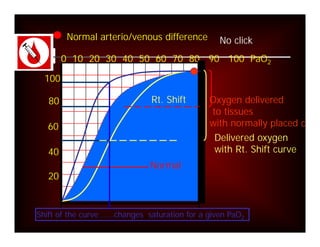
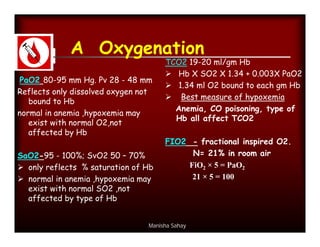
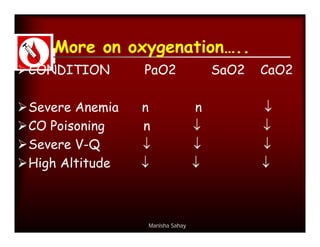
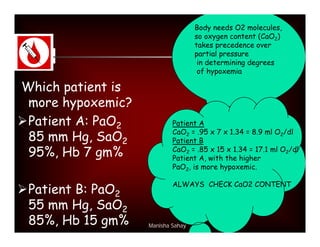
Here are the key points about assessing ventilation from an ABG:
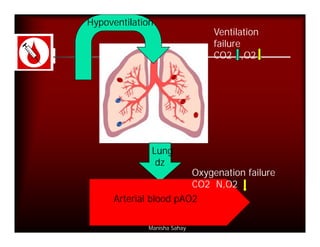
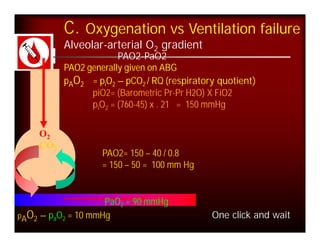
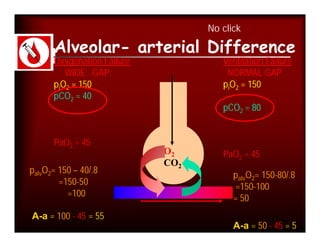
- PaCO2 is used to assess ventilation. The normal range is 35-45 mmHg.
- A PaCO2 higher than 45 mmHg indicates respiratory acidosis from hypoventilation or obstruction.
- A PaCO2 lower than 35 mmHg indicates respiratory alkalosis from hyperventilation.
- The pH and HCO3- will be affected by changes in PaCO2 based on the type of respiratory problem (acidosis vs alkalosis). They move in opposite directions for respiratory issues.
- Compensation by the kidneys will cause the HCO3- to rise or fall in the same direction as PaCO










![Step 3:
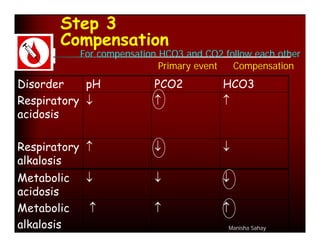
Calculation of compensation
Disorder pH Primary Compensatory Equation
change Response
Metabolic [HCO3-] PCO2 ΔPCO2 1.2 ΔHCO3
Acidosis
Metabolic [HCO3-] PCO2 ΔPCO2 0.7 ΔHCO3
Alkalosis
Respiratory PCO2 [HCO3-] Acute:
Acidosis ΔHCO3- 0.1 ΔPCO2
Chronic:
ΔHCO3- 0.3 ΔPCO2
Respiratory PCO2 [HCO3-] Acute:
Alkalosis ΔHCO3- 0.2 ΔPCO2
Chronic:
ΔHCO3- 0.5 ΔPCO2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dr-manishasahayabg-stanley-cme-100130050430-phpapp02/85/CME-ABG-13-320.jpg)

![What is anion gap?
[Na+] – ([HC03-] + [Cl-])
140 - (24 + 105) = 11
Normal = 12 + 2
Manisha Sahay](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dr-manishasahayabg-stanley-cme-100130050430-phpapp02/85/CME-ABG-16-320.jpg)