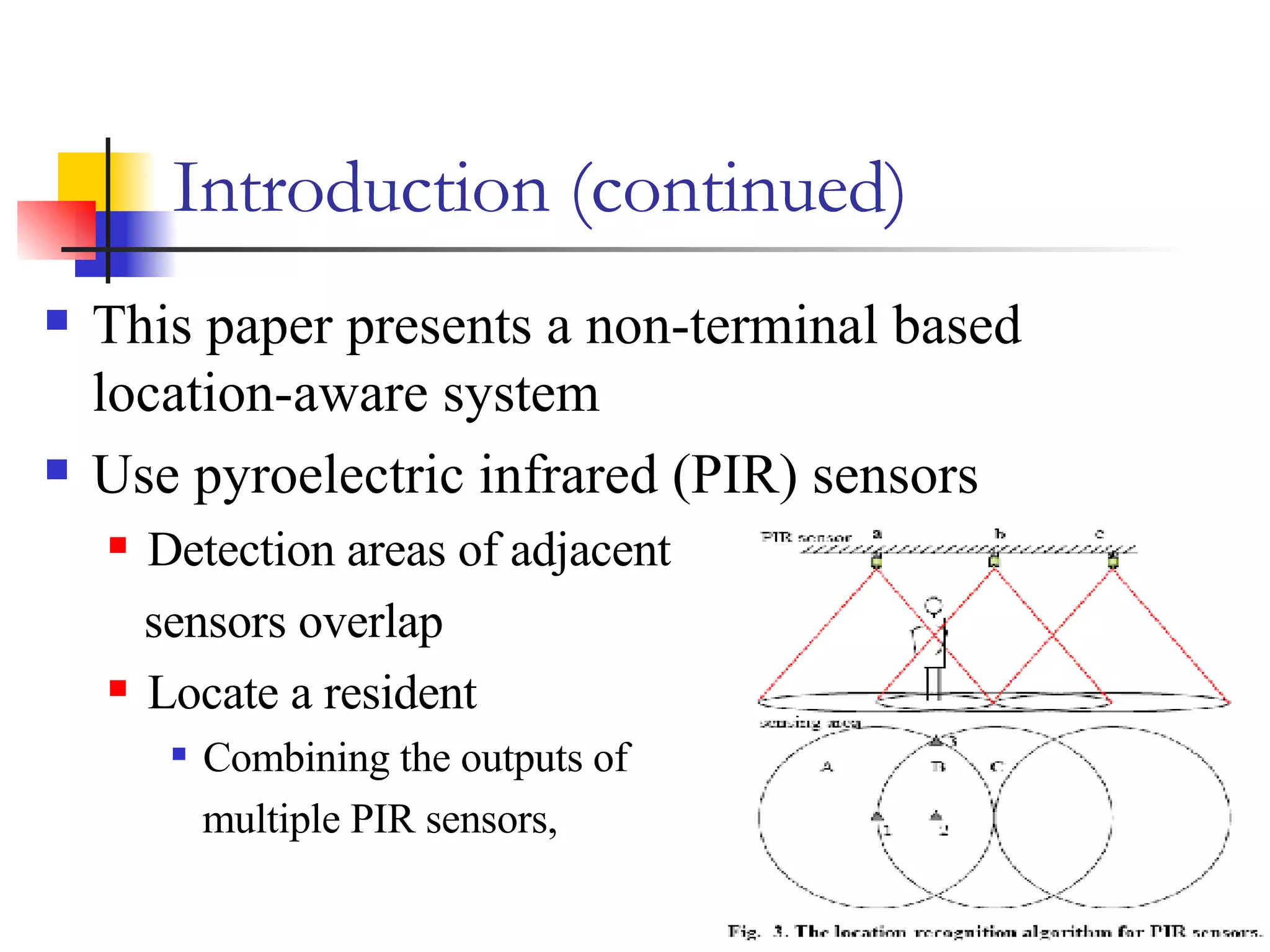
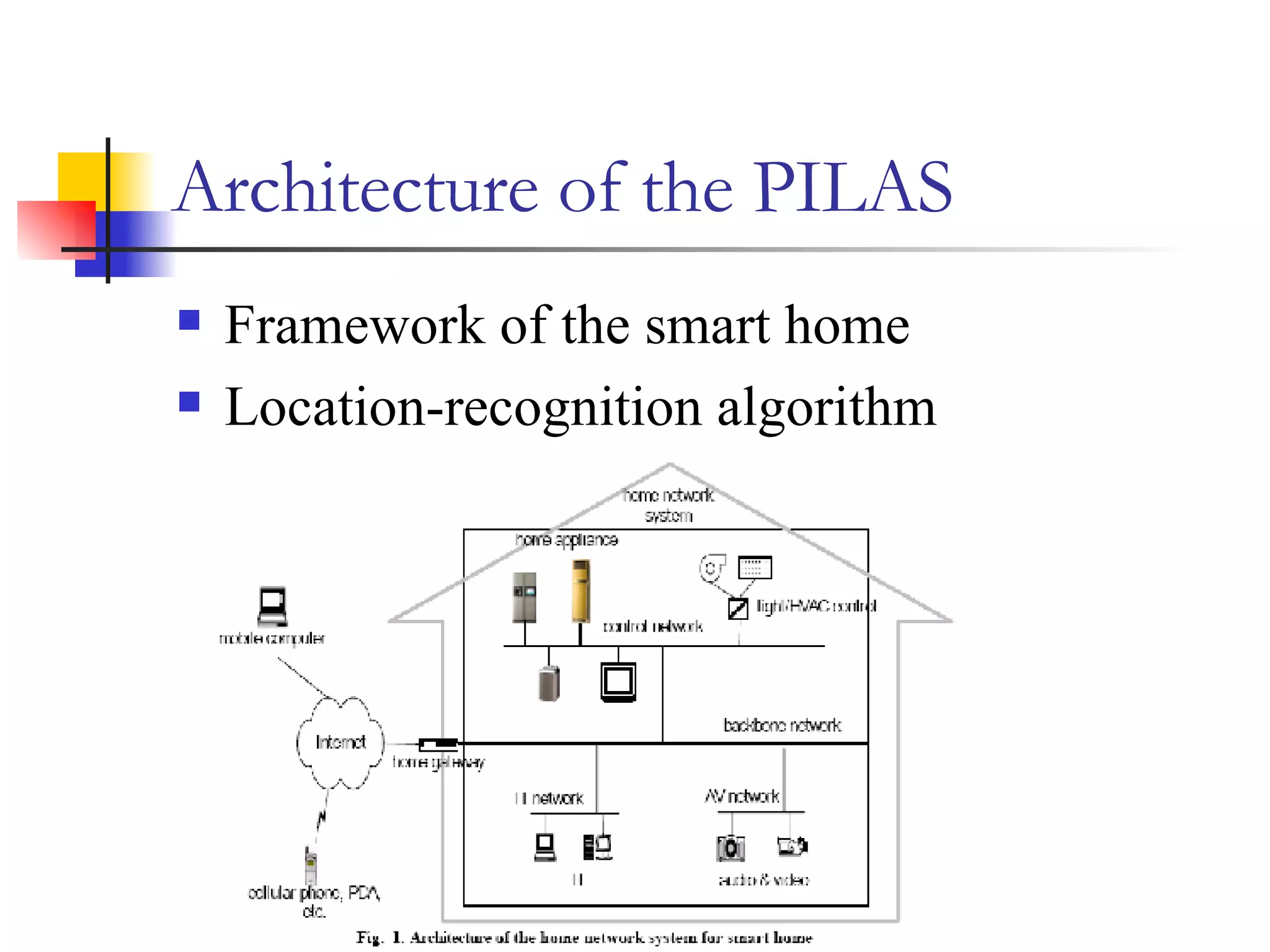
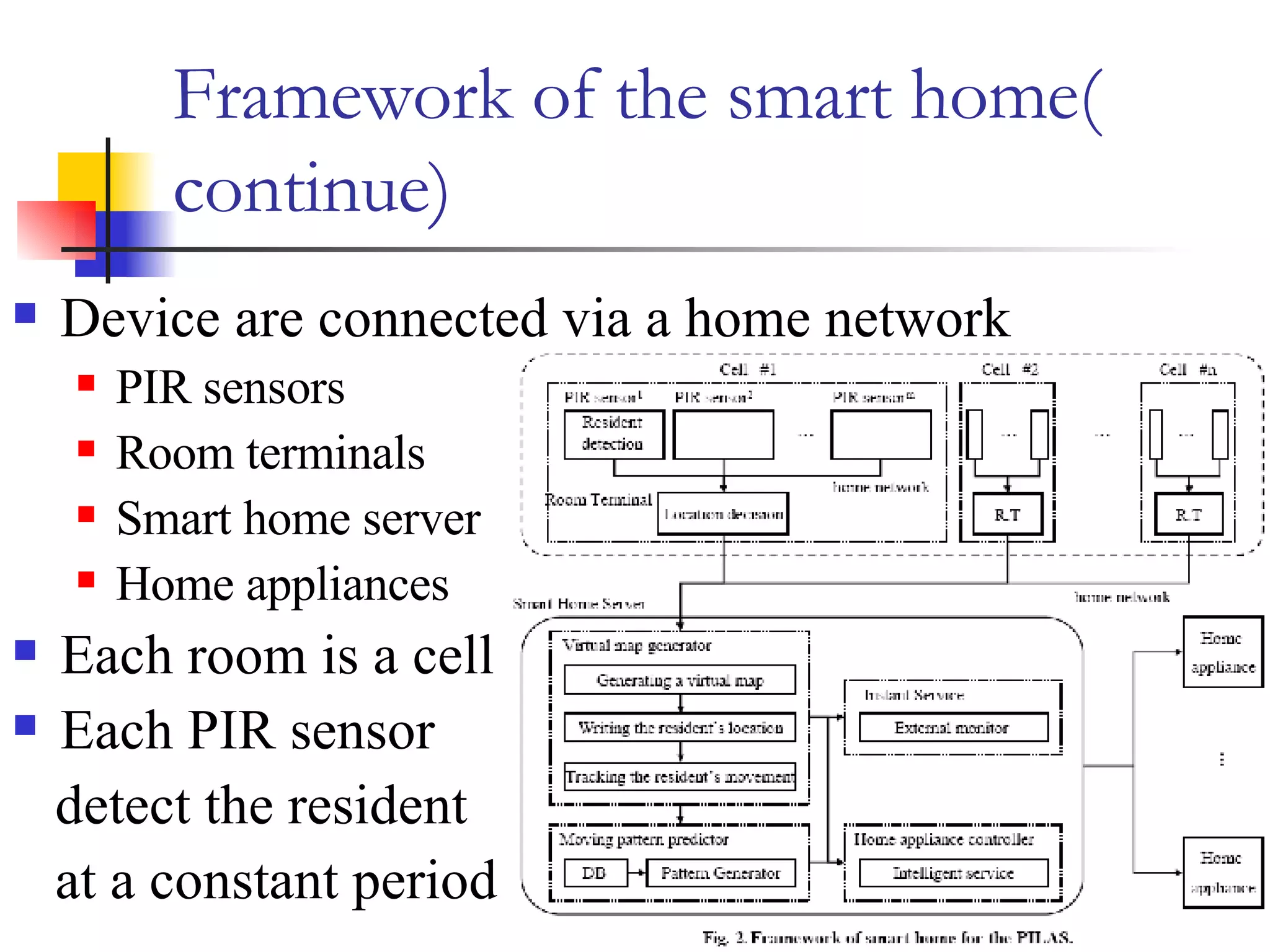
