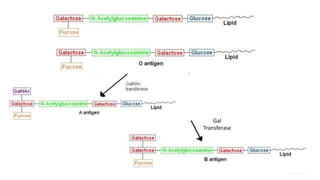
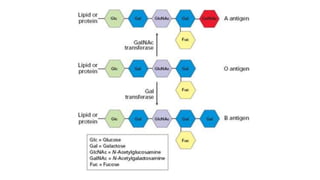
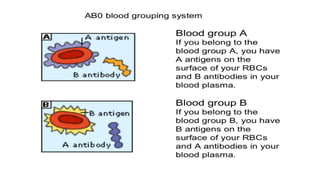
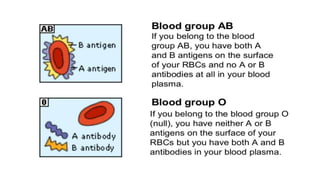
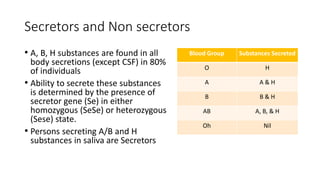
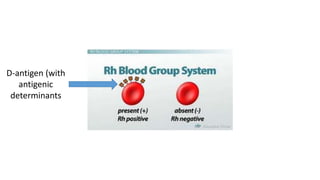
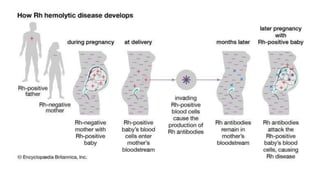
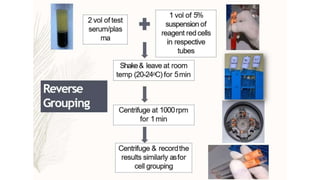
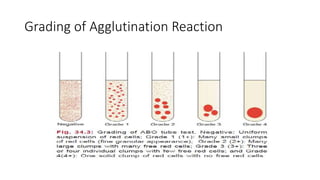
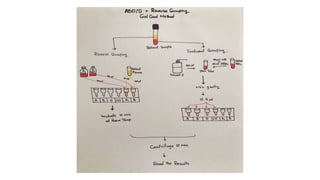
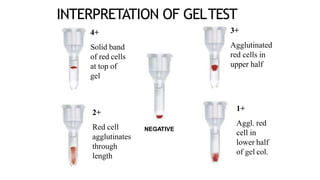
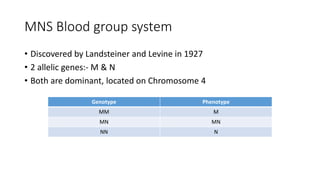
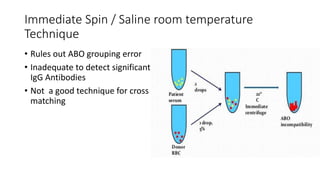
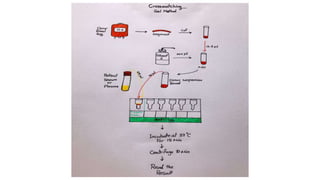
The document discusses blood grouping and cross-matching, focusing on agglutinogens (antigens on red blood cells) and agglutinins (antibodies in plasma), highlighting the ABO blood group system and its historical significance. It details the production of ABO antigens, H-deficient phenotypes, and various blood group systems including the Rh factor, along with methods for blood grouping testing such as slide, tube, and gel card techniques. The document also addresses clinical implications, including transfusion reactions and the importance of compatibility testing.