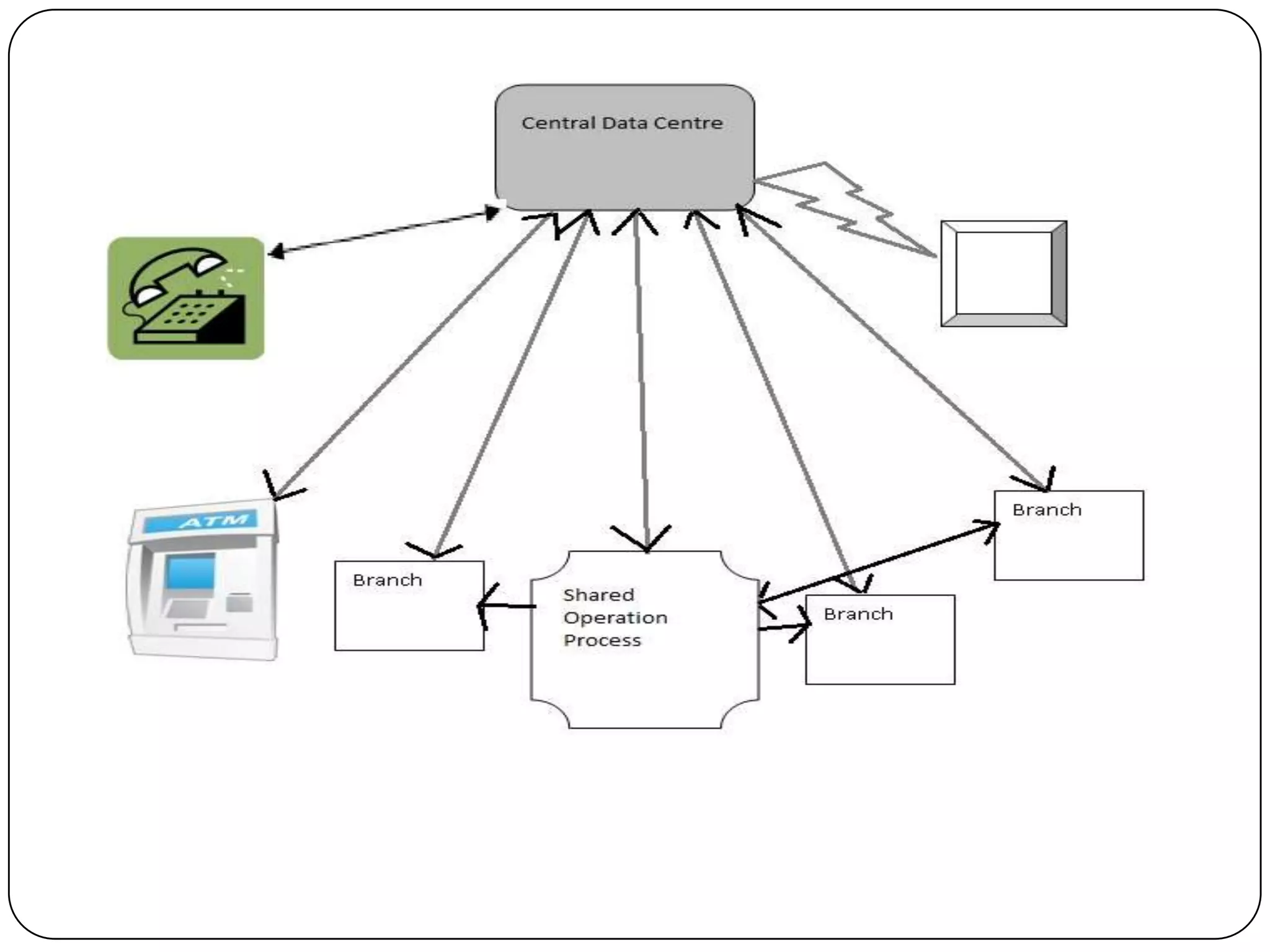
The document discusses the core banking solution implemented by State Bank of India (SBI), the largest bank in India. SBI implemented a core banking solution from Financial Network Services of Australia to enable online, real-time banking across its large network of over 16,000 branches. The solution provides 24/7 banking, strengthens management information systems and decision support, and allows for new delivery channels like ATMs and internet banking. Tata Consultancy Services customized the software for SBI's needs and led the implementation project.