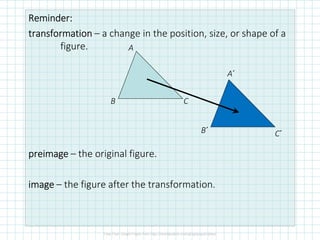
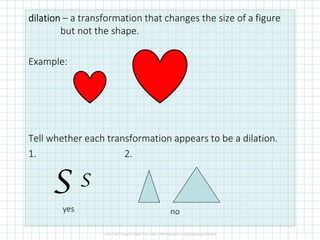
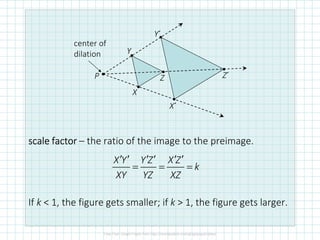
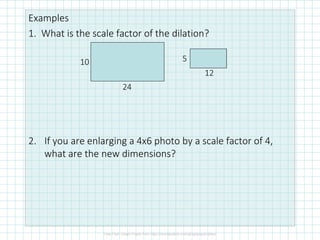
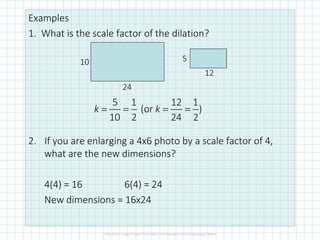
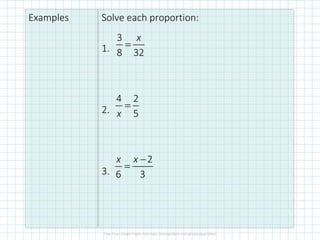
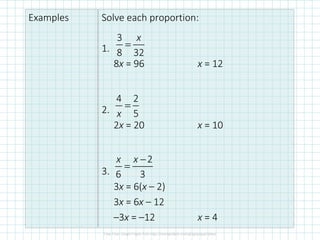
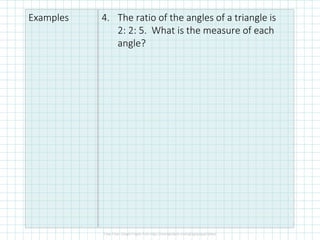
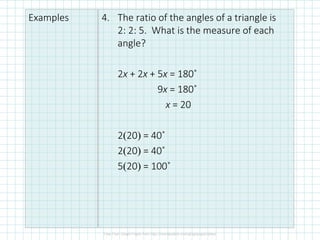
The document covers concepts of dilation, scale factors, ratios, and proportions in mathematics. It defines transformations, particularly dilations that change size but not shape, and explains how to identify and solve problems using these concepts. Examples are provided to illustrate how to calculate scale factors, solve proportions, and determine angles based on ratios.