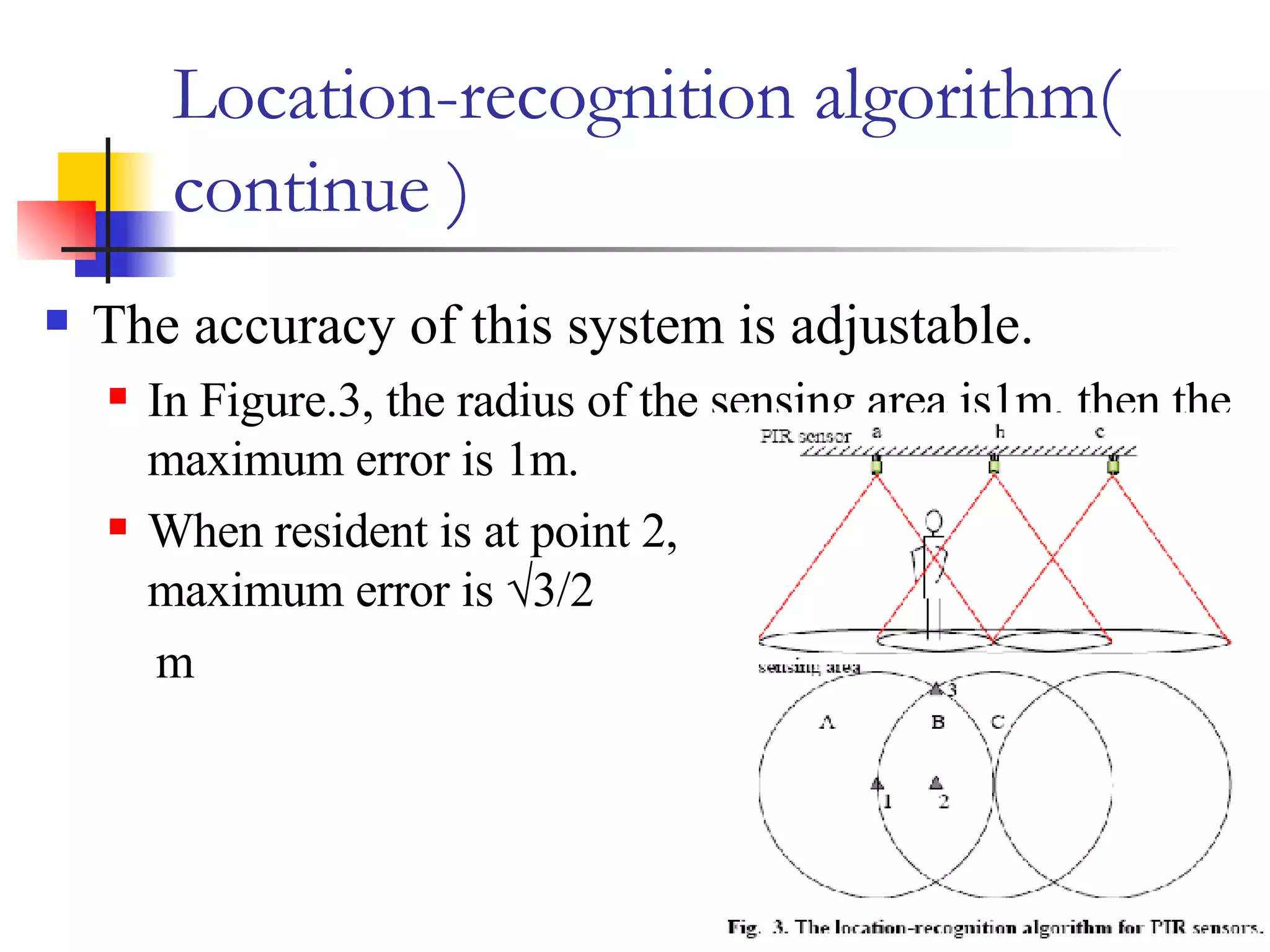
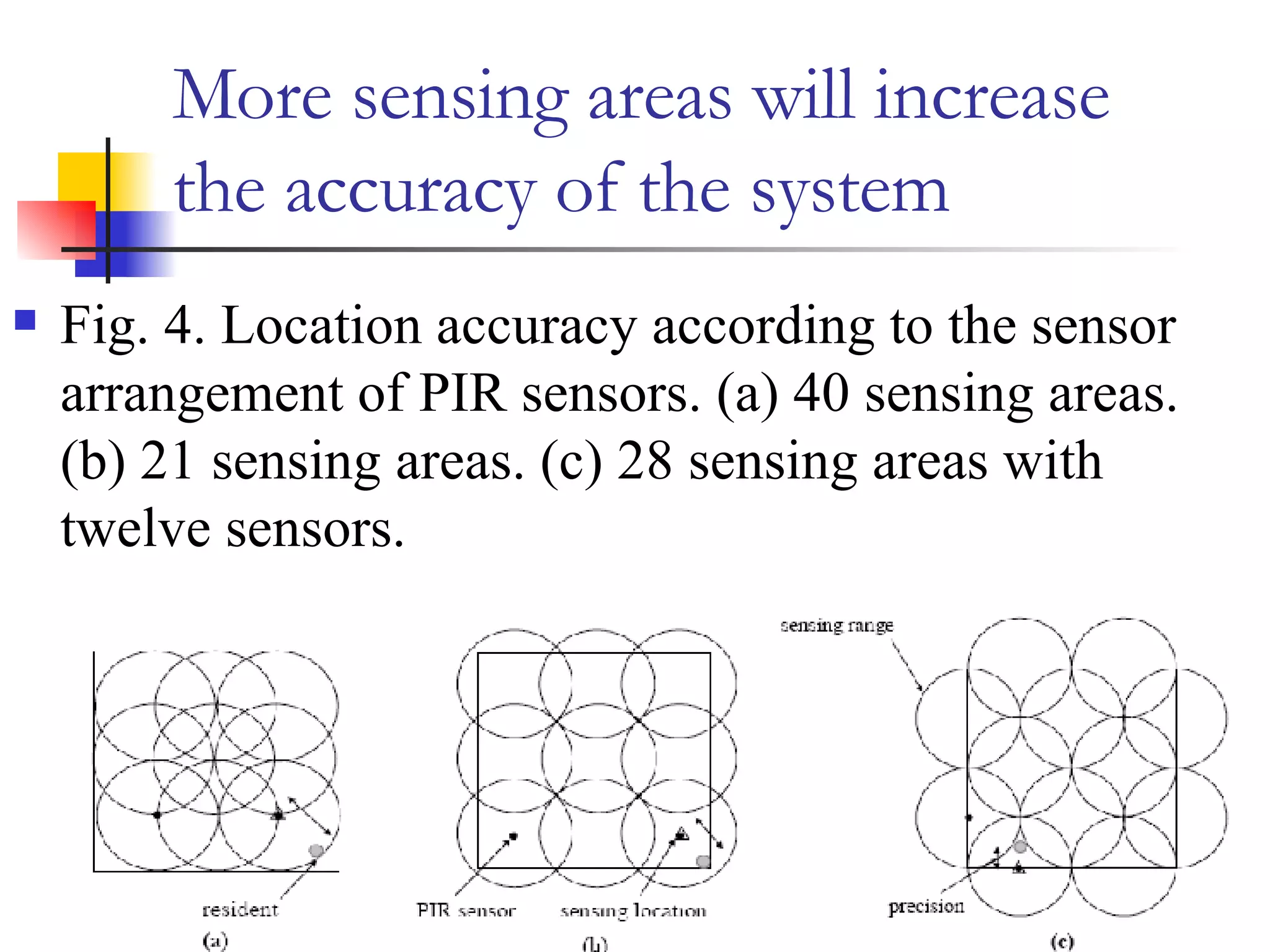
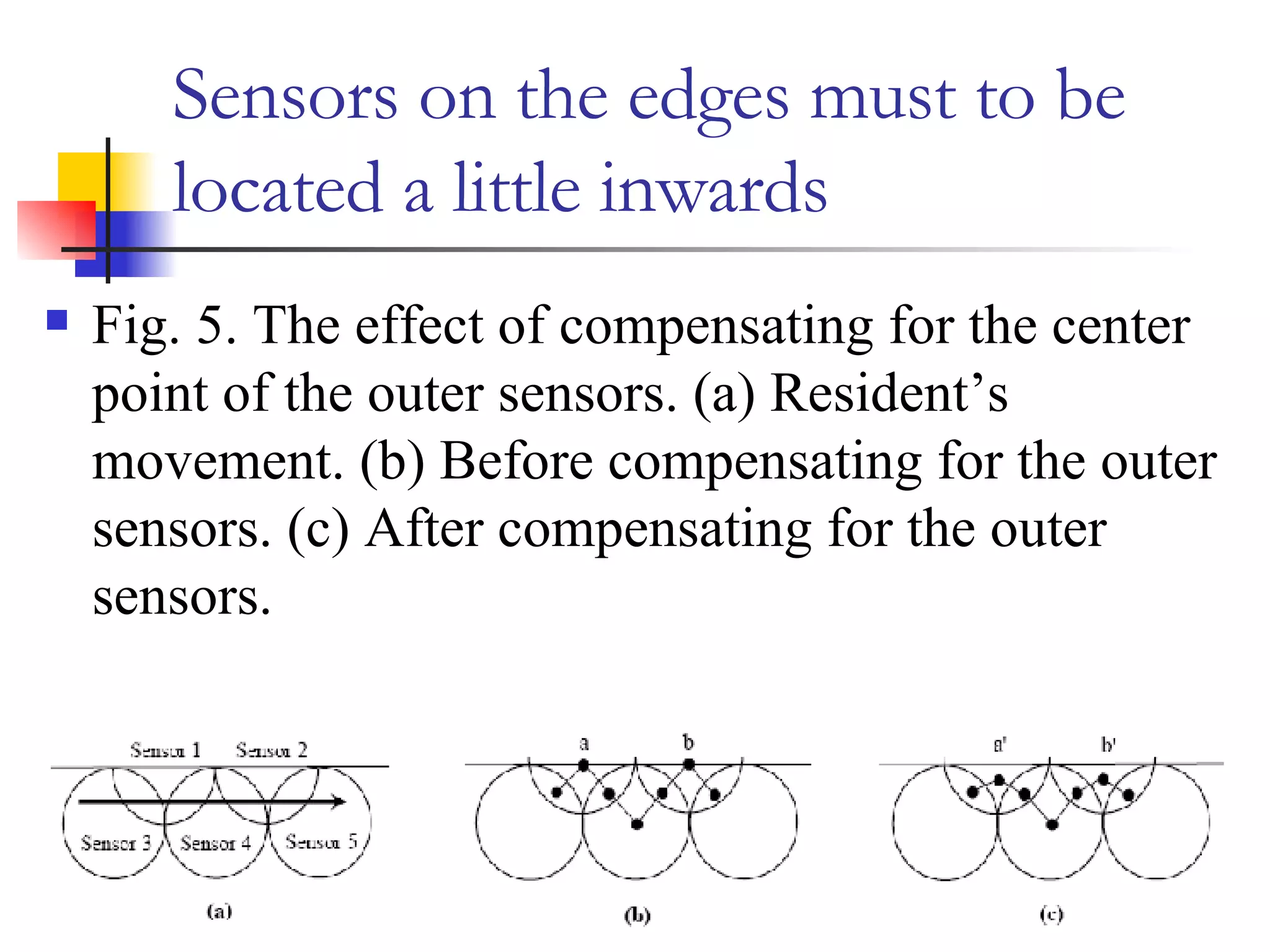
