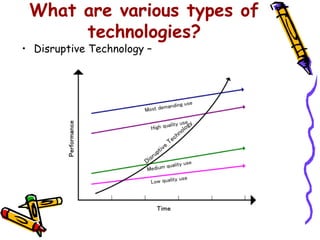
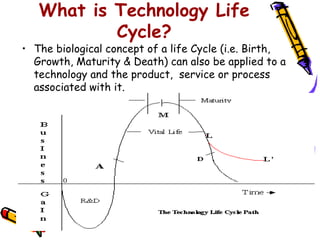
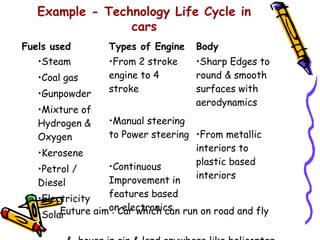
Dr. Vijay Kr Khurana outlines various types of technologies, including disruptive, sustaining, and technologies relevant to national and organizational portfolios, emphasizing their interrelatedness and importance for competitiveness. The document discusses the technology life cycle, detailing its phases from development to decline and how it differs from the product life cycle. Examples from the automotive industry illustrate technological advancements and shifts over time.