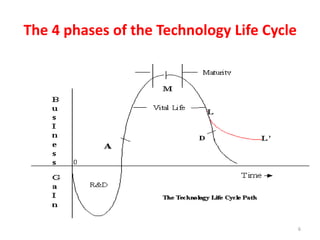
The document discusses the technology life cycle, which outlines the phases a technology goes through from development to decline. It describes the four phases as: 1) research and development, 2) growth, 3) maturity, and 4) decline. During research and development, risks are high and costs are negative. In the growth phase, costs are recovered and popularity increases. Technologies mature as competitors emerge and the market saturates. Finally, technologies decline as newer alternatives substitute them and profits decrease. The document provides examples to illustrate these phases.