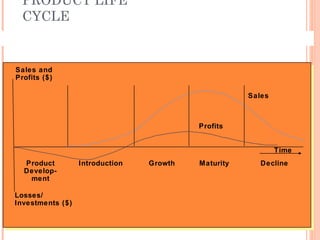
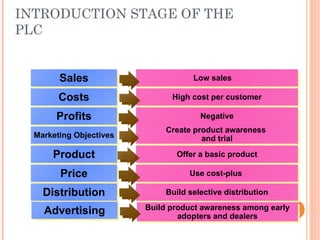
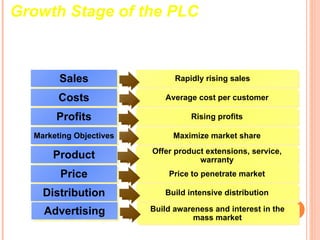
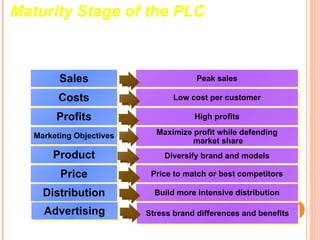
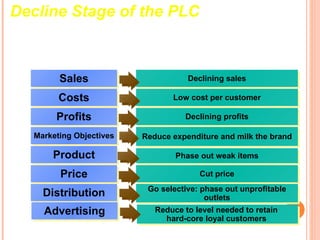
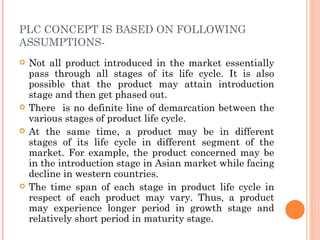
The document discusses the product life cycle, which consists of four stages: introduction, growth, maturity, and decline. Each stage is characterized by different sales volumes, costs, profits, and marketing objectives. The introduction stage involves building product awareness at high costs and negative profits. Growth sees rapidly rising sales through expanded distribution and lower prices. Maturity reaches peak sales with efforts to maximize profits and defend market share. Finally, decline has falling sales and profits as the product is phased out.