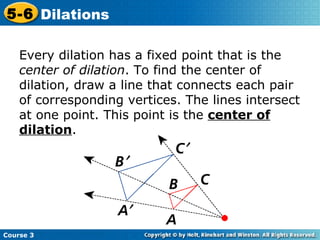
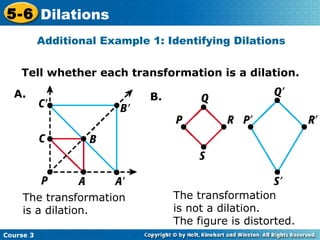
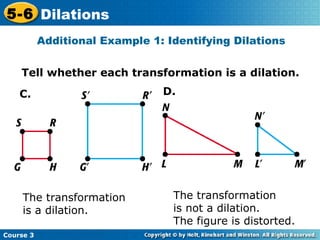
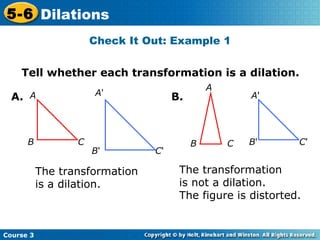
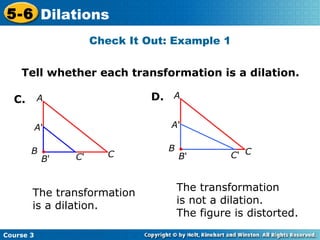
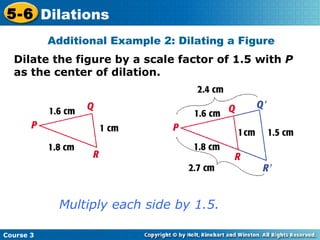
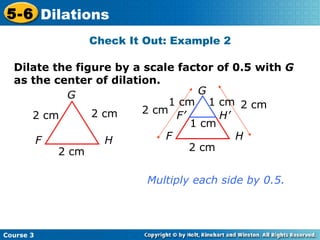
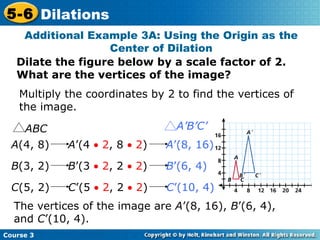
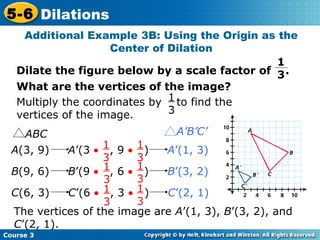
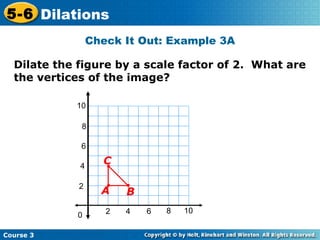
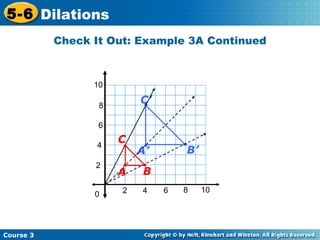
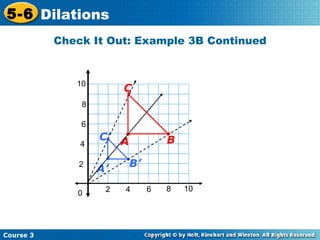
The document provides examples and explanations about dilations in geometry. It defines dilation as a transformation that changes the size but not the shape of a figure. It gives examples of dilating figures by scale factors both greater than and less than 1, with the center of dilation being either a fixed point on the figure or the origin. It shows how to determine the vertices of the dilated image by multiplying the coordinates of the original figure by the scale factor.