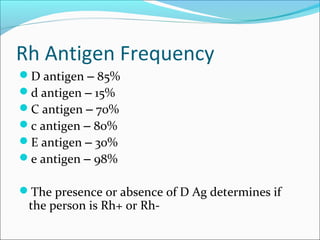
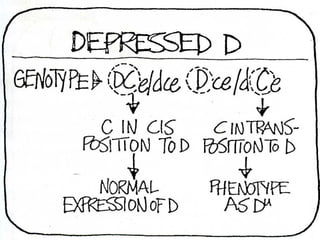
The Rh blood group system is complex, with over 45 antigens. The RhD gene encodes the highly immunogenic D antigen, which is the most important antigen of the Rh system. Approximately 85% of people are RhD positive, while 15% are RhD negative. The Rh system is the second most important blood group system after ABO in transfusion medicine due to the potential for alloimmunization against the D antigen during pregnancy or transfusion. Alloimmunization to the D antigen can cause hemolytic disease of the newborn.