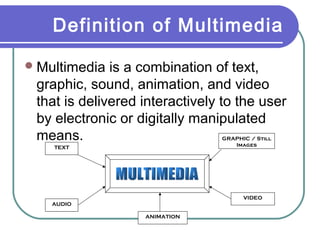
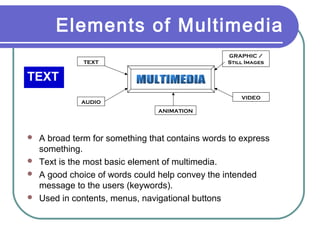
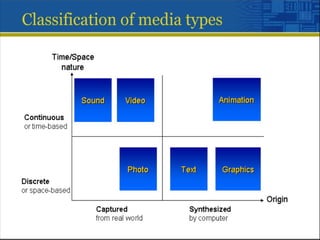
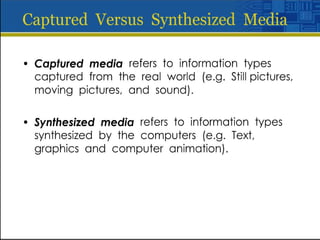
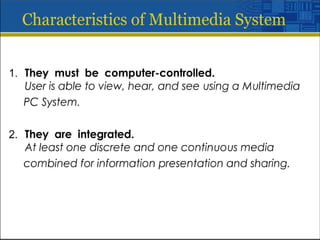
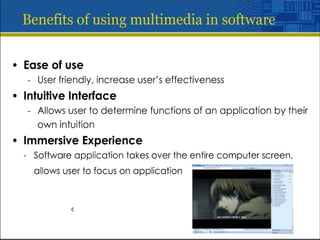
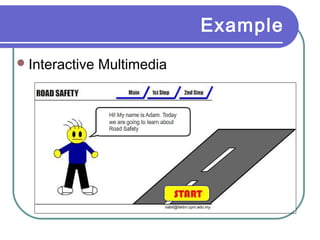
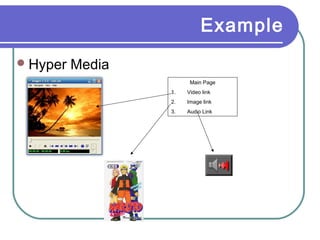
Multimedia is a blend of various content forms, including text, graphics, sound, animation, and video, delivered interactively through electronic means. It can be applied in different fields such as business, education, entertainment, and public spaces, with examples including interactive courses, games, and information kiosks. The document also distinguishes between linear and non-linear multimedia, highlighting the importance of user control and interaction in enhancing the multimedia experience.