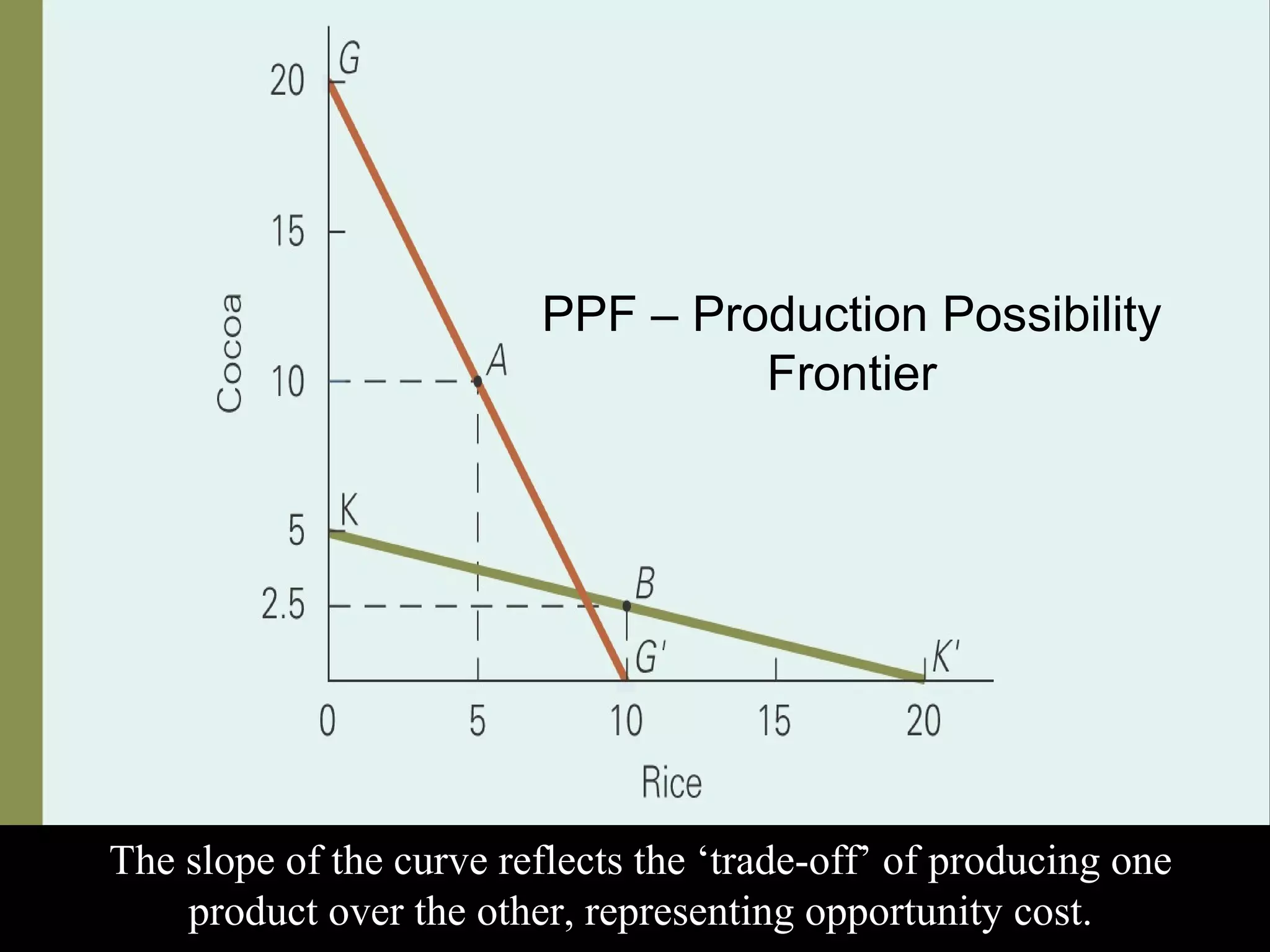
International trade involves the exchange of goods, services, and capital across borders, with increasing significance in modern economies. The theory of absolute advantage, proposed by Adam Smith, emphasizes that countries should specialize in producing goods for which they have efficiency advantages, thus promoting free trade and increasing overall wealth. While this theory offers benefits such as higher productivity and living standards, it has limitations including its narrow focus on labor and assumptions about exchange rates and production capabilities.