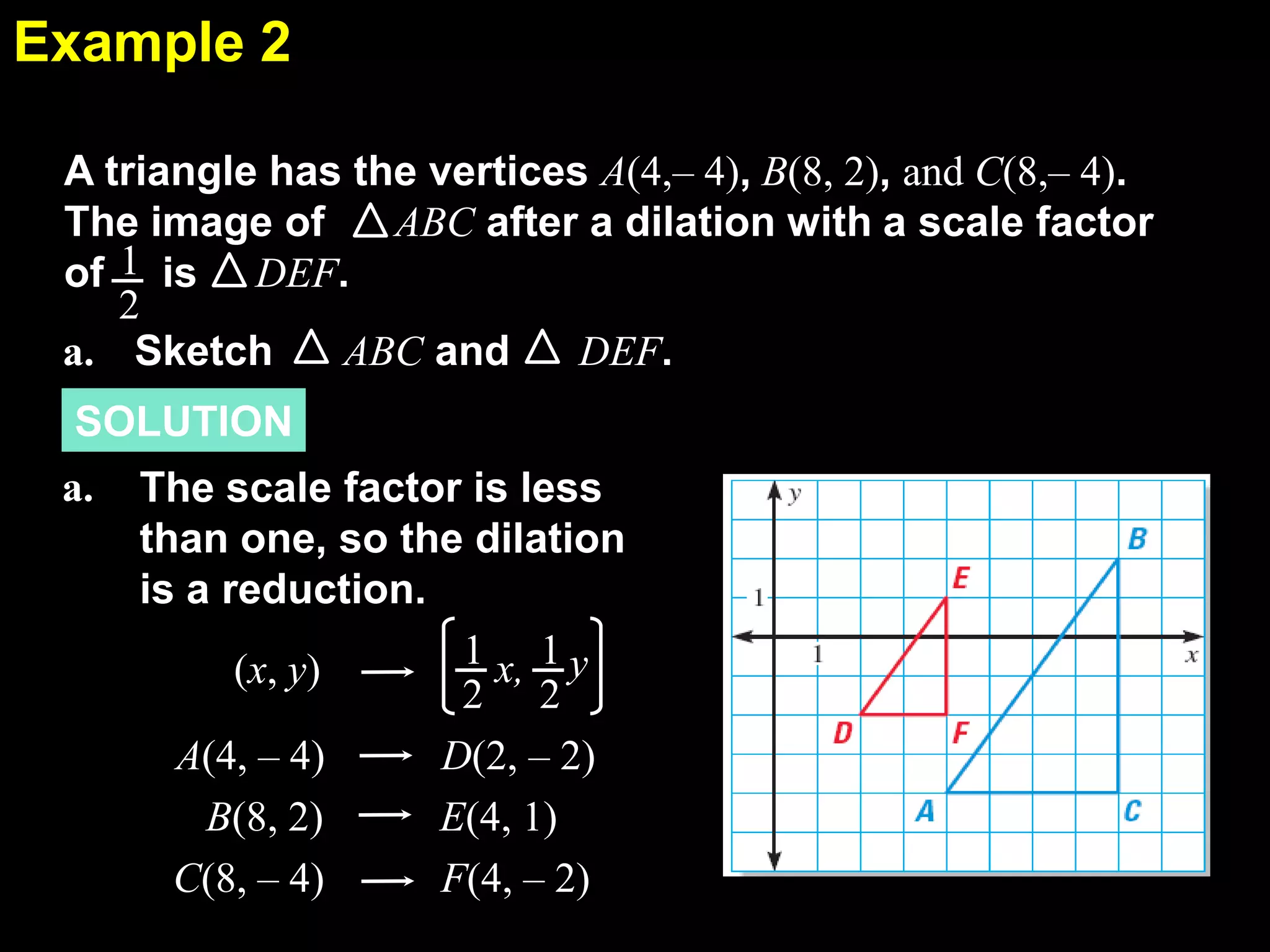
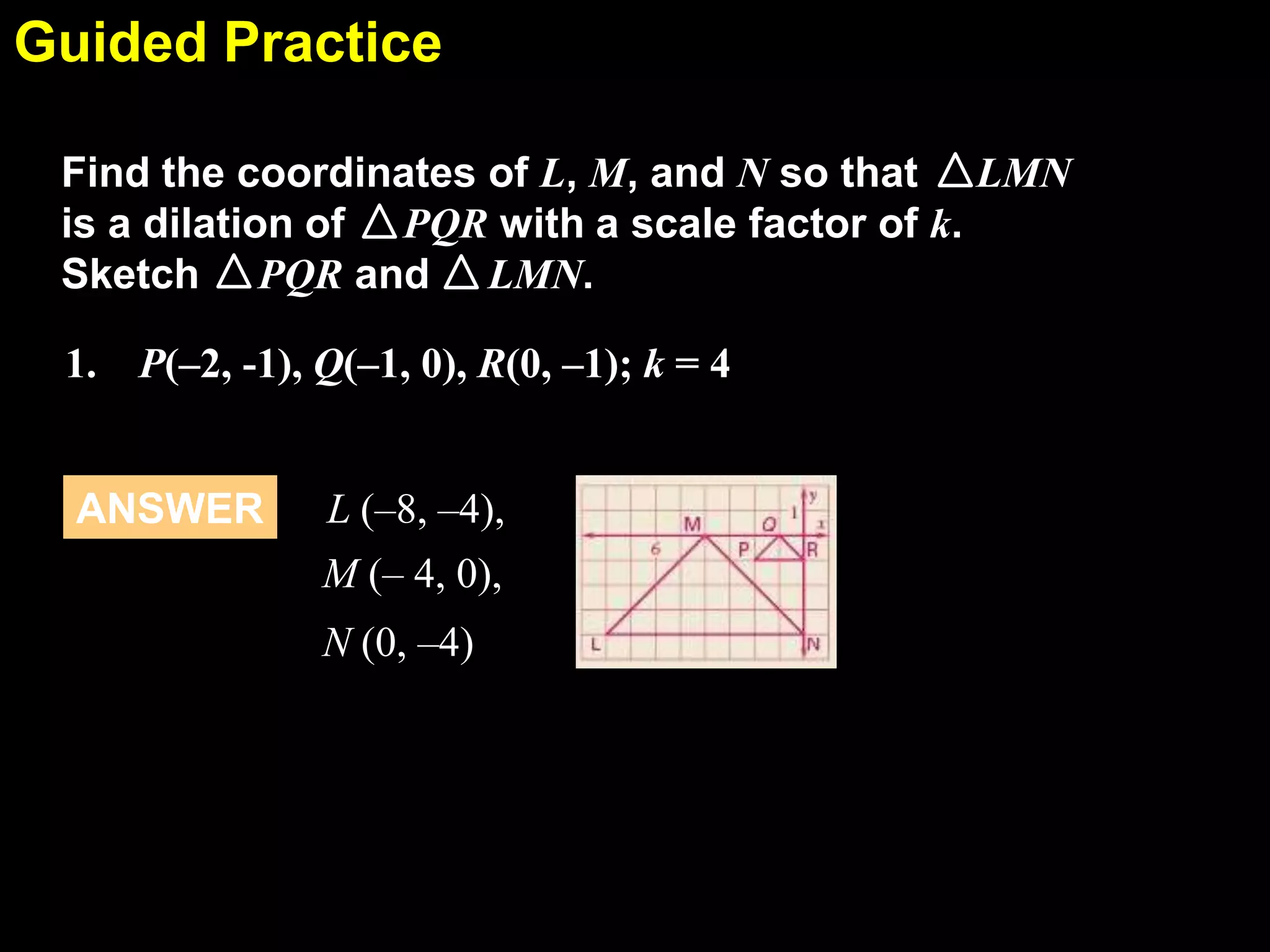
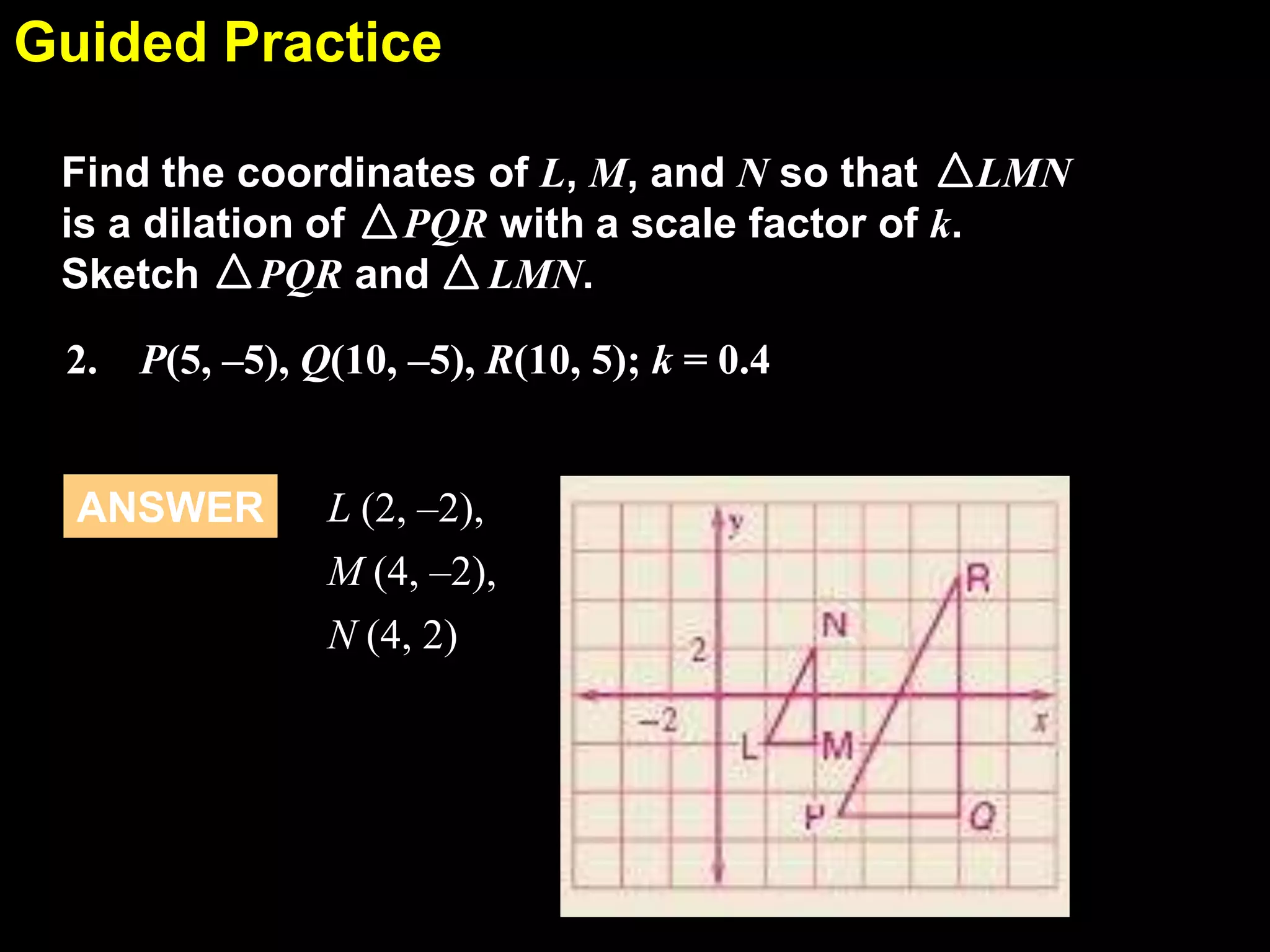
