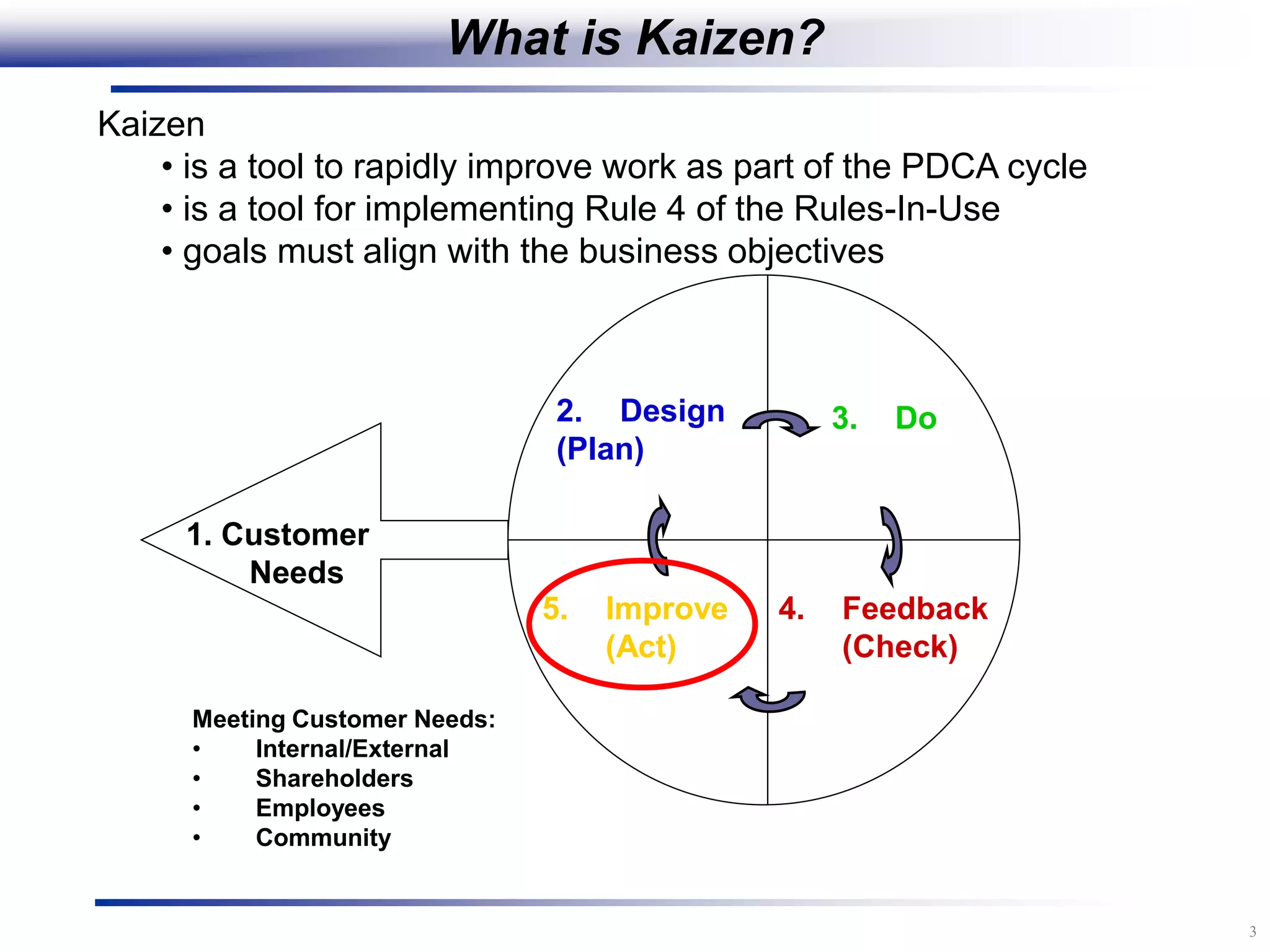
