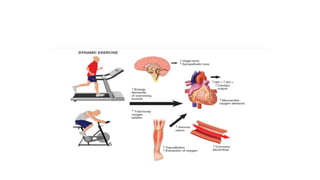
Treadmill testing (TMT) is a widely used test to evaluate cardiovascular disease. It was initially developed to detect coronary artery disease but is now also used to assess other conditions and predict prognosis. TMT measures total body oxygen uptake during exercise to estimate energy requirements. It provides a common form of physical stress and patients are more likely to reach high exertion levels than with stationary cycling. While exercise testing carries some risk, complications are low at less than 1% for events like heart attack and 0.5% for death. Supervision depends on a patient's risk level but a physician should be available. TMT can help diagnose conditions, stratify post-heart attack risk, and guide management of chest pain.




![Physiology of exercise testing
TOTAL BODY OXYGEN UPTAKE:
• Energy requirements at rest and for any given amount of physical
activity (work rate) can be estimated from measurements of total-
body oxygen uptake (V O2).
• VO2 is equal to the product of cardiac output and oxygen extraction
at the periphery.
• VO2 is easily expressed in multiples of resting oxygen requirements
(metabolic equivalents [METs].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/valueoftmt-170228051130/85/Value-of-tmt-5-320.jpg)