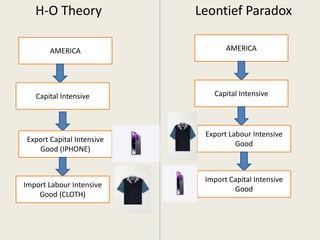
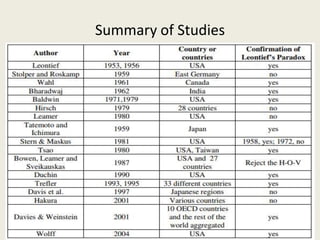
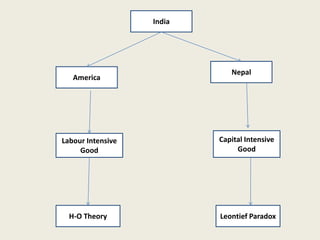
Wassily Leontief was an economist who won the Nobel Prize for his research on input-output analysis. He is known for discovering the Leontief Paradox, in which his empirical tests of trade theory in 1947 and 1951 found that the US exported more labor-intensive goods and imported more capital-intensive goods, contrary to what economic theory predicted for the highly capital-abundant US economy at the time. Leontief's findings challenged mainstream trade theories and sparked debate around alternative explanations.