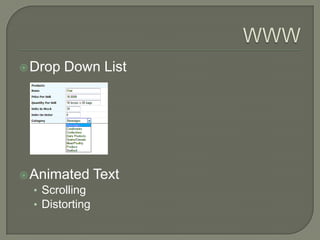
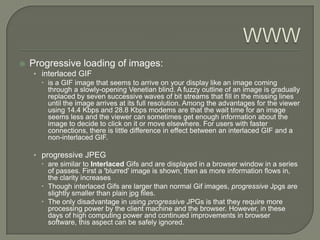
The document discusses the history and development of the World Wide Web including:
- The goals of the W3C to make the social and knowledge sharing benefits of the web available to all people globally.
- Common issues regarding appropriate usage such as following laws, copyright, censorship, and age restrictions.
- Technical aspects of implementing text, graphics, video, audio and other multimedia on the web along with related file formats and protocols.