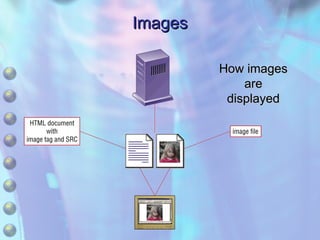
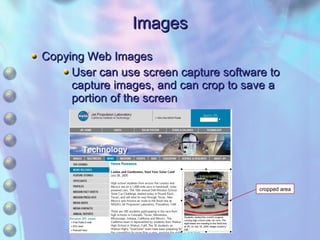
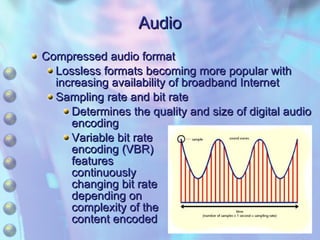
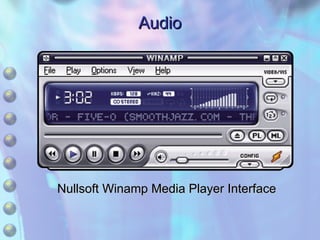
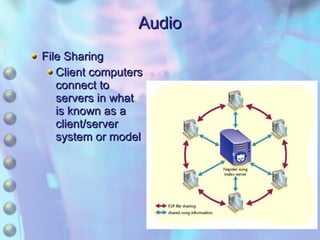
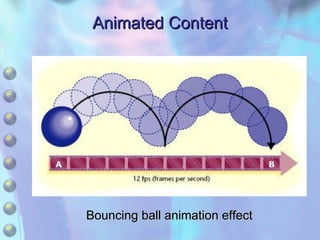
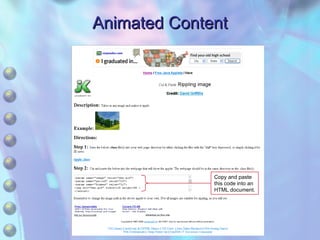
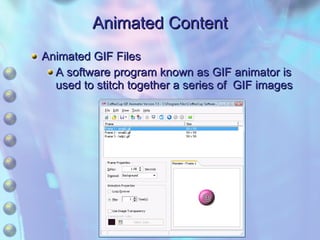
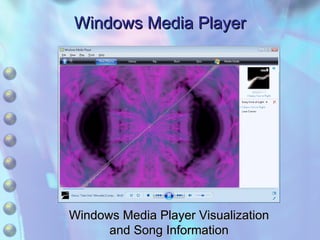
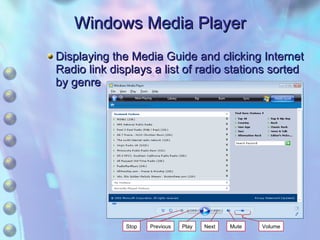
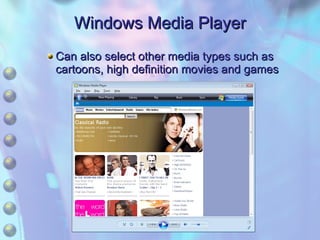
The document discusses multimedia content on the web including images, audio, animated content, and using the Windows Media Player. It explains how browsers handle different media types using plug-ins and helper applications. It also describes common image formats, compressed audio formats, streaming audio, creating animations with JavaScript, Flash and video. Finally, it outlines the features and functionality of the Windows Media Player.