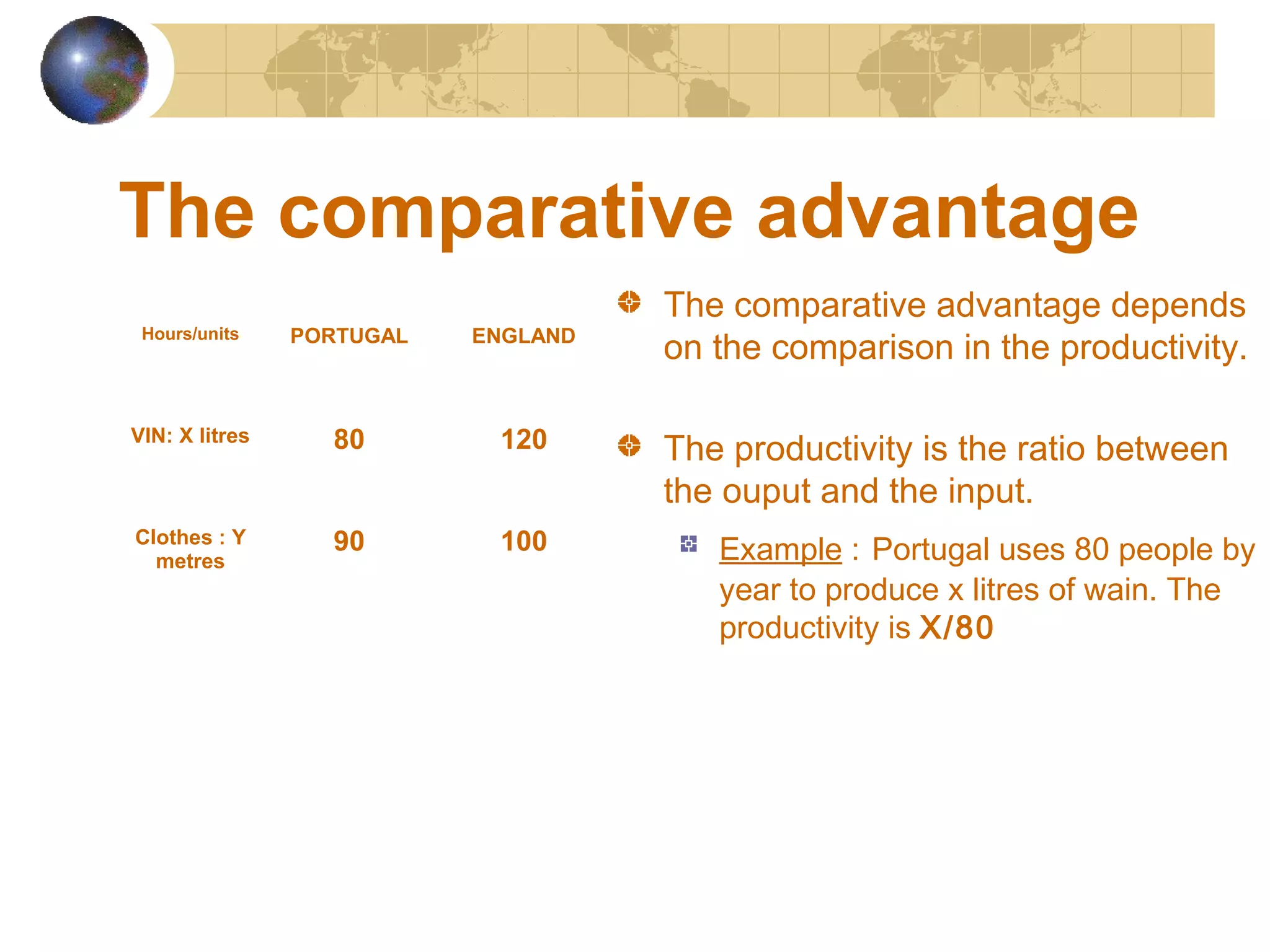
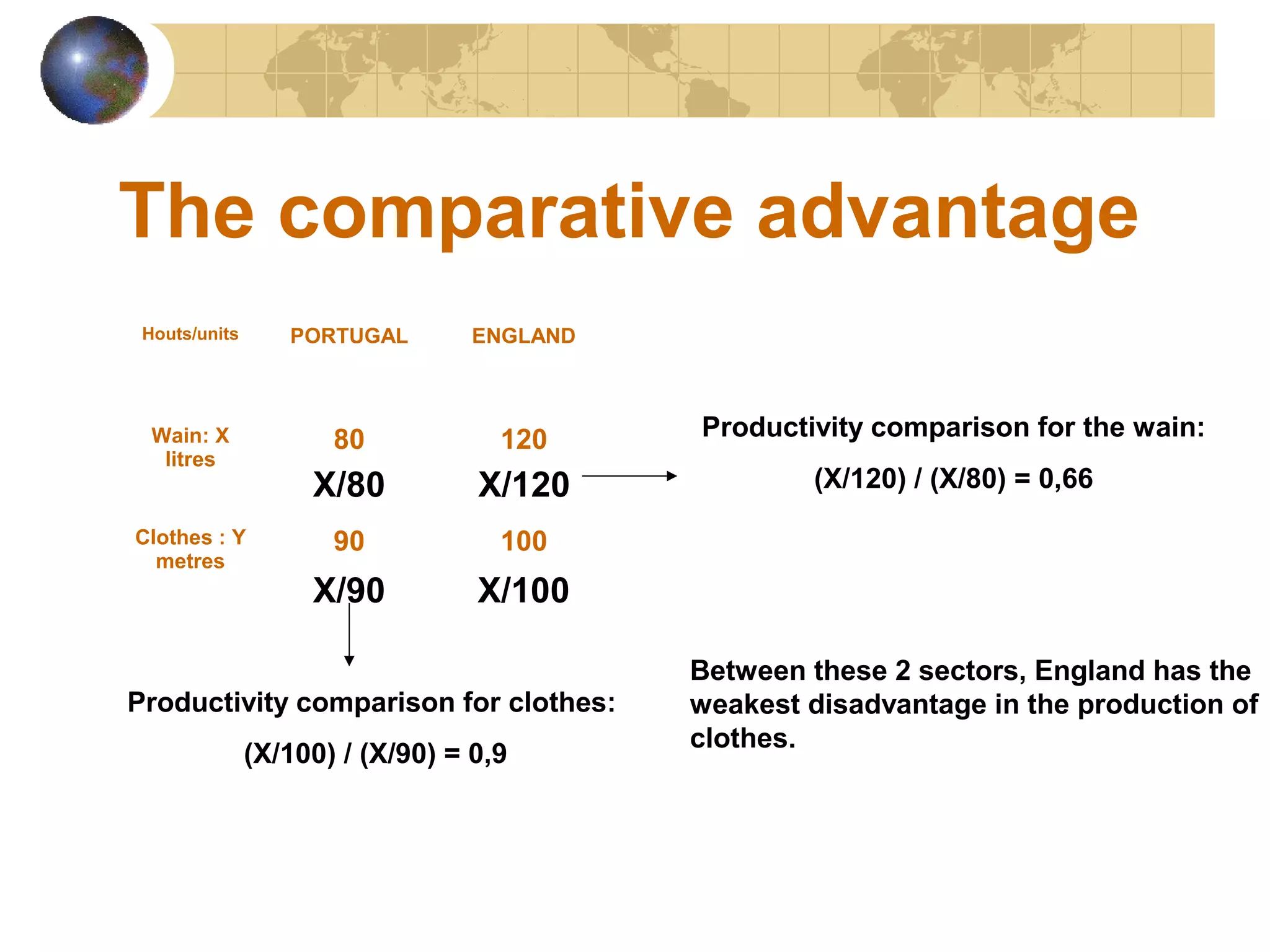
The document discusses comparative advantage and how countries can benefit from international trade. It explains that countries should specialize in producing goods where they have a comparative rather than absolute advantage. This is determined by comparing productivity ratios across sectors. The example shows Portugal has a comparative advantage in wine and England in clothes. Specializing allows each country to produce more of its strong good and trade, benefiting both countries through increased production possibilities and saving labor.