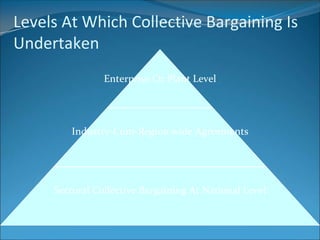
This document provides an overview of collective bargaining, including its definition, evolution, types, process, agreements, levels, conditions for success, trends, and perceptions. Collective bargaining is a negotiation process between labor unions and employers to determine wages, hours, rules and other conditions of employment. It aims to find common ground to reconcile conflicting interests through proposals and counterproposals. The key aspects covered include preparation, discussion, proposals, bargaining and settlement. [/SUMMARY]