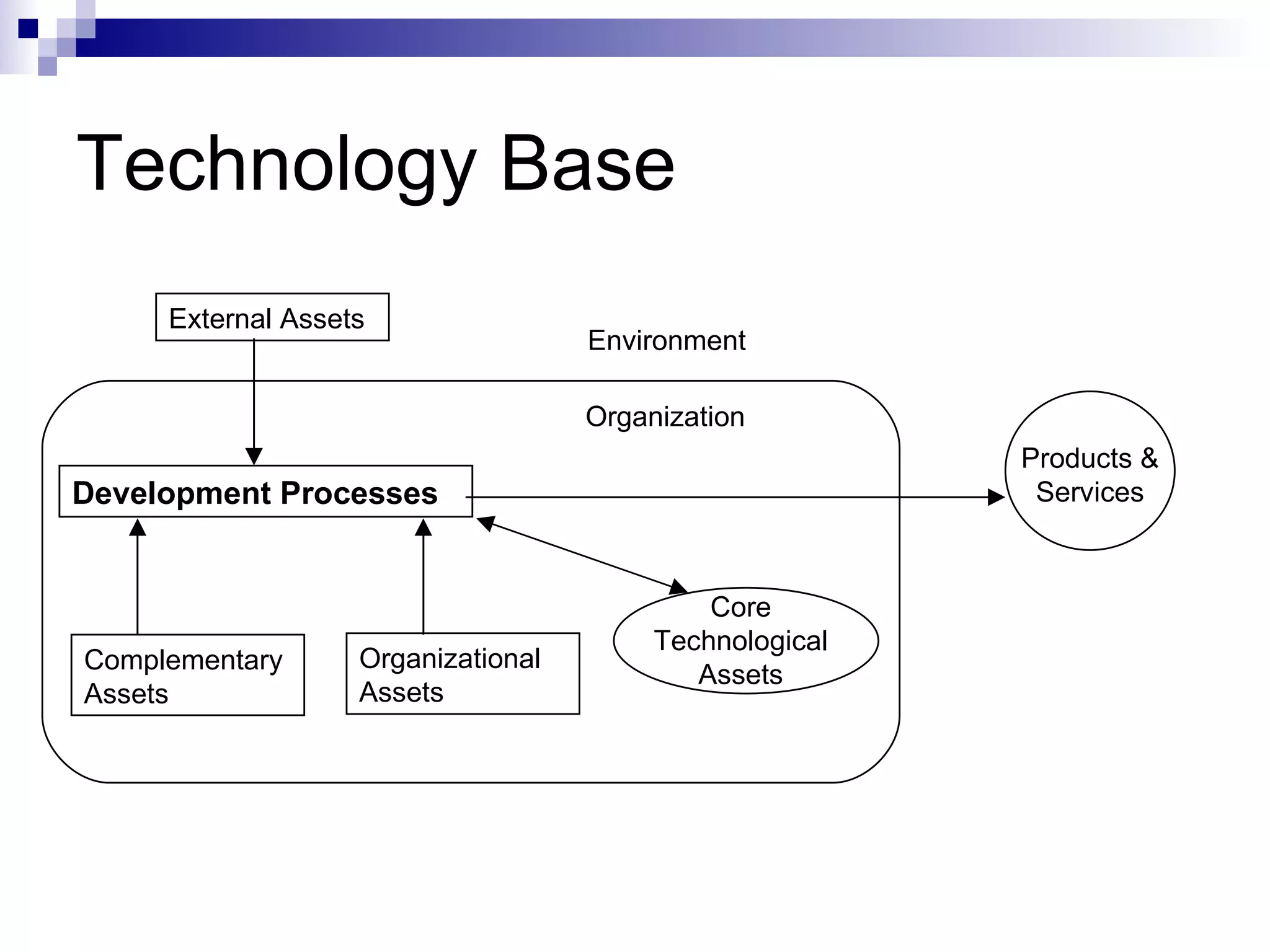
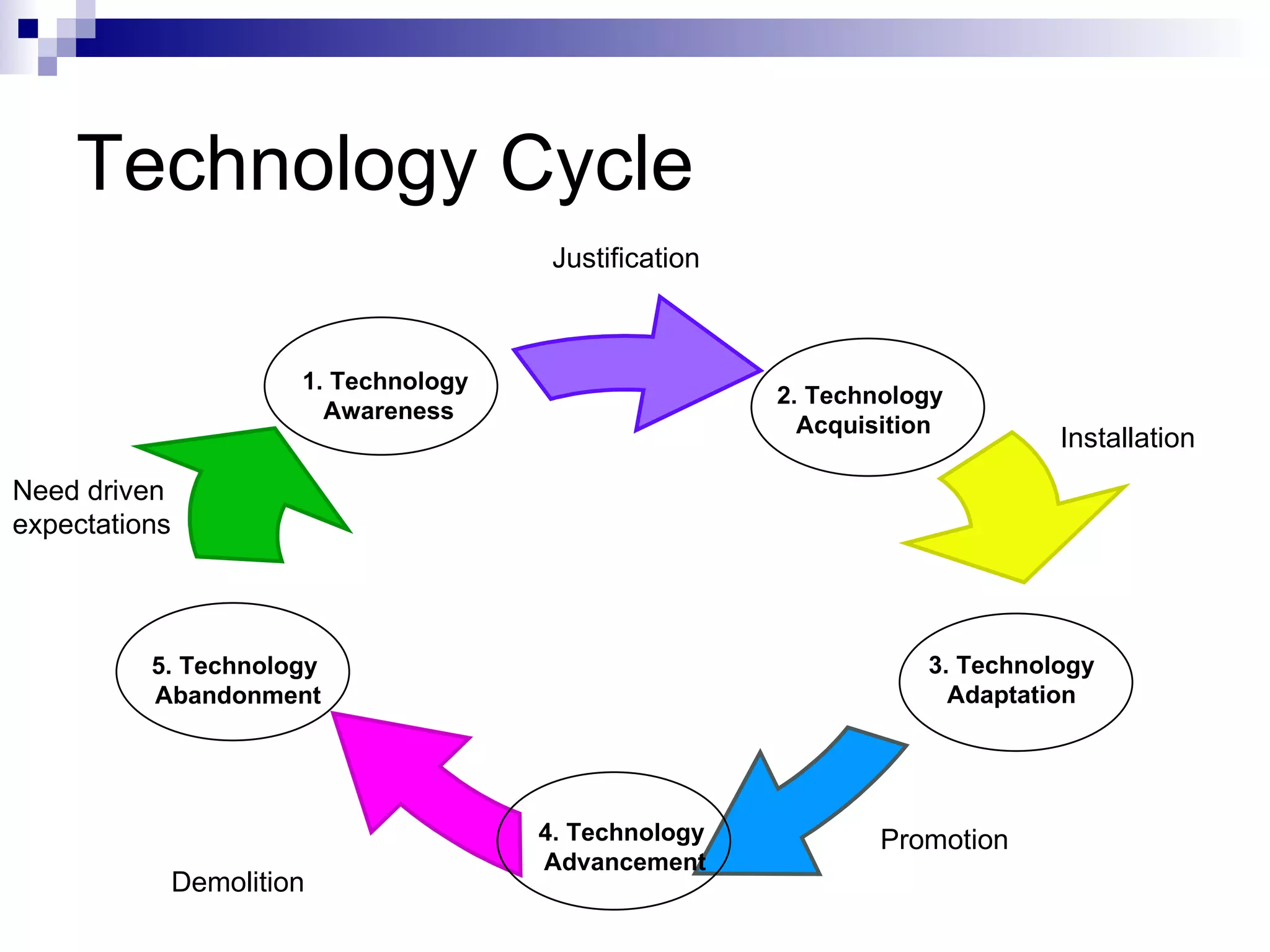
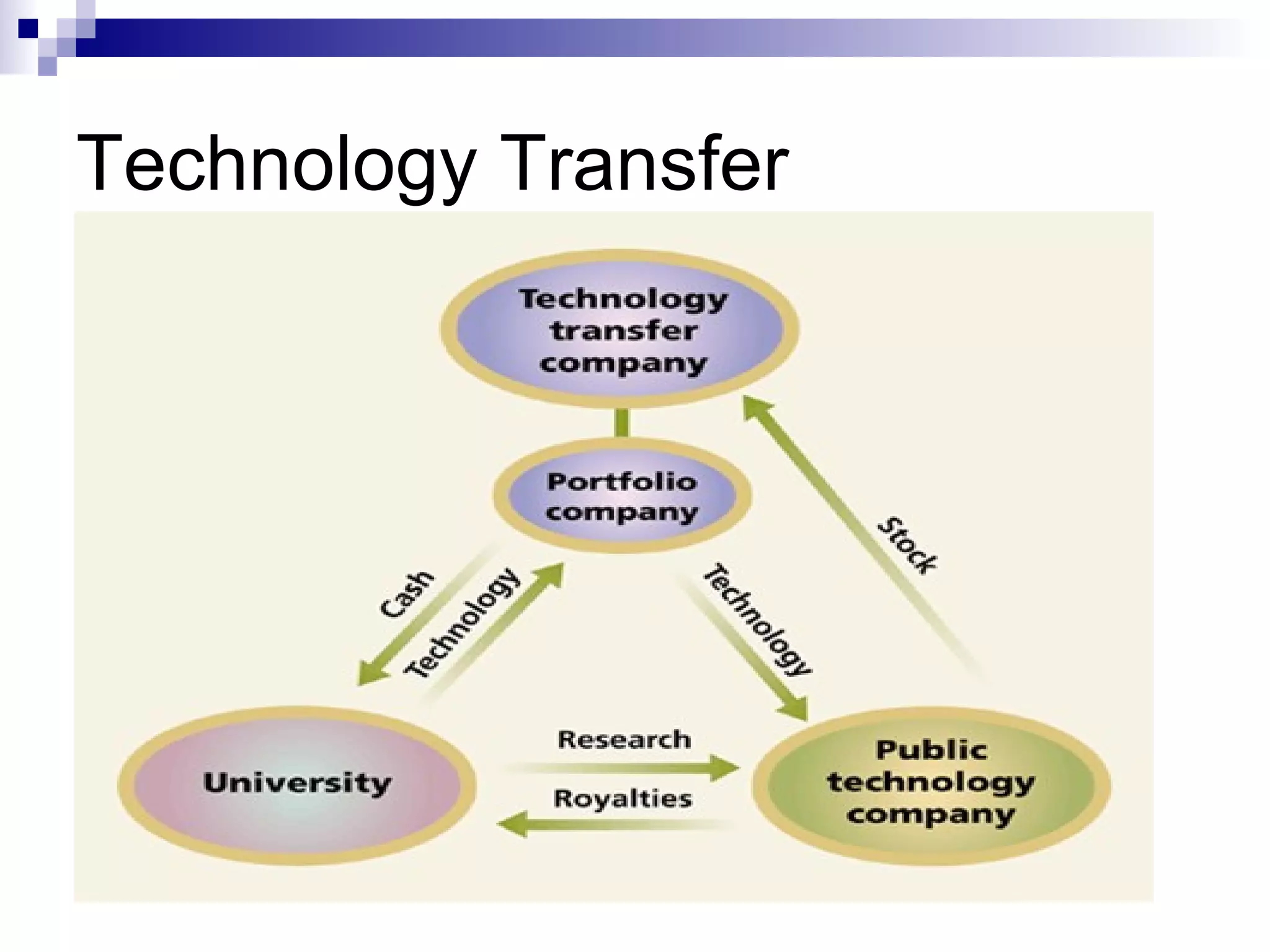
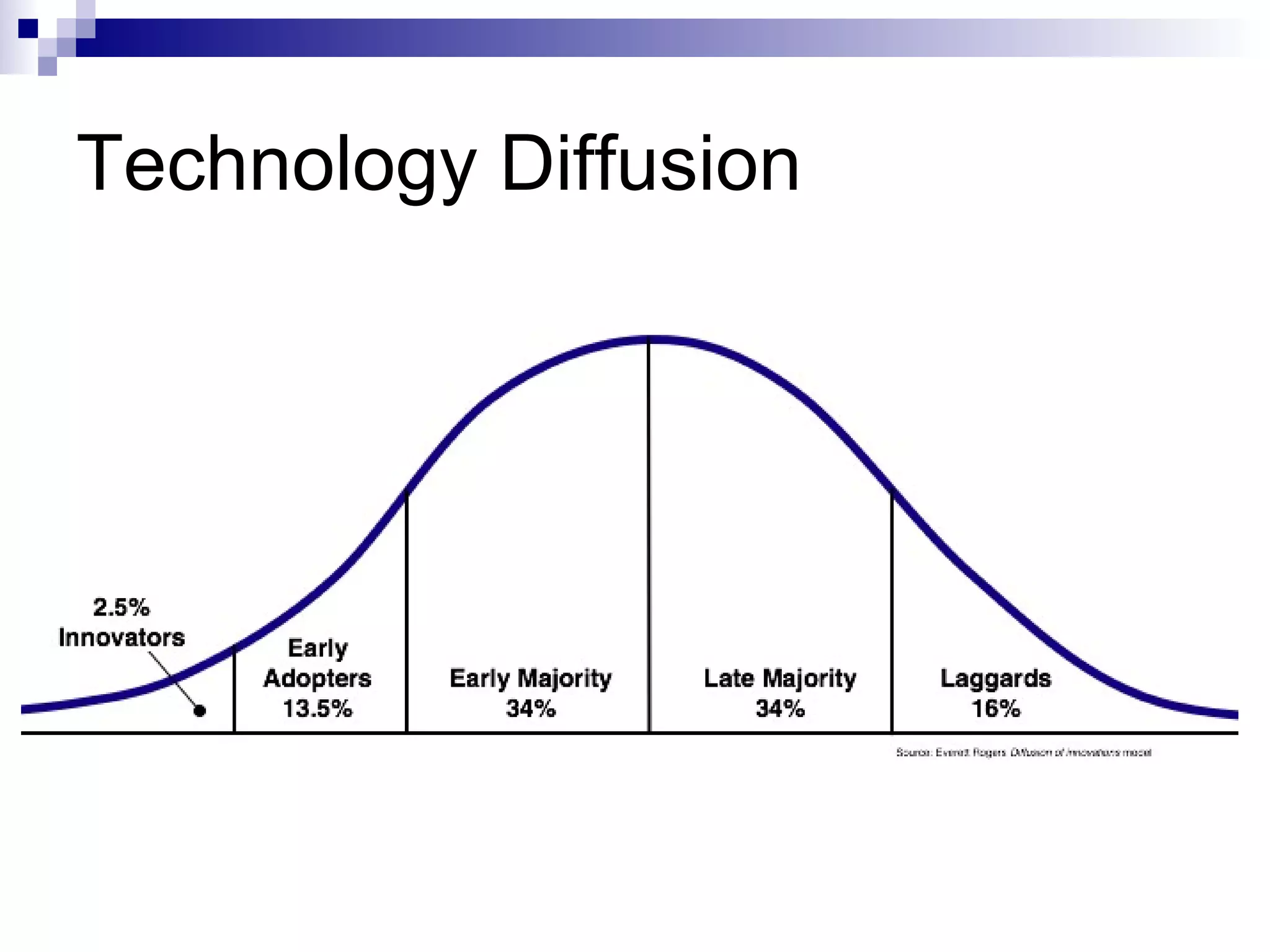
The document discusses technology management at Hewlett-Packard (HP). It provides details on HP's founding, technology portfolio, concepts in technology management, technology assets, technology cycle, technology transfer and diffusion strategies, and use of knowledge mapping. HP manages its technological assets and capabilities to create competitive advantages and has divisions focused on technology transfer and open innovation to acquire new technologies.