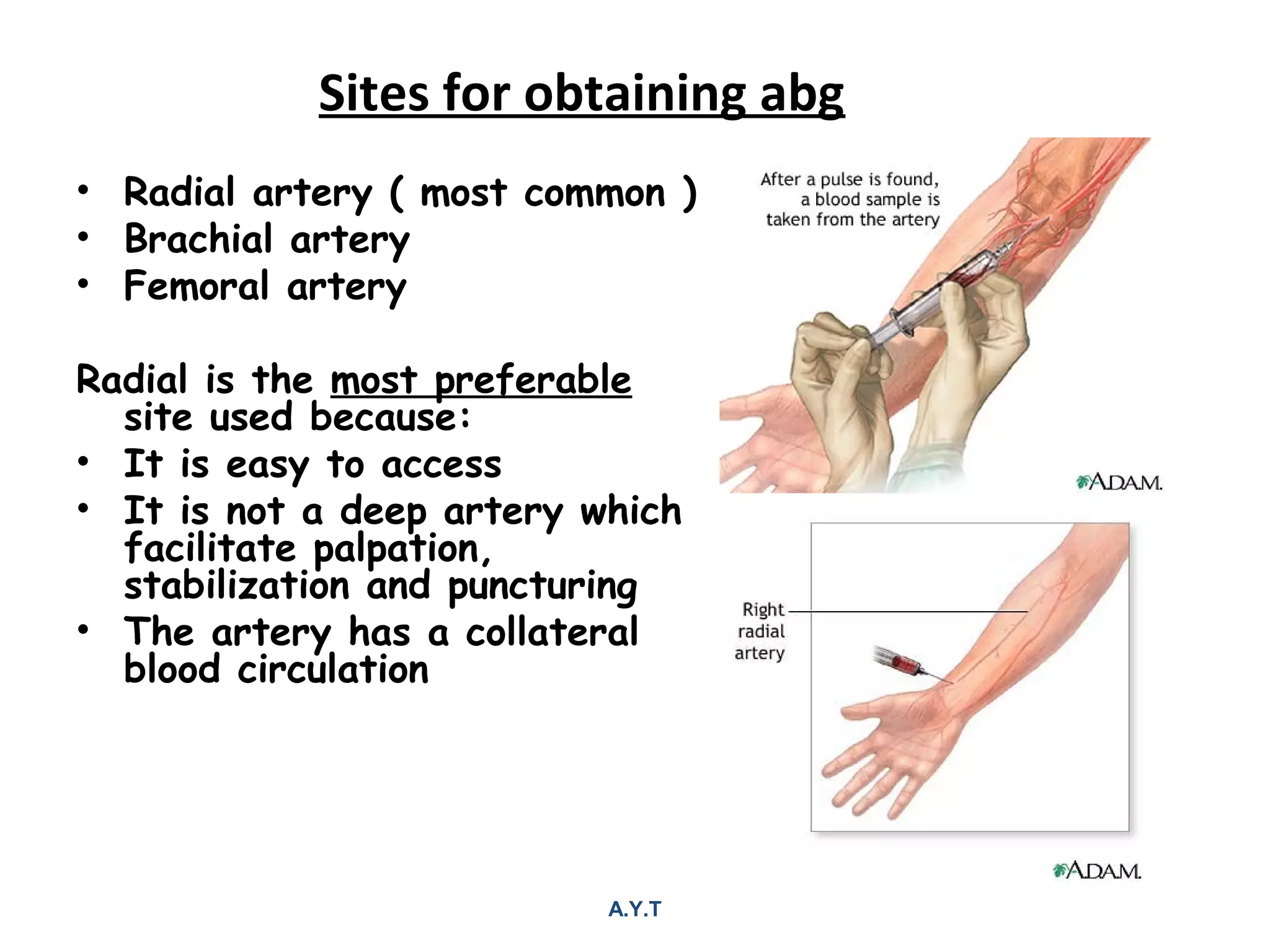
1. Arterial blood gas analysis involves drawing an arterial blood sample to measure pH, PCO2, PO2, and HCO3 levels. It is used to diagnose acid-base imbalances and respiratory disorders.
2. Key steps in analyzing an ABG result include determining if the pH is acidic or alkaline, identifying the primary disorder, assessing the degree of compensation, and calculating anion and delta gaps if metabolic acidosis is present.
3. Common causes of acid-base imbalances include respiratory acidosis/alkalosis from lung disease and metabolic acidosis/alkalosis involving the kidneys. Mixed disorders with both respiratory and metabolic components can also occur.
















![Calculation of pH
203.0
log10.6 3
PaCO
HCO
pH
×
+=
−
[ ] −
+
×=
3
2
24
HCO
PaCO
H
Henderson-
Hesselbach
equation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meenaabg-170228051905/75/ABG-18-2048.jpg)


![Step 4:
Calculation of compensation
Mean "whole body" response equations for simple acid-base disturbances.
Note: The formula calculates the change in the compensatory parameter.
Disorder pH Primary
change
Compensatory
Response
Equation
Metabolic
Acidosis
↓ ↓ [HCO3
-
] ↓ PCO2
ΔPCO2
≈ 1.2 × ΔHCO3
Metabolic
Alkalosis
↑ ↑ [HCO3
-
] ↑ PCO2
ΔPCO2
≈ 0.7 × ΔHCO3
Respiratory
Acidosis
↓ ↑ PCO2
↑ [HCO3
-
] Acute:
ΔHCO3
-
≈ 0.1 × ΔPCO2
Chronic:
ΔHCO3
-
≈ 0.3 × ΔPCO2
Respiratory
Alkalosis
↑ ↓ PCO2
↓ [HCO3
-
] Acute:
ΔHCO3
-
≈ 0.2 × ΔPCO2
Chronic:
ΔHCO3
-
≈ 0.5 × ΔPCO2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meenaabg-170228051905/75/ABG-21-2048.jpg)


![Step 3-4: Is there appropriate
compensation?
Metabolic Acidosis
Winter’s formula: Expected pCO2 = 1.5[HCO3] + 8 ± 2
OR
∆ pCO2 = 1.2 (∆ HCO3)
If serum pCO2 > expected pCO2 -> additional
respiratory acidosis and vice versa
Metabolic Alkalosis
Expected PCO2 = 0.7 × HCO3 + (21 ± 2)
OR
∆ pCO2 = 0.7 (∆ HCO3)
If serum pCO2 < expected pCO2 - additional respiratory
alkalosis and vice versa](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meenaabg-170228051905/75/ABG-24-2048.jpg)

![Contd…
AG corrected = AG + 2.5[4 – albumin]
If there is an anion Gap then calculate the
Delta/delta gap (step 6) to determine
additional hidden nongap metabolic acidosis
or metabolic alkalosis
If there is no anion gap then start analyzing
for non-anion gap acidosis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meenaabg-170228051905/75/ABG-26-2048.jpg)

![Step 5: Calculate the “gaps”
Anion gap = Na+
− [Cl−
+ HCO3
−
]
Δ AG = Anion gap − 12
Δ HCO3 = 24 − HCO3
Δ AG = Δ HCO3
−
, then Pure high AG Met. Acidosis
Δ AG > Δ HCO3
−
, then High AG Met Acidosis + Met. Alkalosis
Δ AG < Δ HCO3
−
, then High AG Met Acidosis + HCMA](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meenaabg-170228051905/75/ABG-28-2048.jpg)





