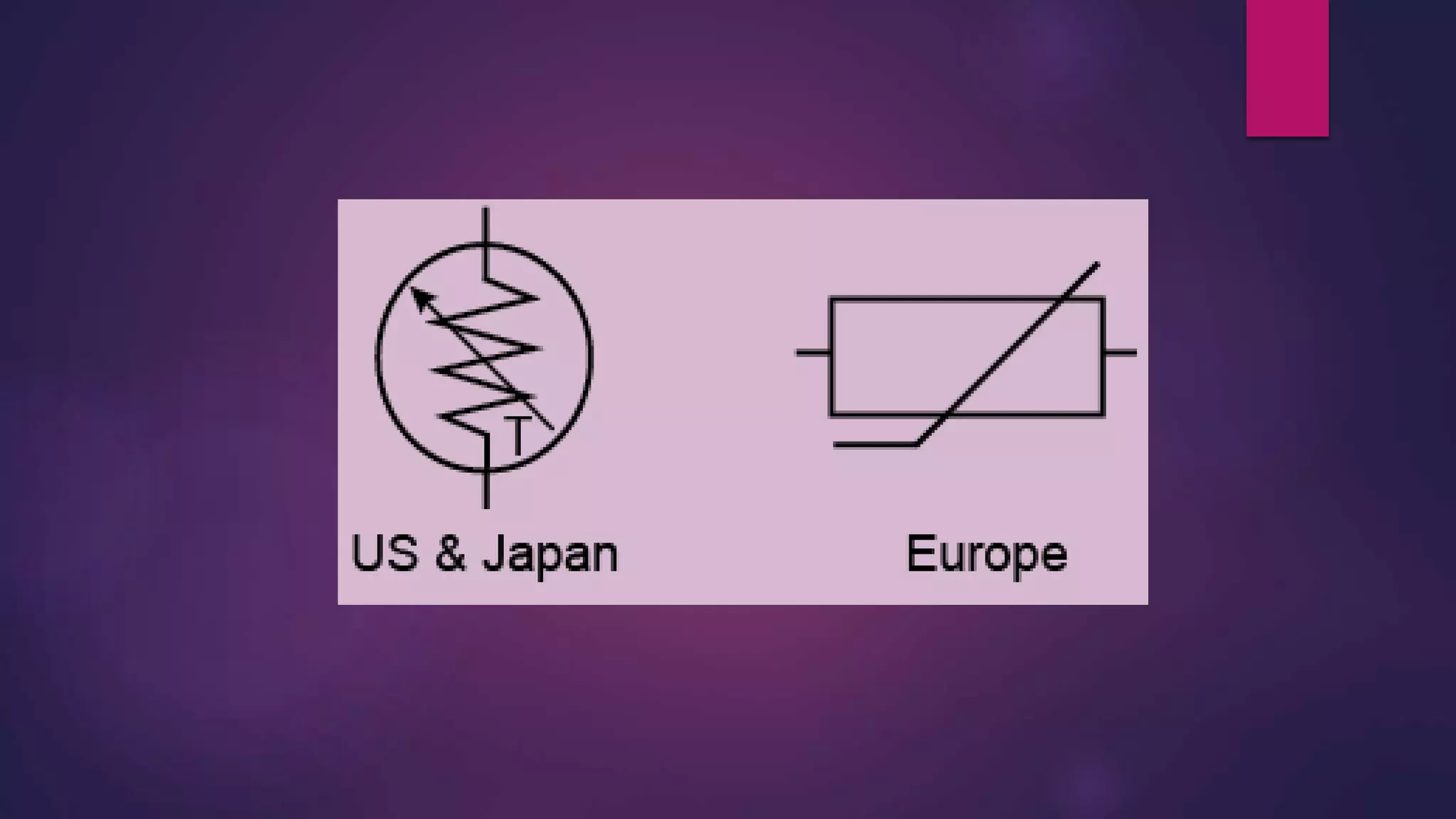
This document discusses thermistors, which are temperature sensing elements that measure temperature through changes in resistance. It describes how thermistors are constructed from sintered semiconductor materials and come in various shapes. The document outlines the working principle of thermistors, types including positive and negative temperature coefficient thermistors, advantages like low cost and high sensitivity, disadvantages such as non-linear output, and applications including current limiting devices, digital thermostats, and battery pack monitors.