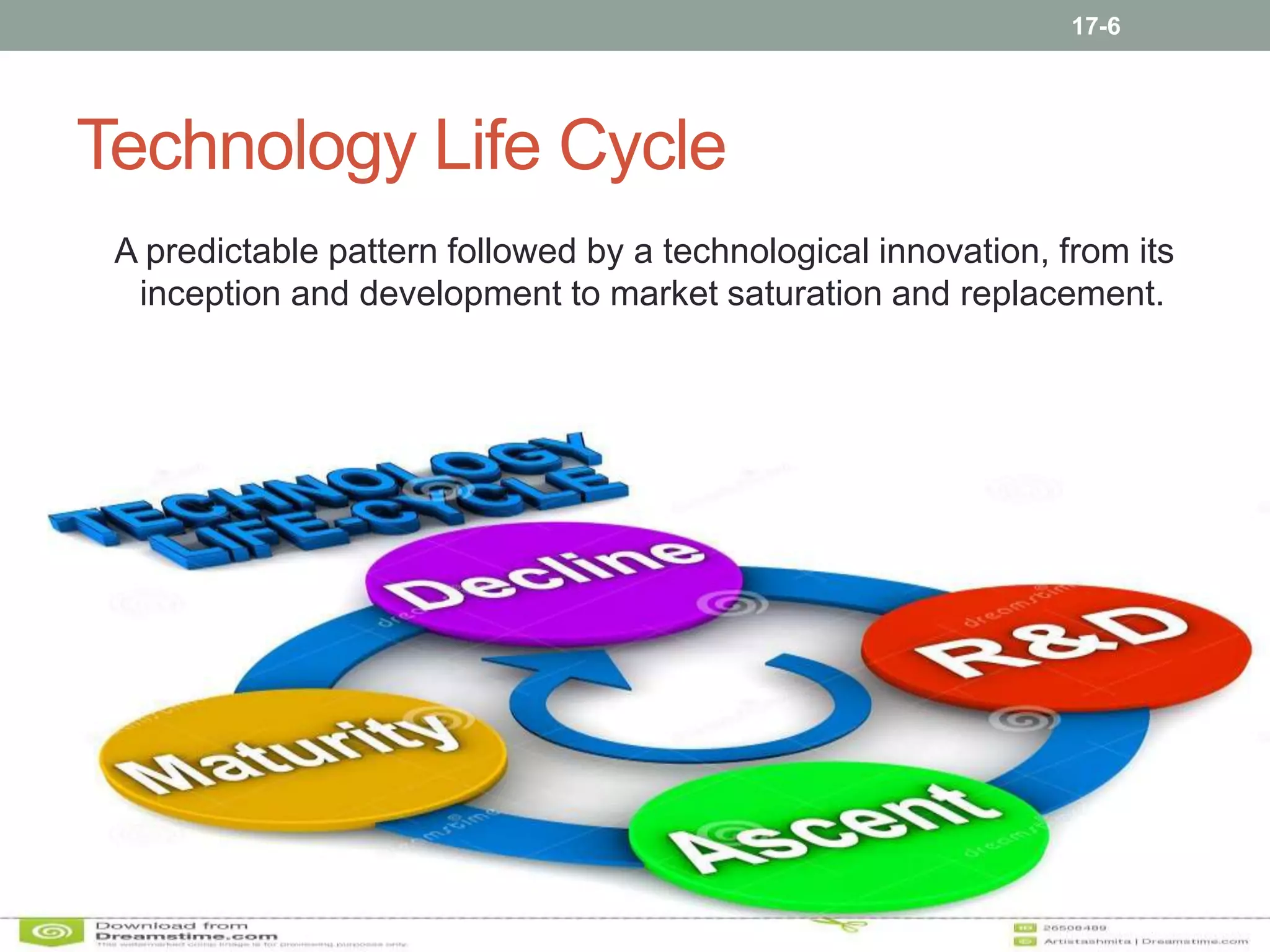
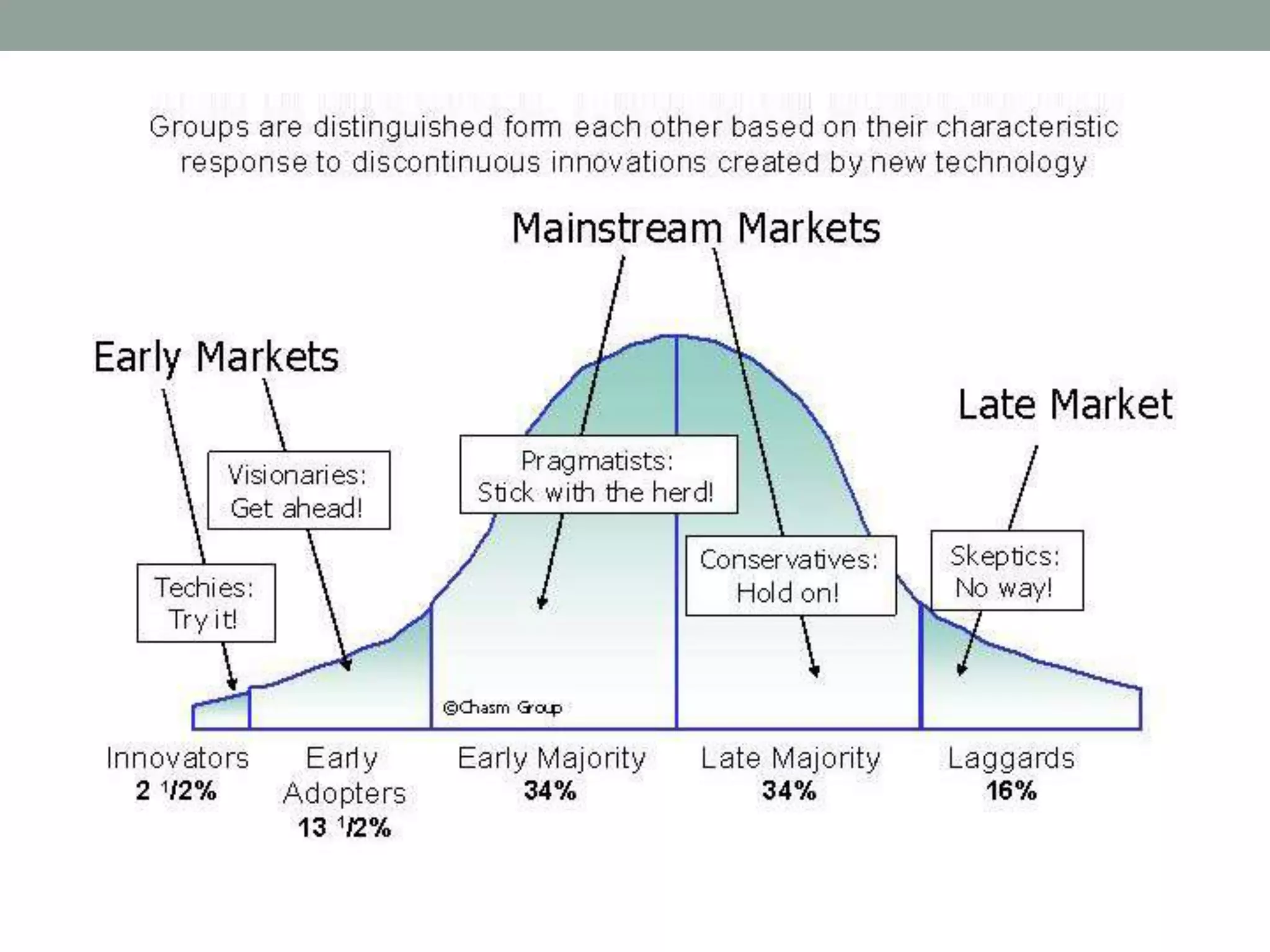
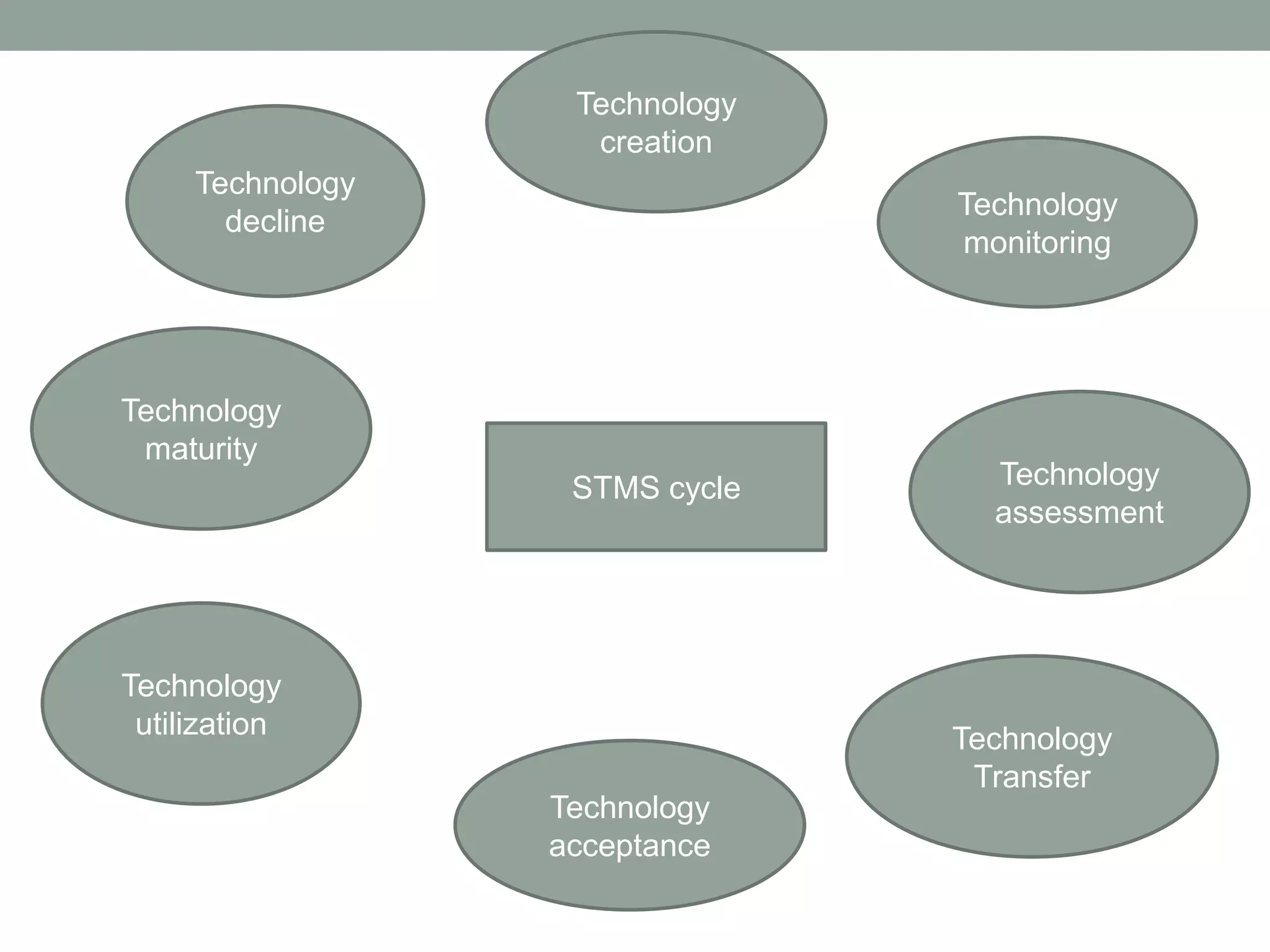
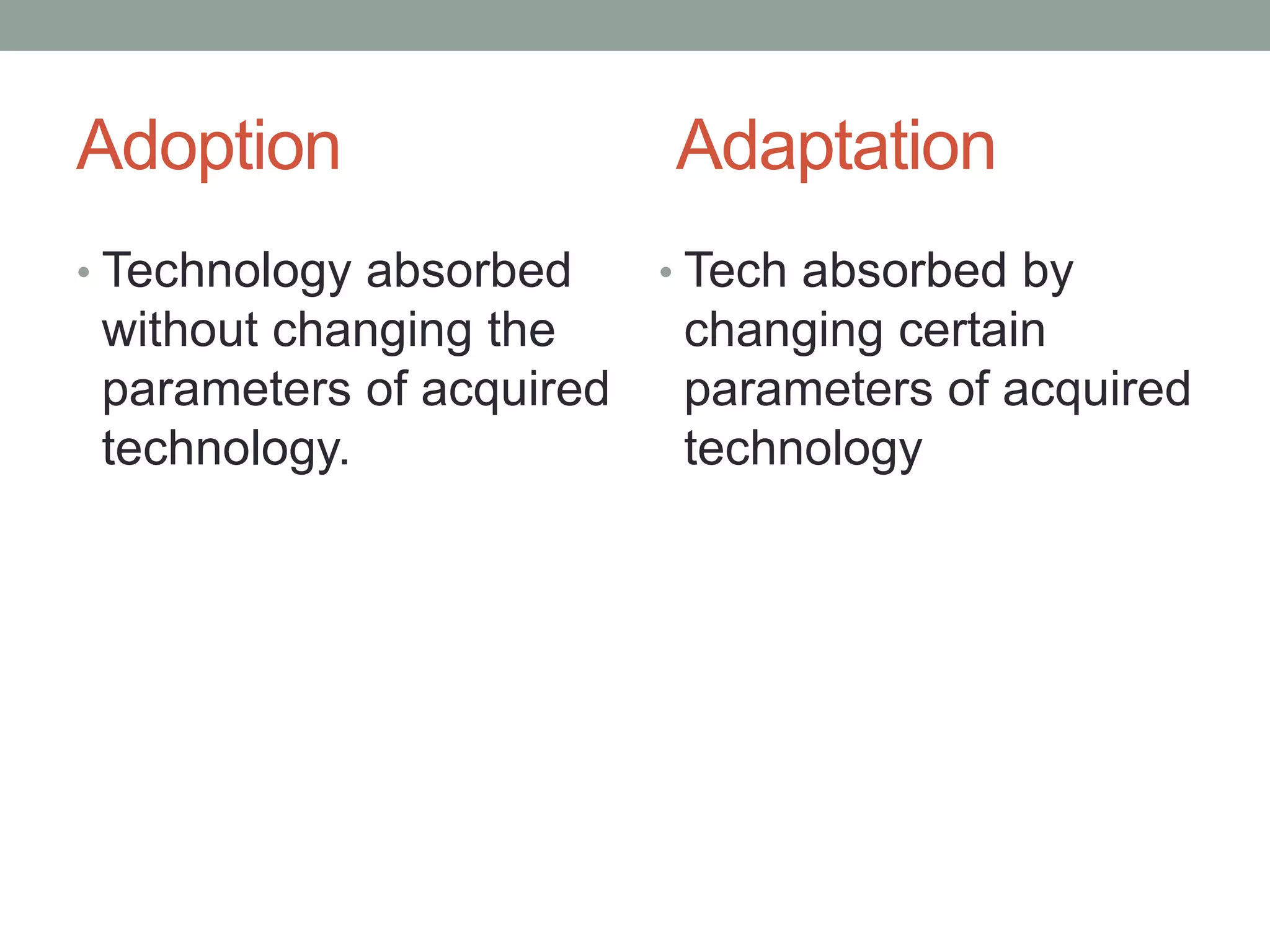
Technology management involves the planning, design, optimization, operation and control of technological products, processes and services. It includes assessing technologies, acquiring them internally or externally, absorbing the technology through assimilation and utilization, and managing the technology life cycle from development to decline. Effective technology management requires monitoring technological developments, evaluating technologies, transferring technologies within and between organizations, and ensuring technologies are accepted and fully utilized before they mature or degrade.