This document provides information about arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis, including:
- ABG analysis measures pH, PCO2, PO2, and HCO3 to evaluate respiratory and metabolic function.
- It indicates how well the lungs are oxygenating blood and the kidneys are regulating acid-base balance.
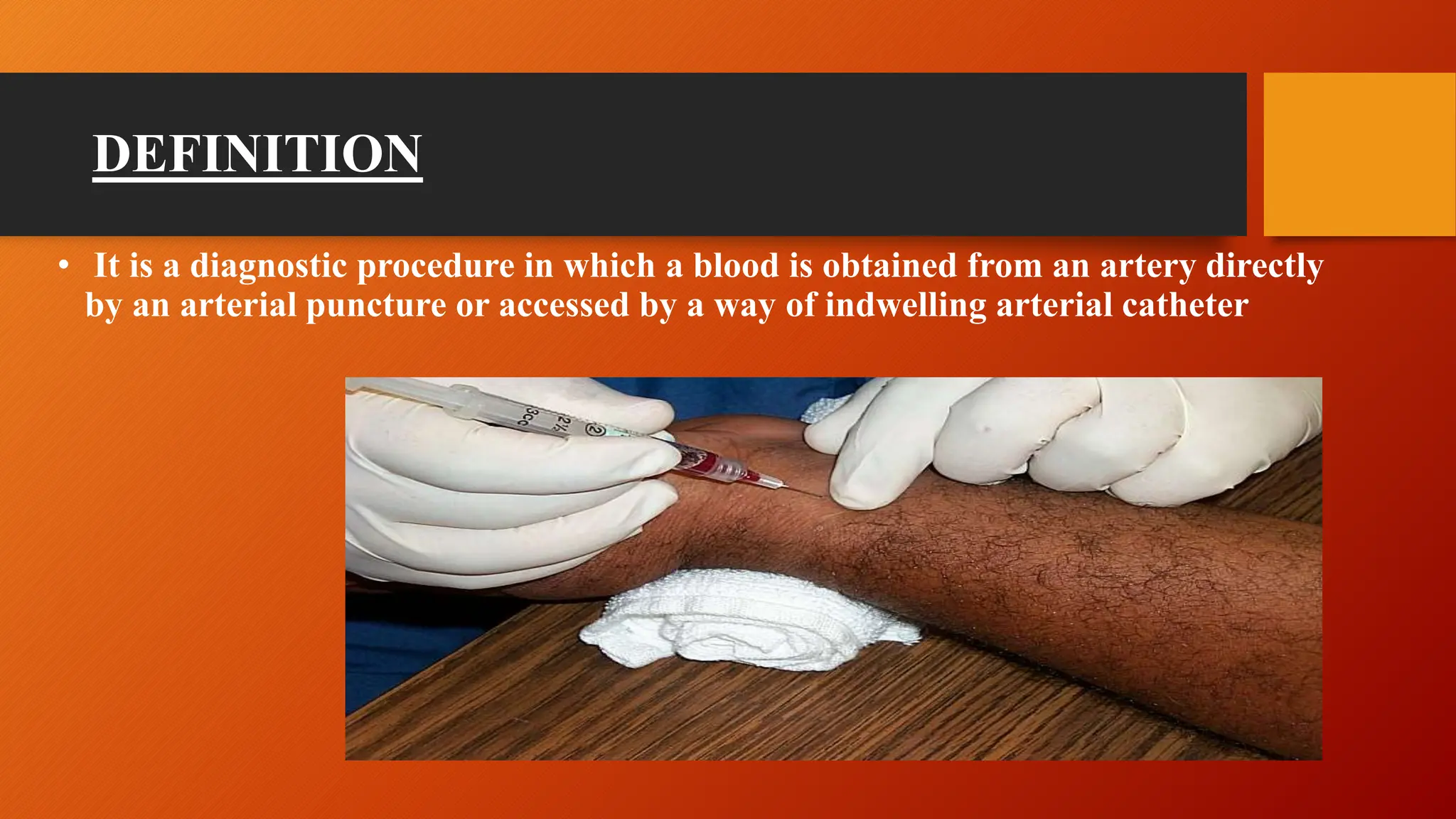
- The test involves drawing an arterial blood sample, usually from the radial artery. Normal values and factors that can affect the results are defined.
- The document describes how to interpret ABG results to diagnose acid-base imbalances like respiratory acidosis or metabolic alkalosis.













![ACID BASE PHYSIOLOGY
• pH is negative logarithm to the Base of 10 of the hydrogen ion
concentration in mmol/L
• pH=log[H+]
• An Increse in pH indicates a proportionate decerese in [H+] and a decrese
in the pH indicates a proportionate increase in [H+]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arterialbloodgasanalysis-231009144002-88c69ecd/75/Arterial-Blood-Gas-Analysis-pptx-15-2048.jpg)



![Calculation of pH
• pH is Negative Logarithm to the base of 10 of the Hydrogen ion concentration in mmol/L
means pH = log [H+]
• An Incresein pH indicates a proportionate decrese in the [H+] and a decerese in the pH
indicates proportionate increase in the [H+]
Henderson Hasselbalch Equation
• pH = pKA + log [HCO3-]/PaCO2 X 0.03
• Since [H+] = 24 x (pco2/[HCO3]) the stability of the extracellular pH is determined by the
stability of the pCO2 /HCO3 ratio
• Maintaining a constant Pco2/HCO3 ratio will maintain a constant extracellular pH](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arterialbloodgasanalysis-231009144002-88c69ecd/75/Arterial-Blood-Gas-Analysis-pptx-19-2048.jpg)
![Compensation
•When the Primary disorder is metabolic (a
change in [HCO3]) the compensatory
response is respiratory(a change in pCO2)
and vice versa.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arterialbloodgasanalysis-231009144002-88c69ecd/75/Arterial-Blood-Gas-Analysis-pptx-20-2048.jpg)




![STEP 1
• Check for internal consistency by Henderson equation
• [H+] = 24 X Pco2 /HCO3
= 24 X 40 /24
= 40
So [H+] is 40 at pH of 7.4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arterialbloodgasanalysis-231009144002-88c69ecd/75/Arterial-Blood-Gas-Analysis-pptx-25-2048.jpg)
![Continue..
• (A) First calculate [H+] BY PUTTING PaCO2 and HCO3 in equation
• then
• (B) for every 0.1 decrease in pH ,multiply [H+] sequentially by 1.25
• For every 0.1 increase in pH ,Multiply [H+] sequentially by 0.8
• (C) Match H+ by both (A) And (B),if matches then ABG is valid](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arterialbloodgasanalysis-231009144002-88c69ecd/75/Arterial-Blood-Gas-Analysis-pptx-26-2048.jpg)

![Continue…
• Metabolic Alkalosis occurring due to irreversible genetic defecs are also
saline unresponsive
• Saline ResponsiveVomiting,diuretic use,RT Aspiration ,Post [
[Urine CL<20 meq/L] Hypercapnic
Saline Unresponsive Hyperaldosteronism,,Renin secreting tumour
[Urine CL<20 meq/L] liddle Syndrome ,renin Angiotensin system,
Bitter syndrome,Gittleman syndrome](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arterialbloodgasanalysis-231009144002-88c69ecd/75/Arterial-Blood-Gas-Analysis-pptx-28-2048.jpg)




