Embed presentation
Downloaded 189 times





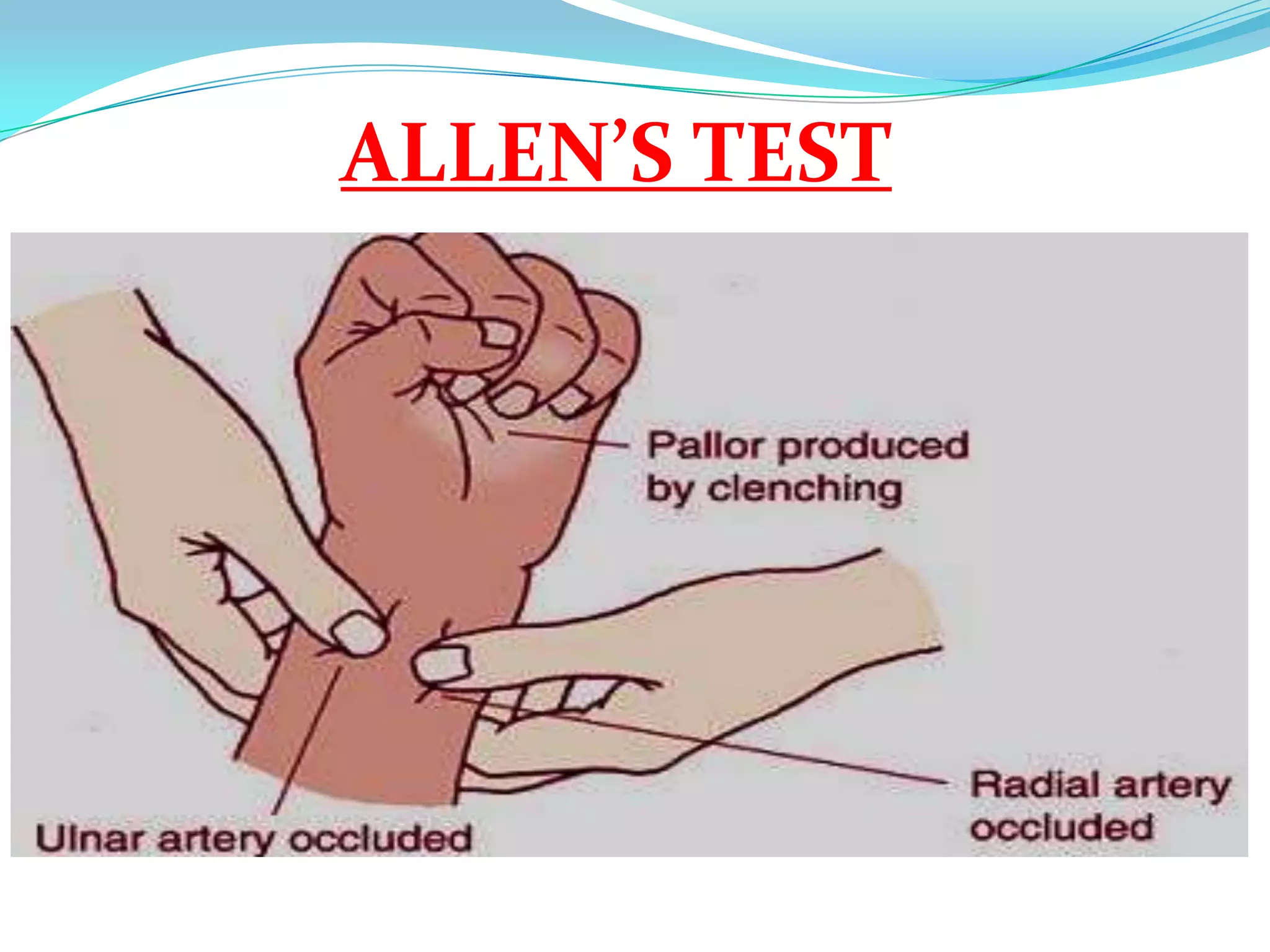
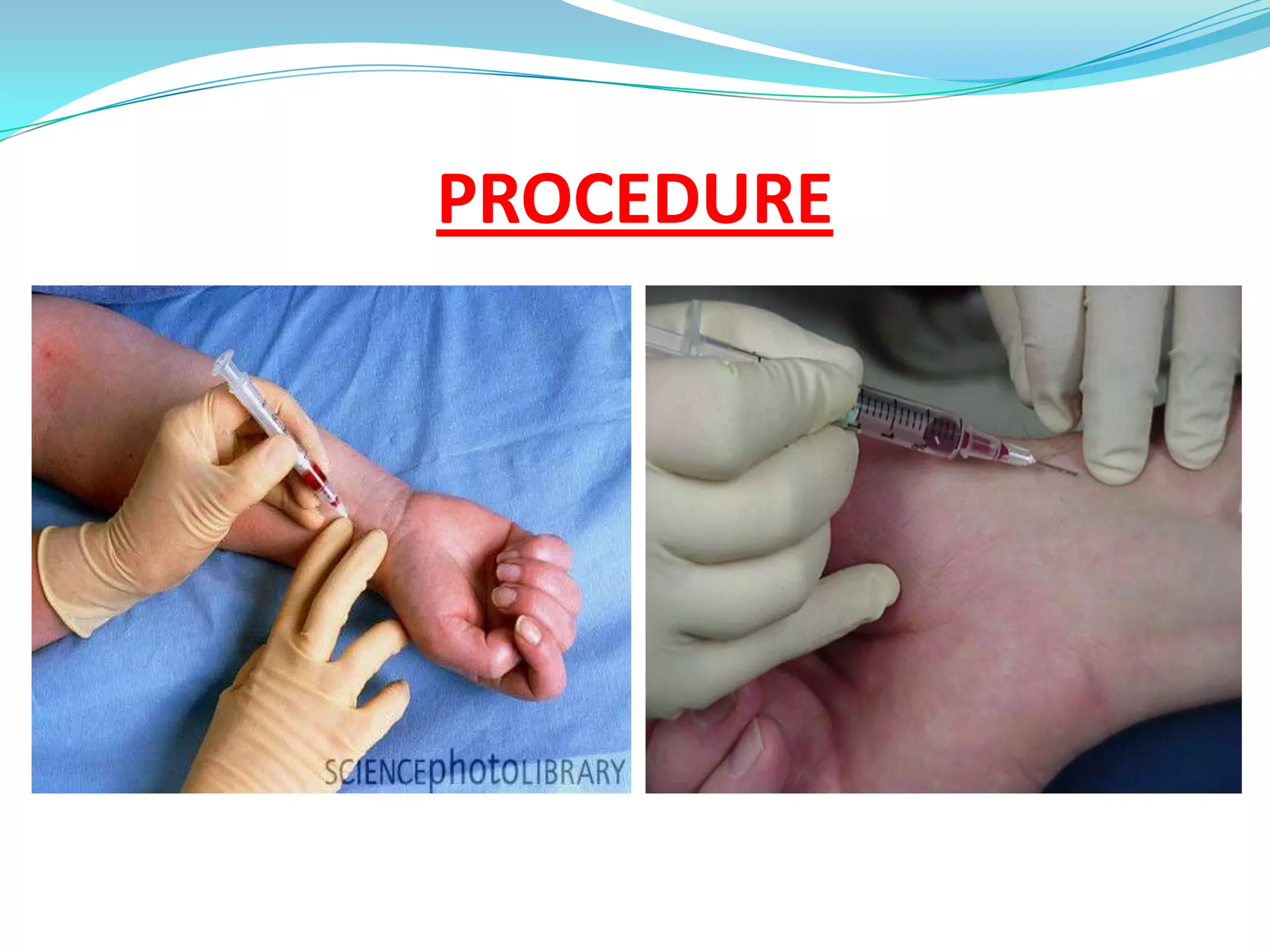
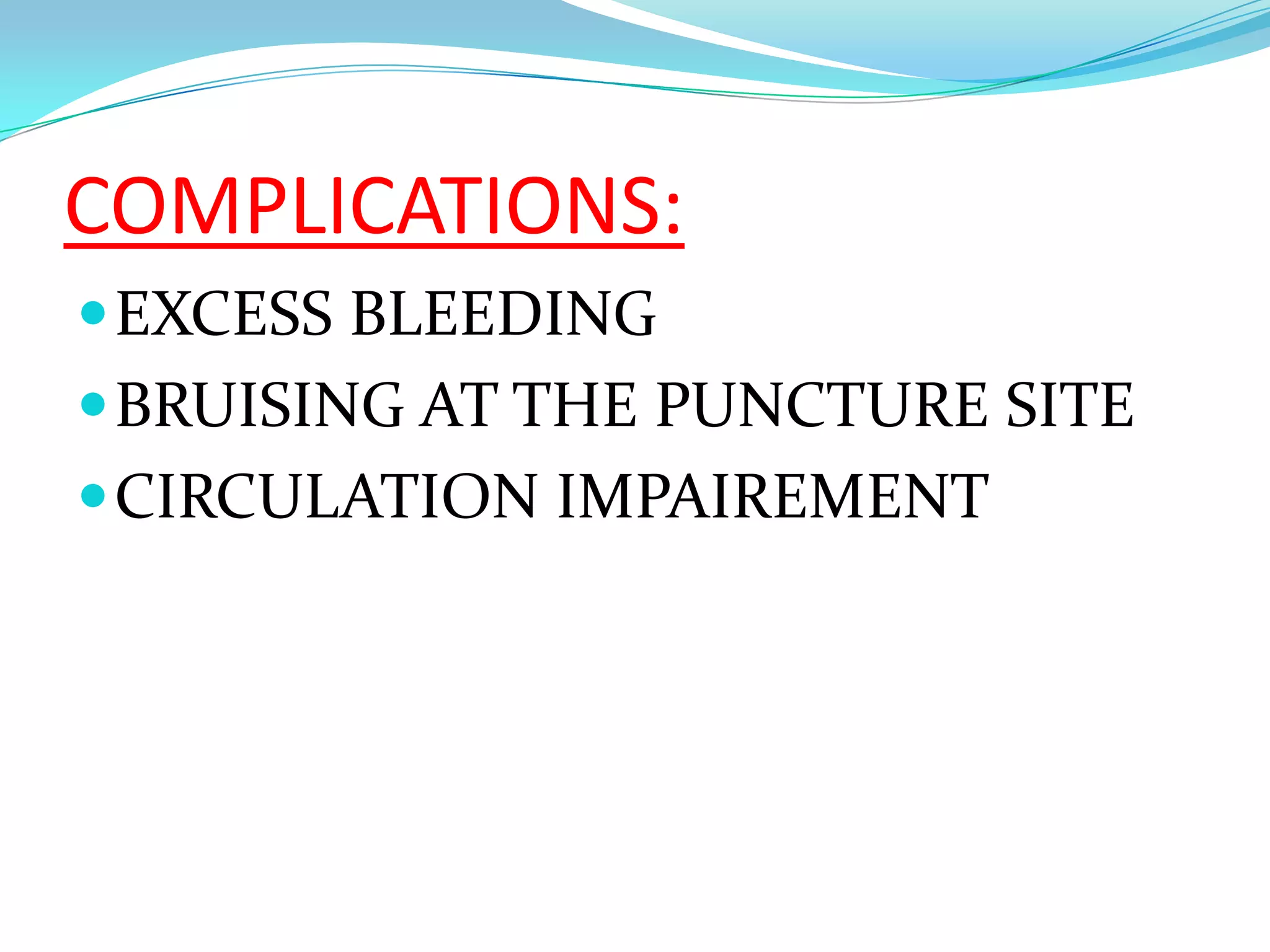
