The document discusses the ABO blood group system, including its discovery, genetics, biochemistry, antigens, antibodies, and implications for transfusion. Some key points:
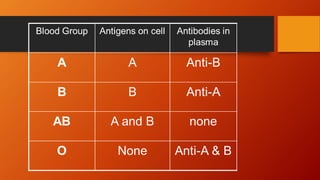
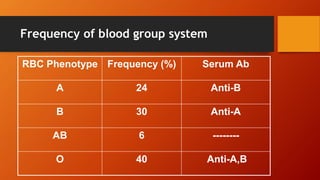
- Karl Landsteiner discovered the main ABO blood groups (A, B, AB, O) in 1900. The ABO blood type is determined by alleles at a single gene locus.
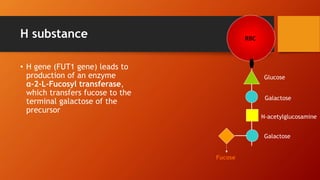
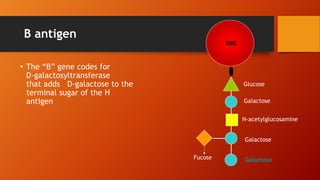
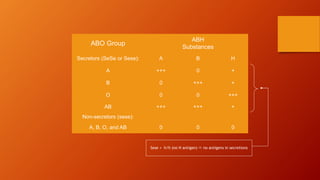
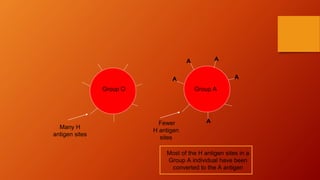
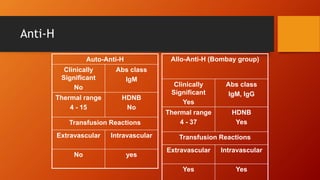
- The antigens are carbohydrate structures on red blood cells. People naturally produce antibodies against antigens they lack.
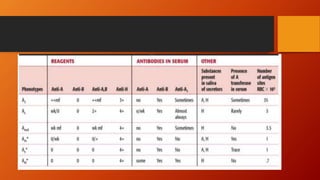
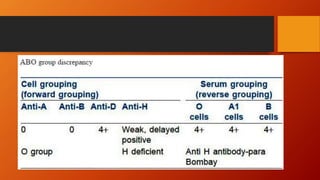
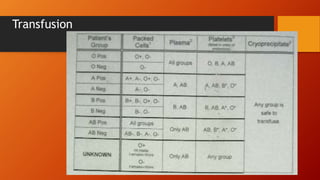
- ABO typing must be accurate to avoid transfusion reactions. Discrepancies can occur due to weak subgroups, diseases, or test issues. Resolving discrepancies helps ensure patient and donor safety.