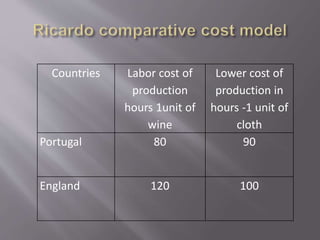
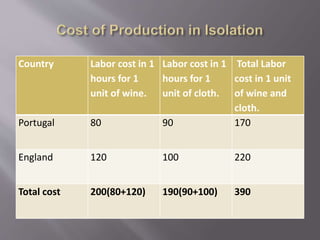
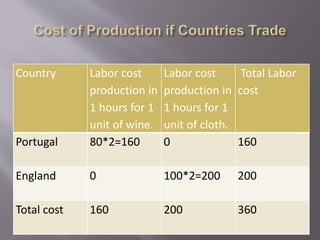
The document summarizes David Ricardo's theory of comparative advantage. It explains that according to Ricardo, countries can benefit from trade even if they do not have an absolute advantage in producing goods, as long as they have a comparative advantage in at least one good. This is illustrated using data showing that while England has higher absolute costs of production than Portugal for both wine and cloth, it has a lower relative production cost for cloth, giving it a comparative advantage. International trade allows both countries to specialize in the goods they have a comparative advantage in, increasing total world output.