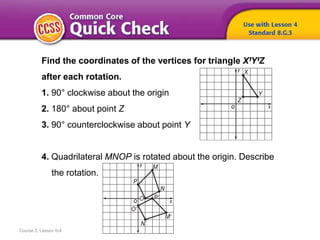
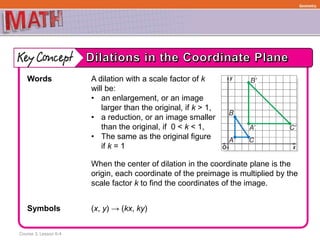
This document discusses how to find the coordinates of vertices for a triangle after various rotations and describes a quadrilateral being rotated about the origin. It provides examples of finding coordinates after a 90° clockwise rotation, 180° rotation about a point Z, 90° counterclockwise rotation about a point Y. It also discusses dilating figures using scale factors and providing examples of dilating triangles and finding the scale factor of a dilation based on diameters.





![1
Need Another Example?
2
3
Step-by-Step Example
1. A triangle has vertices A(0, 0), B(8, 0), and C(3, –2).
Find the coordinates of the triangle after a dilation
with a scale factor of 4.
The dilation is (x, y) → (4x, 4y). Multiply
the coordinates of each vertex by 4.
So, the coordinates after the dilation are
A'(0, 0), B'(32, 0), and C'(12, –8).
A(0, 0) → (4 • 0, 4 • 0) → (0, 0)
B(8, 0) → (4 • 8, 4 • 0) → (32, 0)
C(3, –2) → [4 • 3, 4 • (–2)] → (12, –8)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter6lesson4presentationcourse3-180913152733/85/8-Lesson-6-4-Dilations-8-320.jpg)







