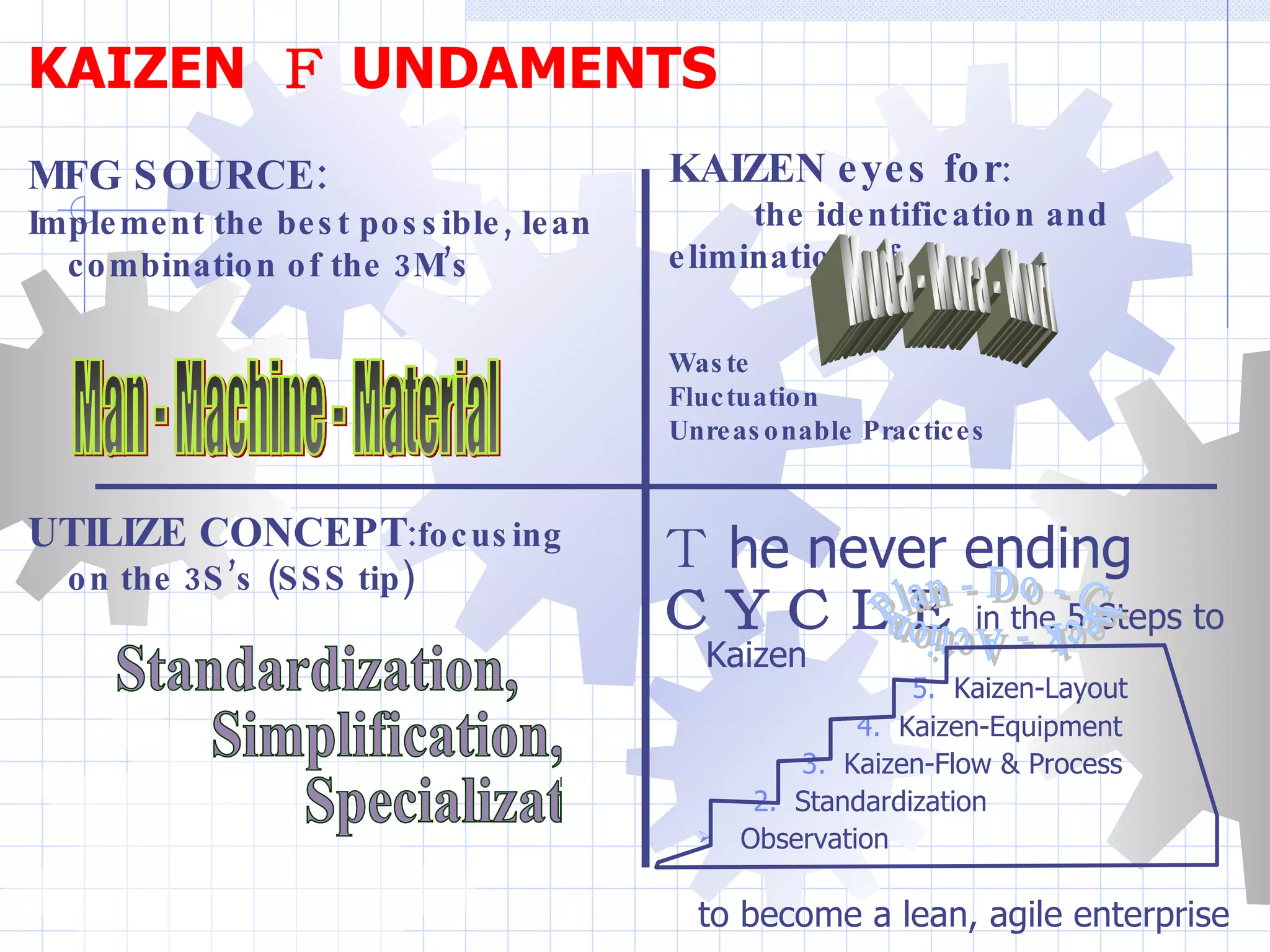
The document outlines the five steps to continuous improvement (Kaizen): 1) Observation, 2) Standardization, 3) Flow & Process Kaizen, 4) Equipment Kaizen, and 5) Layout Kaizen. The goal is to identify and eliminate waste, reduce variation, and improve the flow of materials and information through small, incremental changes. Key aspects include establishing standards, managing interruptions, improving processes, equipment, and layout to better support operators.