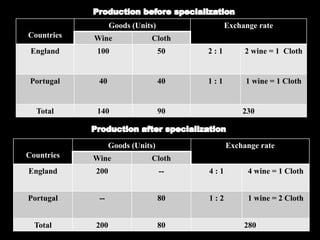
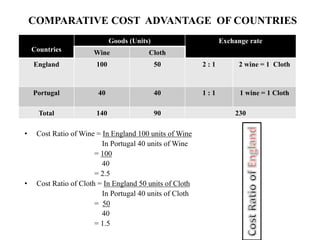
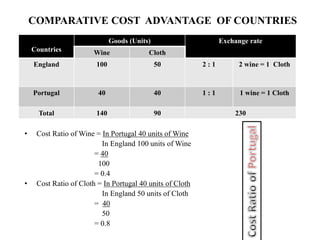
David Ricardo originated the theory of comparative cost advantage in his 1817 book. The theory states that countries will export goods that they have a lower relative production cost in and import goods with higher relative costs, even if one country may have an absolute cost advantage in all goods. The theory assumes two countries and goods, homogeneous and mobile factors of labor, no transportation or trade barriers, and constant returns to scale. England has a lower relative cost (cost advantage) in cloth and Portugal has a lower cost in wine, so each country specializes and gains from trade by exporting their lower cost good and importing the other good. However, the theory makes unrealistic assumptions and does not consider all real-world complexities of international trade.