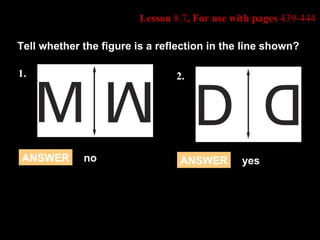
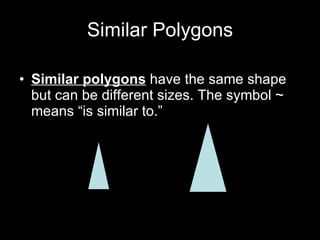
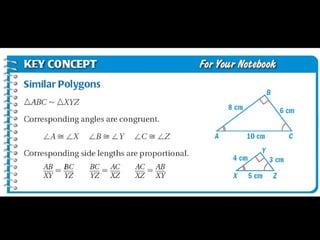
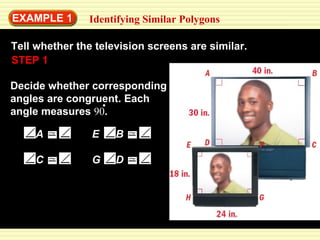
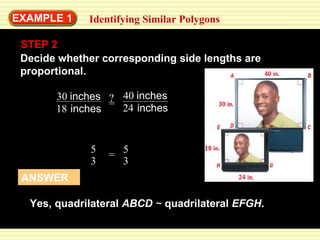
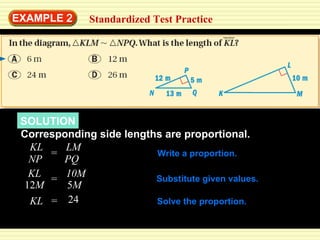
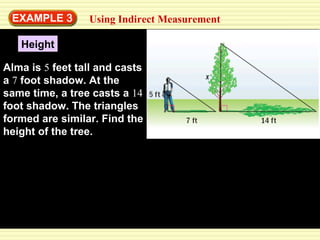
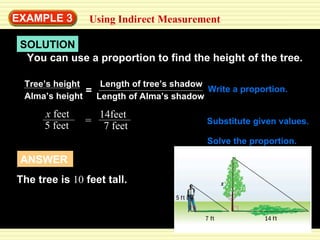
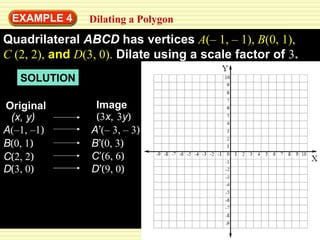
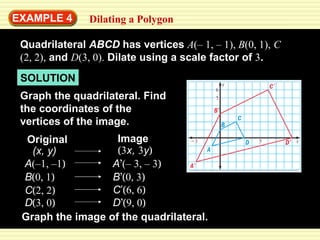
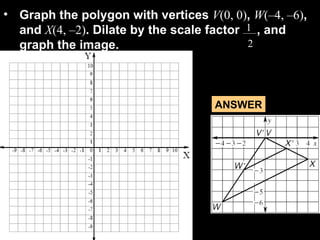
This document discusses transformations in geometry, including reflections, similarities, dilations, and their applications. It provides examples of determining if figures are reflections or similar, using proportions to find unknown side lengths, and dilating polygons by multiplying the coordinates by a scale factor. Key points covered are defining similar polygons as those with the same shape but different sizes, using proportions to solve similarity problems, and dilating figures by multiplying the original coordinates by the scale factor.