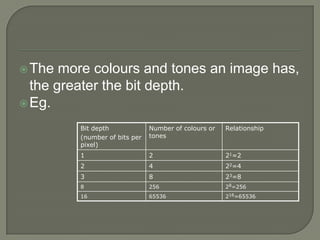
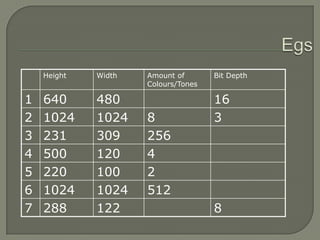
This document provides information about different types of graphics, including bitmapped and vector images. It discusses common file formats for images like JPEG, GIF, PNG, and TIFF. It also covers topics like resolution, color depth, importing images through scanning and digital cameras. Graphics tablets, stock photos, and image editing techniques like layering, filters, and manipulation are briefly mentioned.