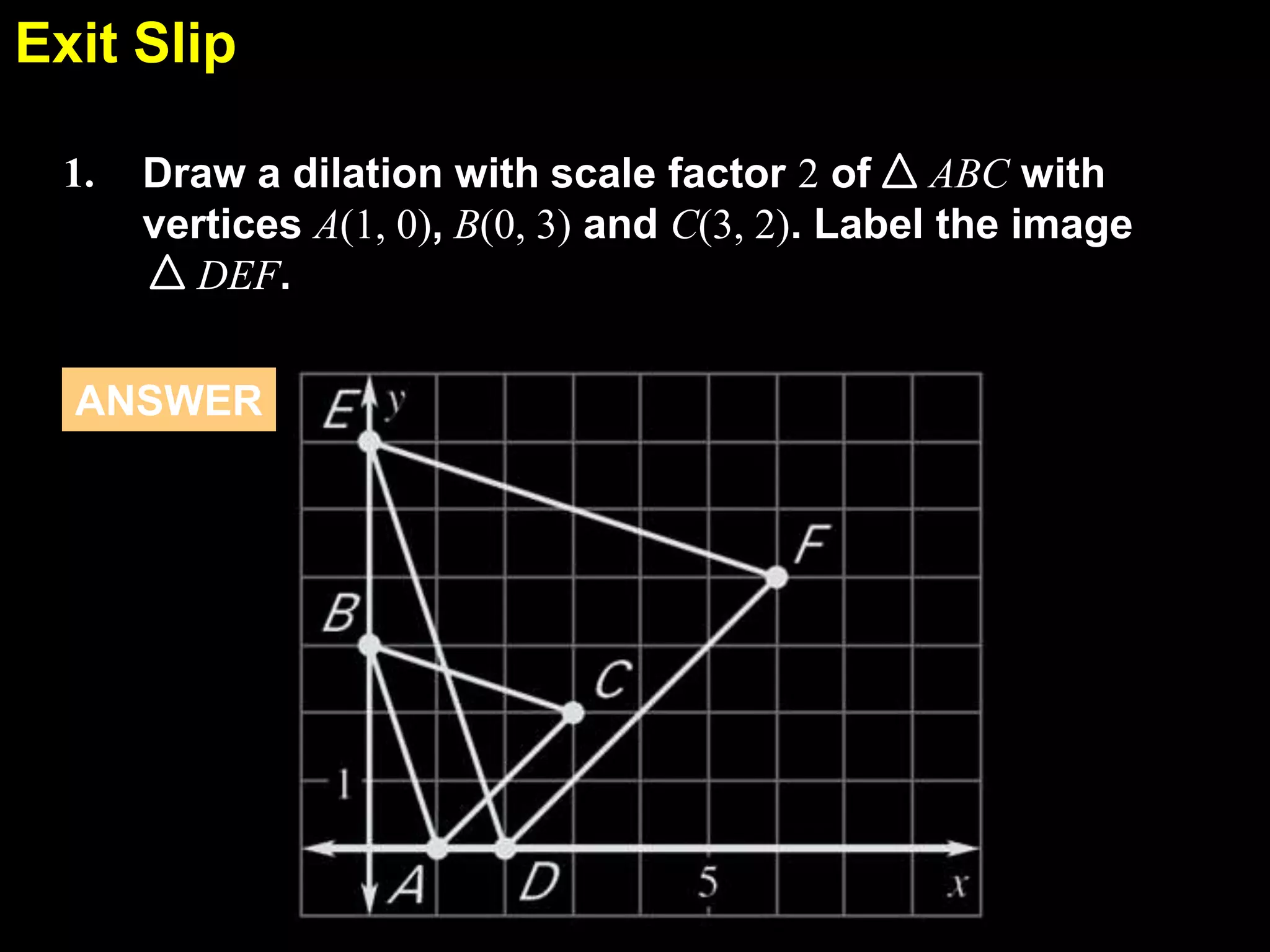
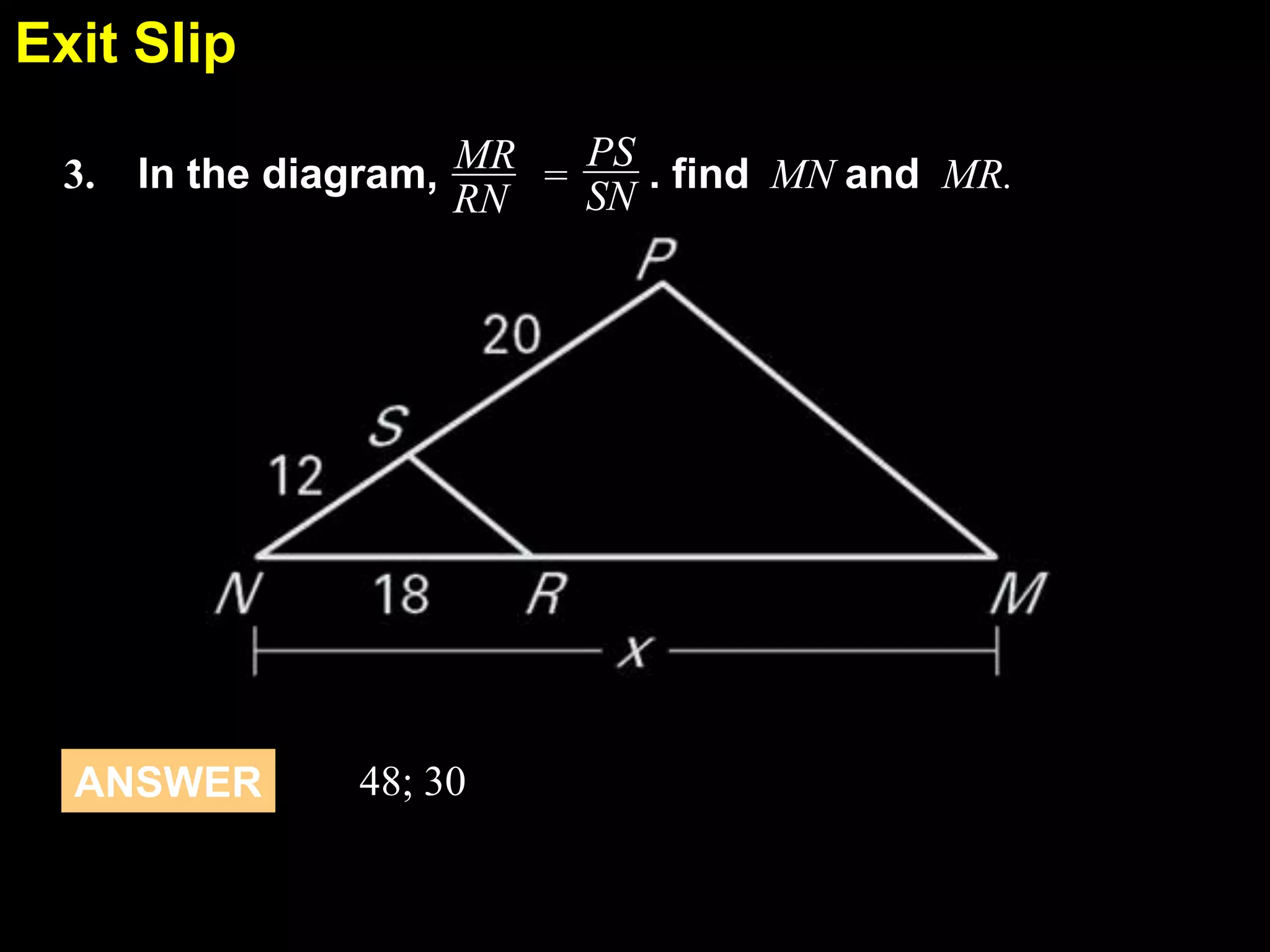
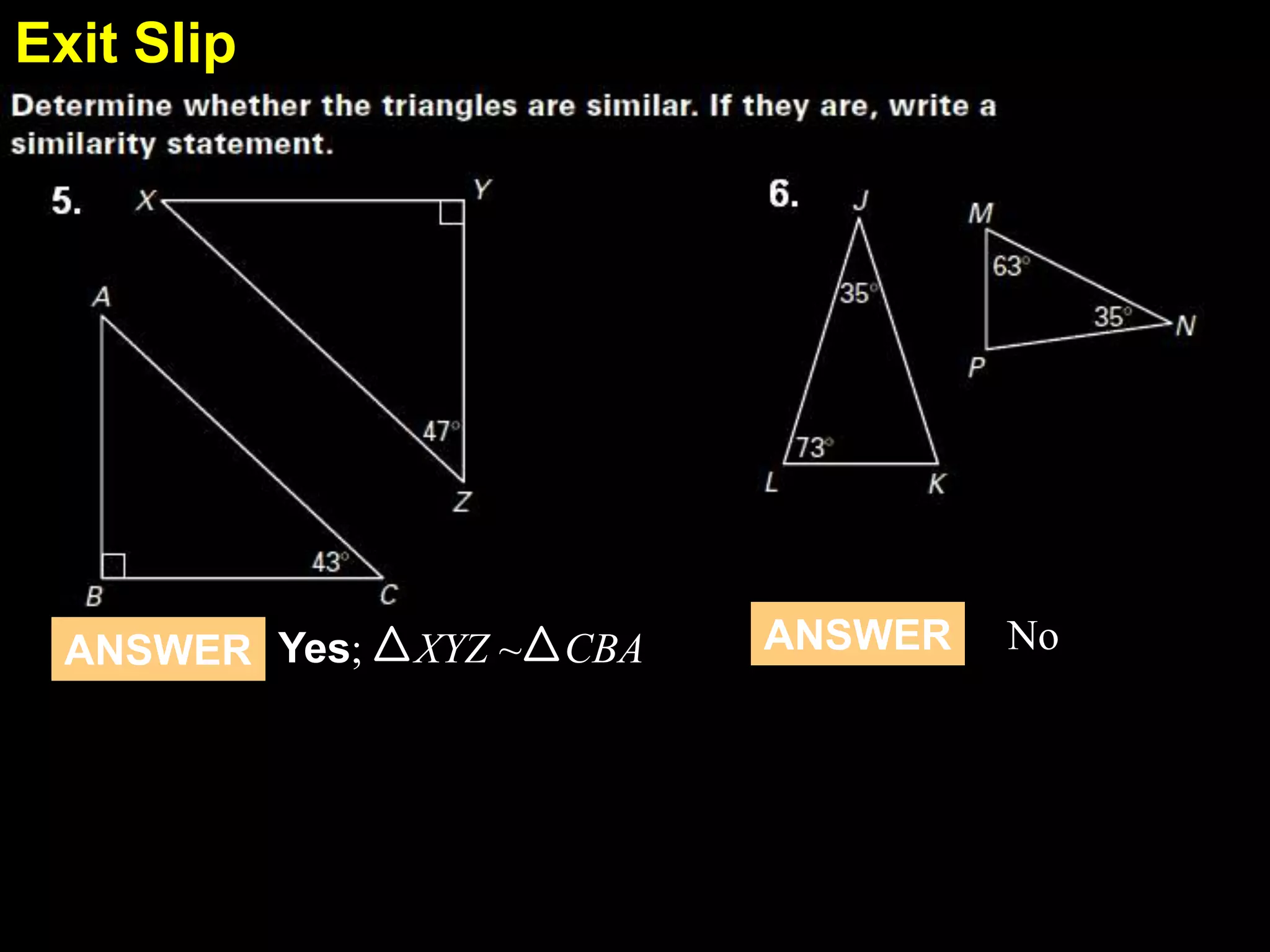
This document discusses similarity transformations and coordinate geometry. It includes examples of dilating figures by multiplying the coordinates of each point by a scale factor. It explains how to determine if two figures are similar by checking if they have the same scale factor. It provides guided practice problems on finding the coordinates of a dilated figure and explaining why the origin remains fixed under dilation. An exit slip includes drawing dilated figures and determining if figures are similar.