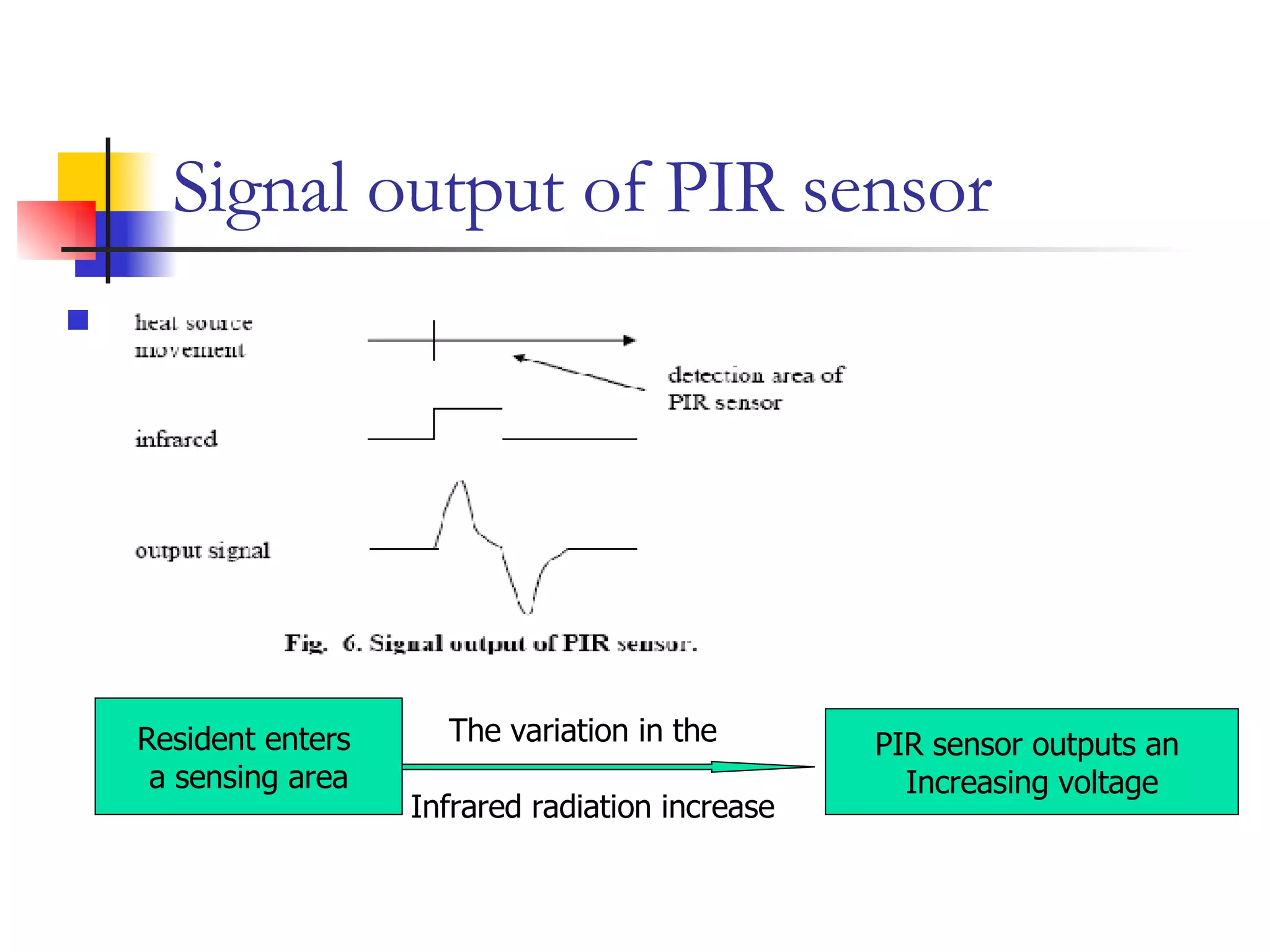
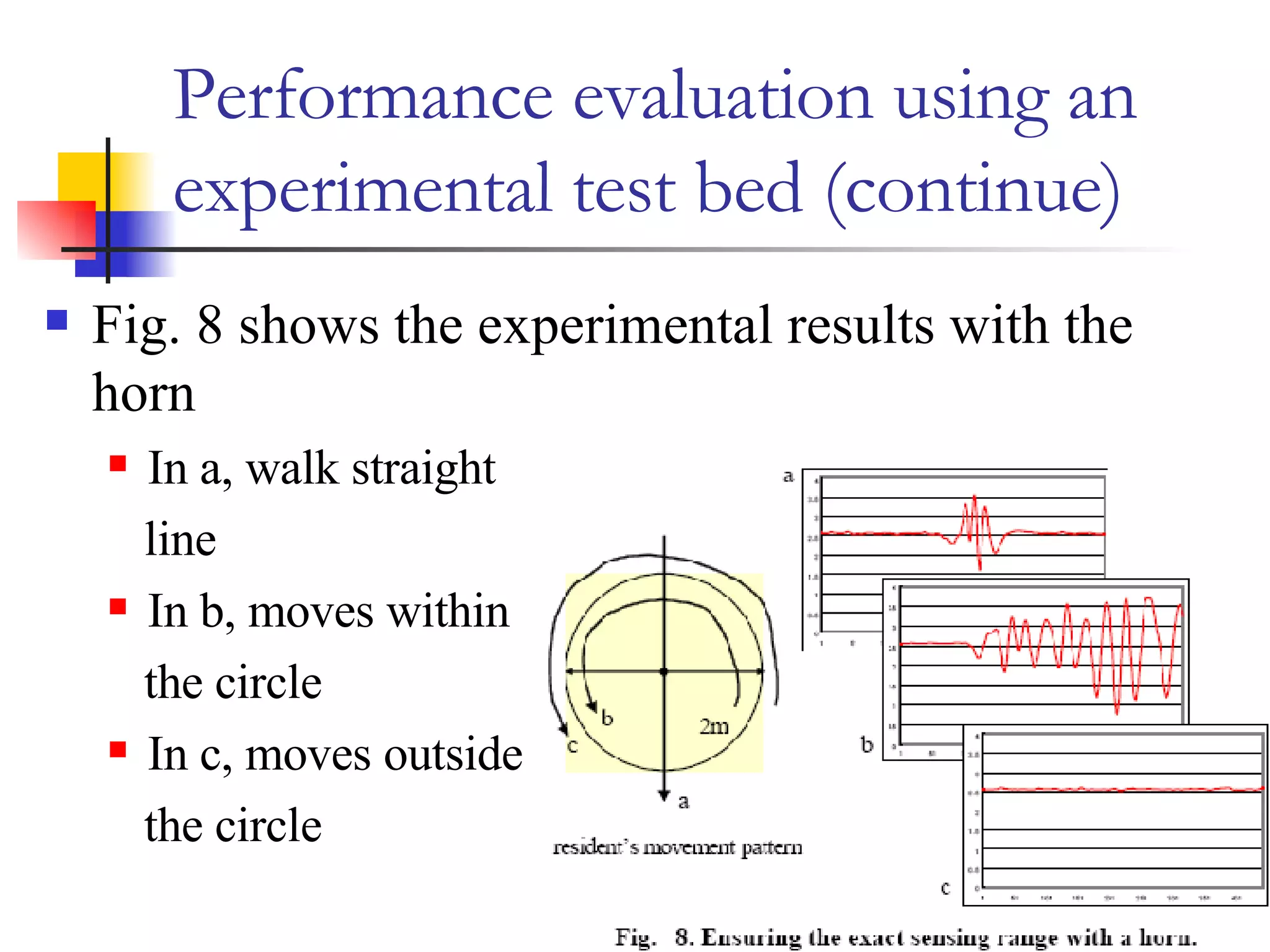
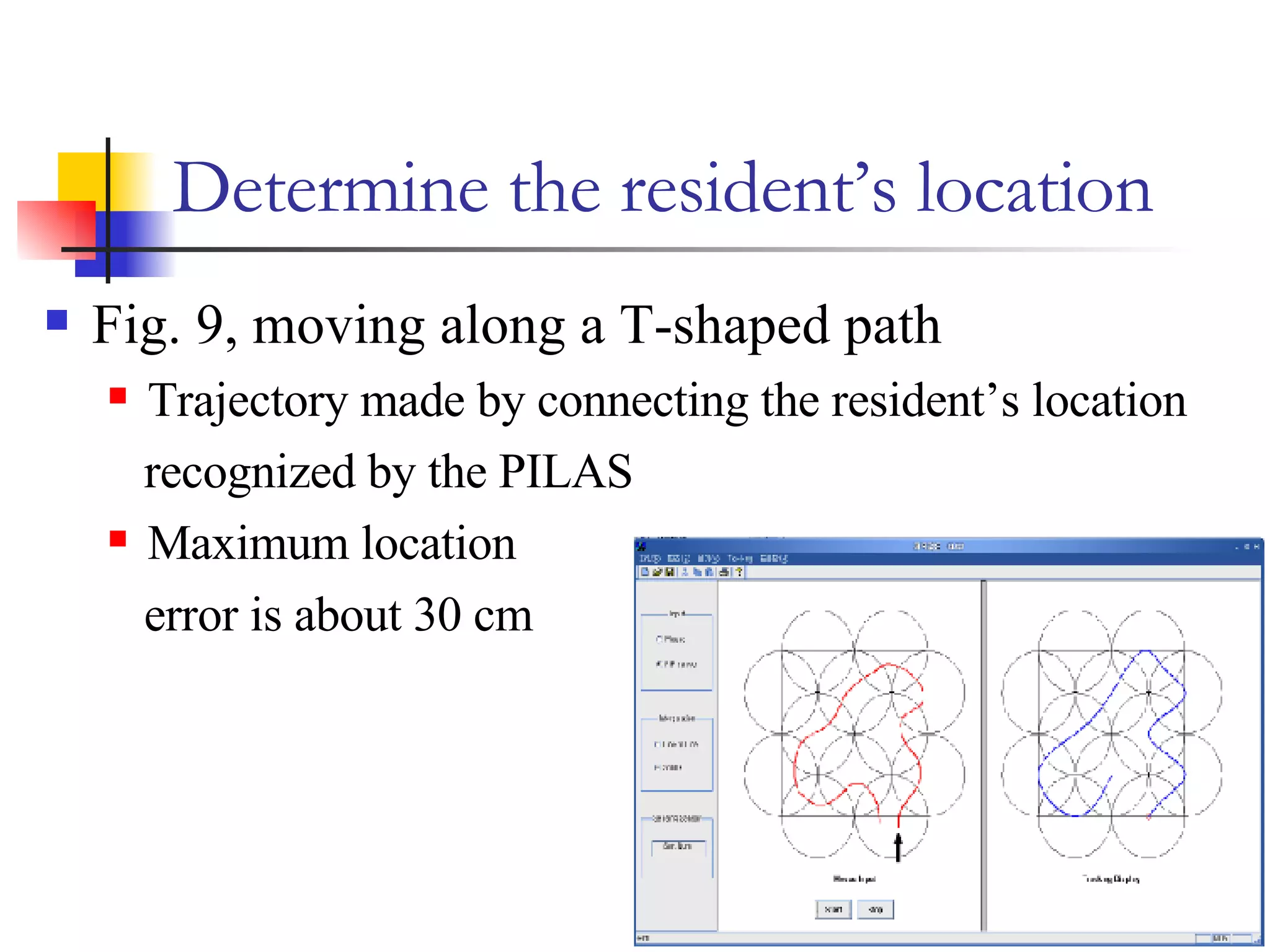
This document presents a non-terminal based indoor location system called PILAS that uses pyroelectric infrared (PIR) sensors. The PILAS system architecture includes PIR sensors installed in each room, room terminals, and a smart home server that generates a virtual map and provides intelligent services. The PILAS system can locate residents within a room by analyzing the output patterns of overlapping PIR sensors without requiring residents to carry any devices. An experimental test bed demonstrated that the PILAS system can accurately track a resident's movements and locate them with a maximum error of less than 30 cm.