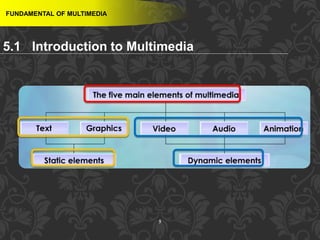
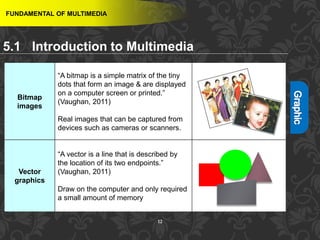
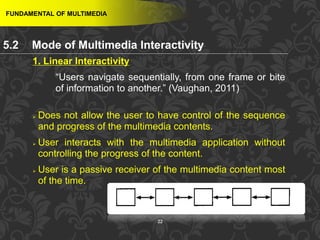
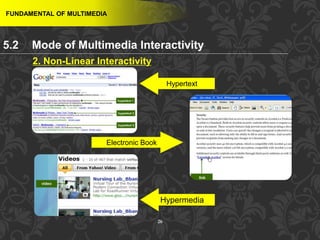
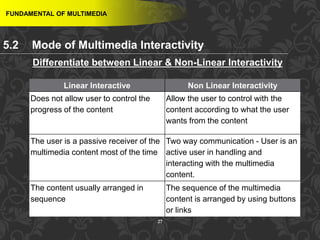
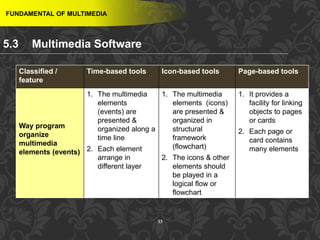
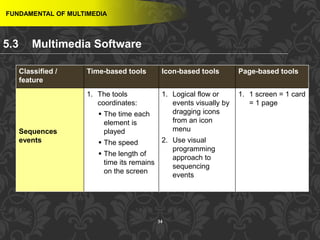
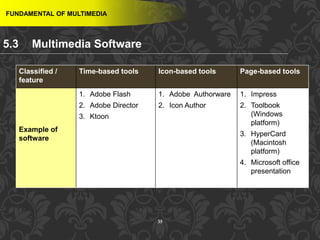
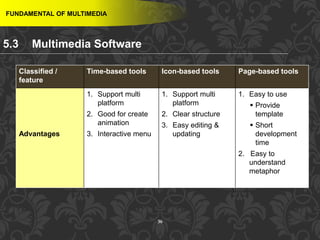
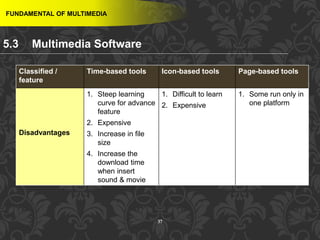
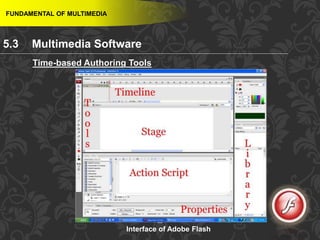
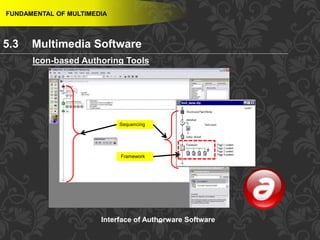
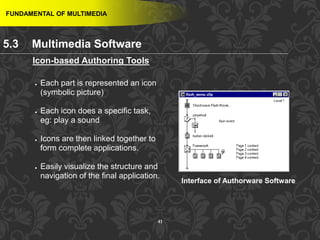
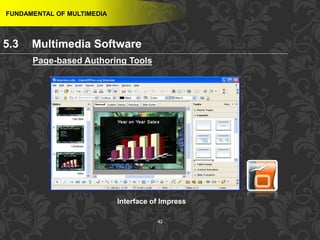
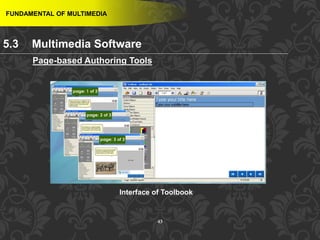
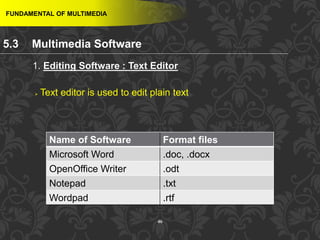
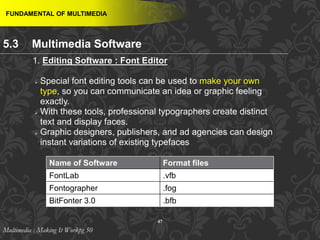
This document discusses multimedia and multimedia authoring tools. It defines multimedia as the combination of various media types, such as text, graphics, audio, video and animation, delivered by computer. There are several types of authoring tools for creating multimedia content, including time-based tools that organize elements on a timeline, page-based tools that link objects between pages, and icon-based tools that sequence events through a flowchart of icons. Examples of popular authoring tools mentioned are Adobe Flash, Adobe Director, and Authorware. The document also covers the different media elements that make up multimedia, such as text, graphics, video, audio and animation.