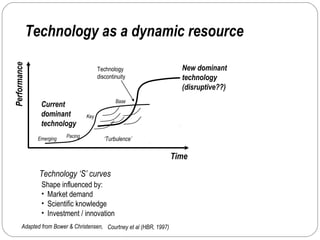
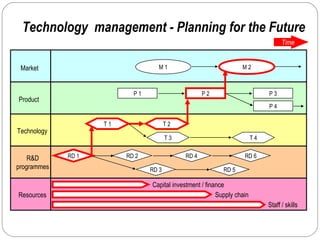
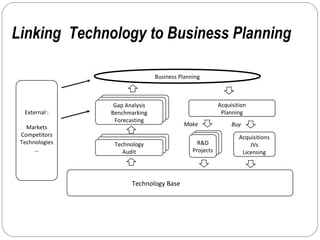
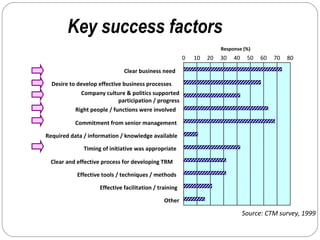
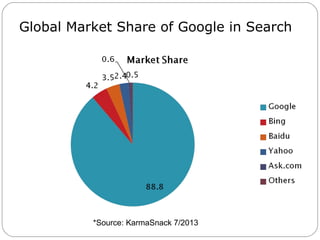
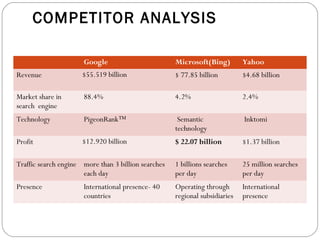
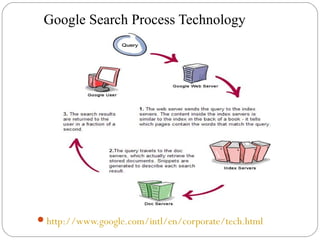
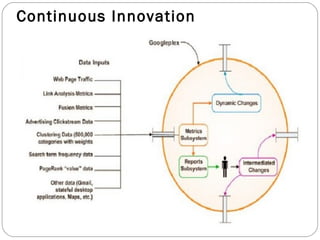
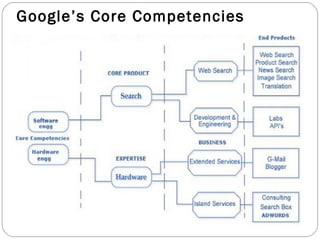
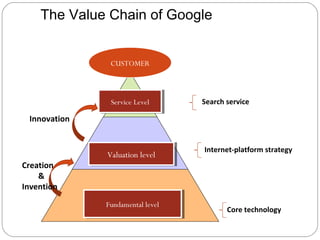
By discussing the need for technology management in a competitive global environment, the document outlines how proper management of technological change has become important for business success. It then provides examples of how technology can be planned for and linked to business goals through audits, benchmarking, forecasting and resource allocation. The document emphasizes continuous innovation, acquisition of complementary technologies, and leveraging powerful cloud computing as keys to Google's continued dominance in search and other business areas.