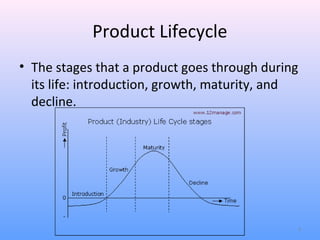
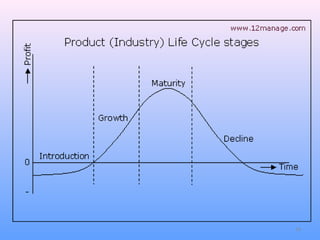
The document discusses the product lifecycle (PLC) which consists of four stages: introduction, growth, maturity, and decline. During the introduction stage, products are initially promoted to raise public awareness using either a penetration or skimming pricing strategy. In the growth stage, heavy advertising is used to increase sales and market share. The maturity stage sees sales growth stabilize. Finally, the decline stage occurs when sales begin to fall as customers are satisfied or replaced by newer products. However, the document notes that not all products follow the same cycle and stages may be skipped. Close monitoring is needed throughout a product's lifecycle.