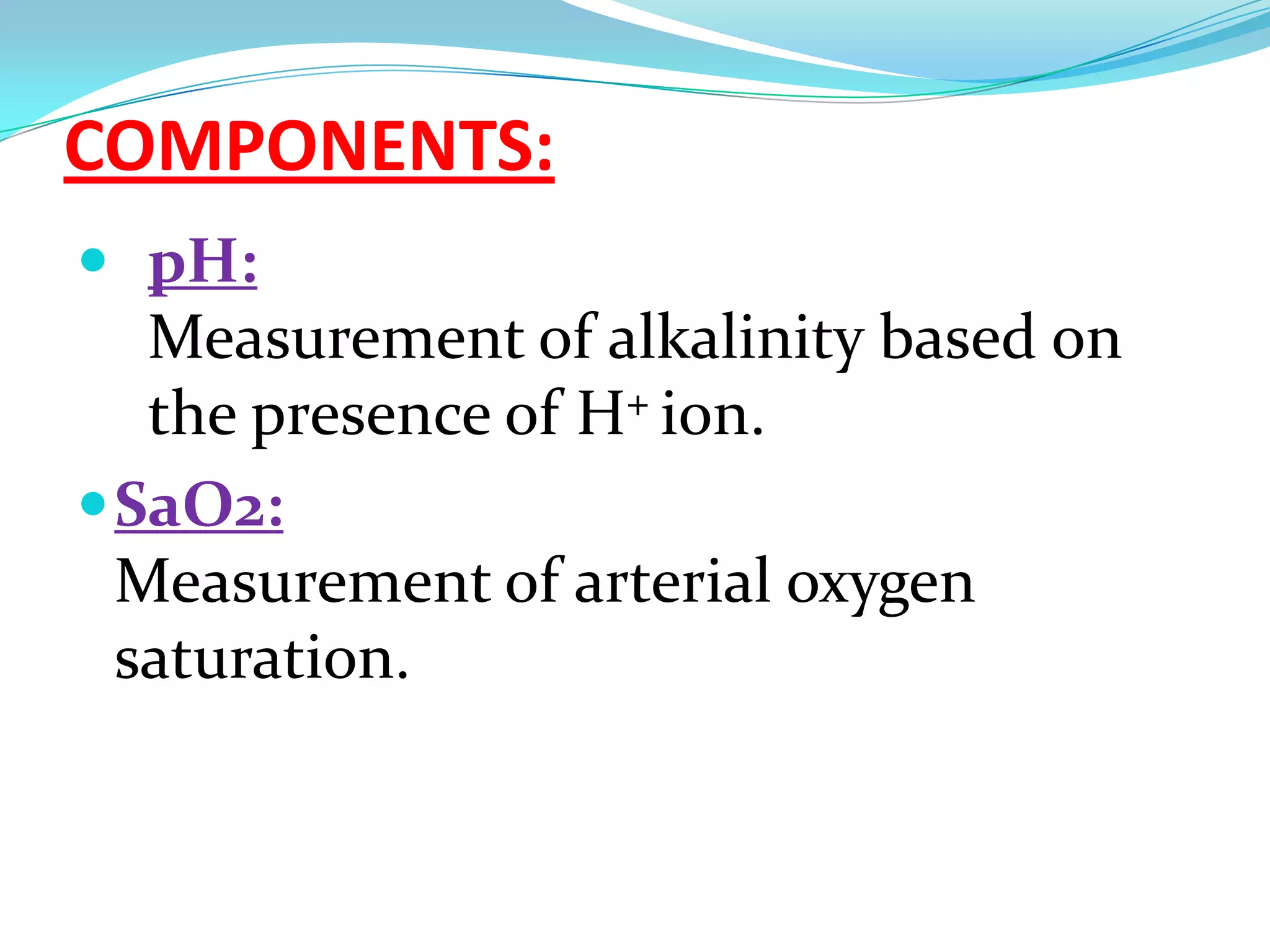



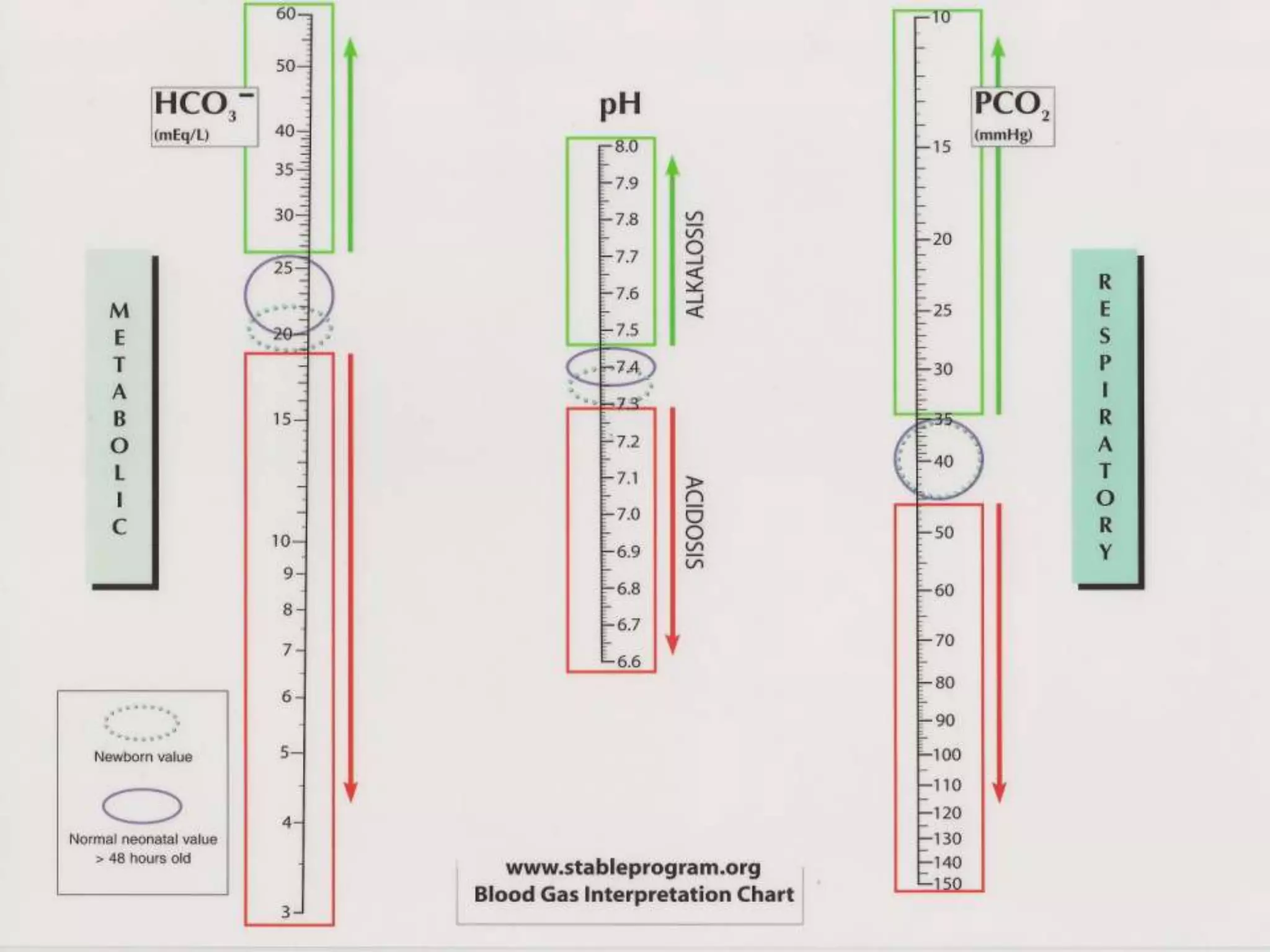
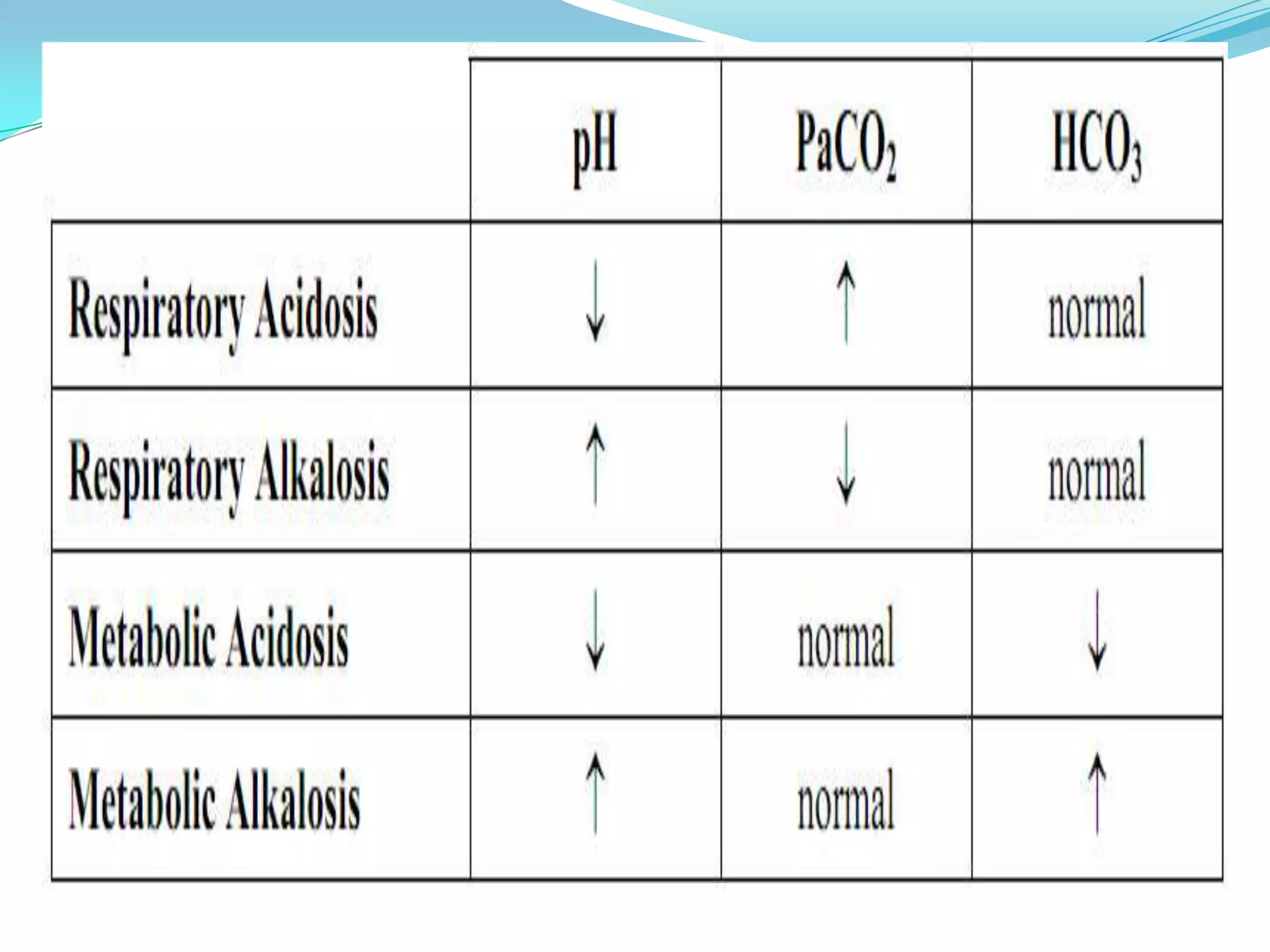




This document defines and discusses arterial blood gas analysis. It is a blood test taken from an artery that measures oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in the blood. It is used to evaluate respiratory status, metabolic status, and acid-base balance. Common sites for extraction are the radial, brachial, and femoral arteries. The procedure involves performing Allen's test before extraction to ensure adequate blood flow after puncture. Components measured include pH, oxygen saturation, bicarbonate, and base excess. Normal values for several components are provided. Sources of error in results can include air bubbles in the syringe or an inadvertent venous sample.
