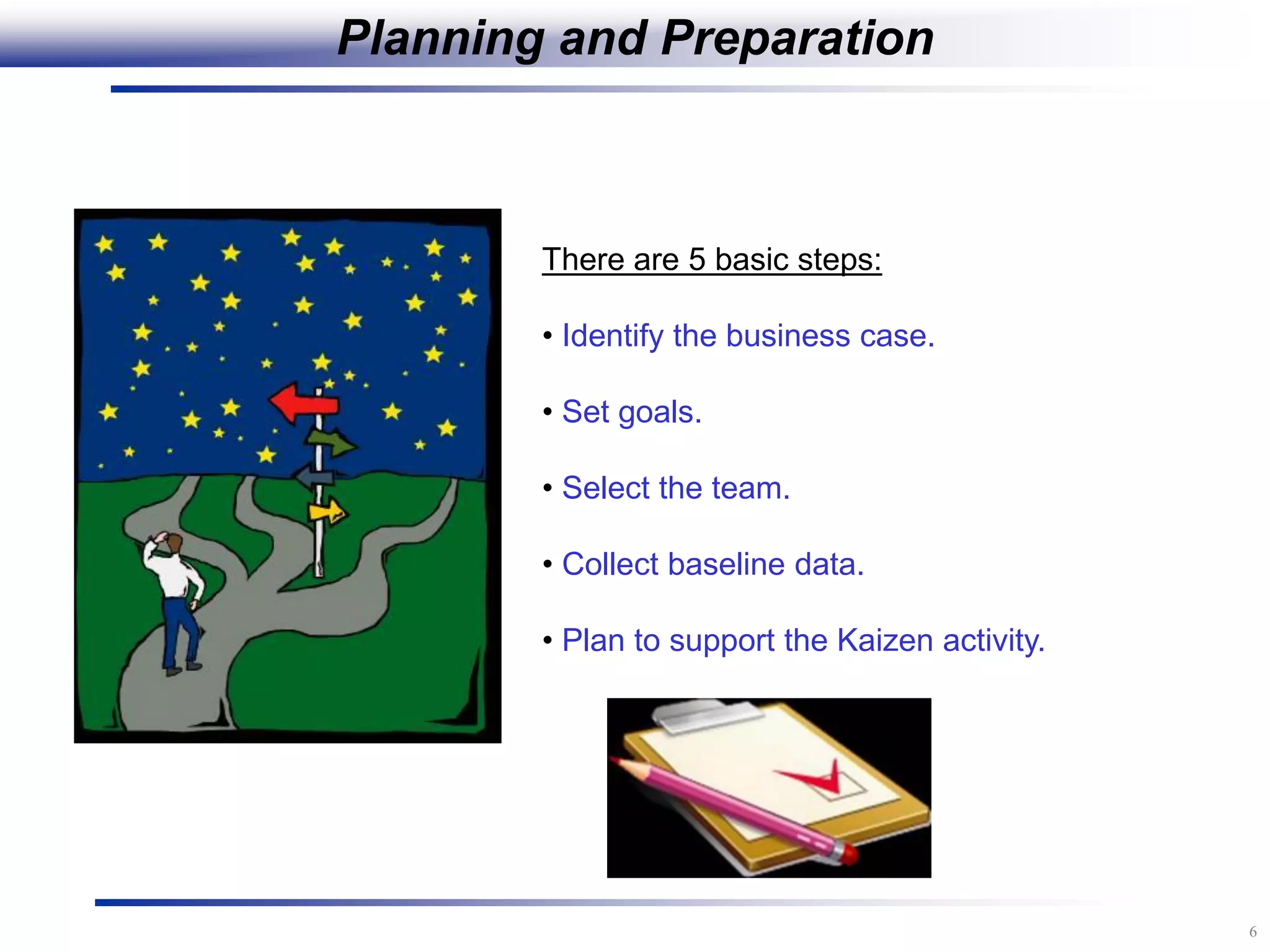
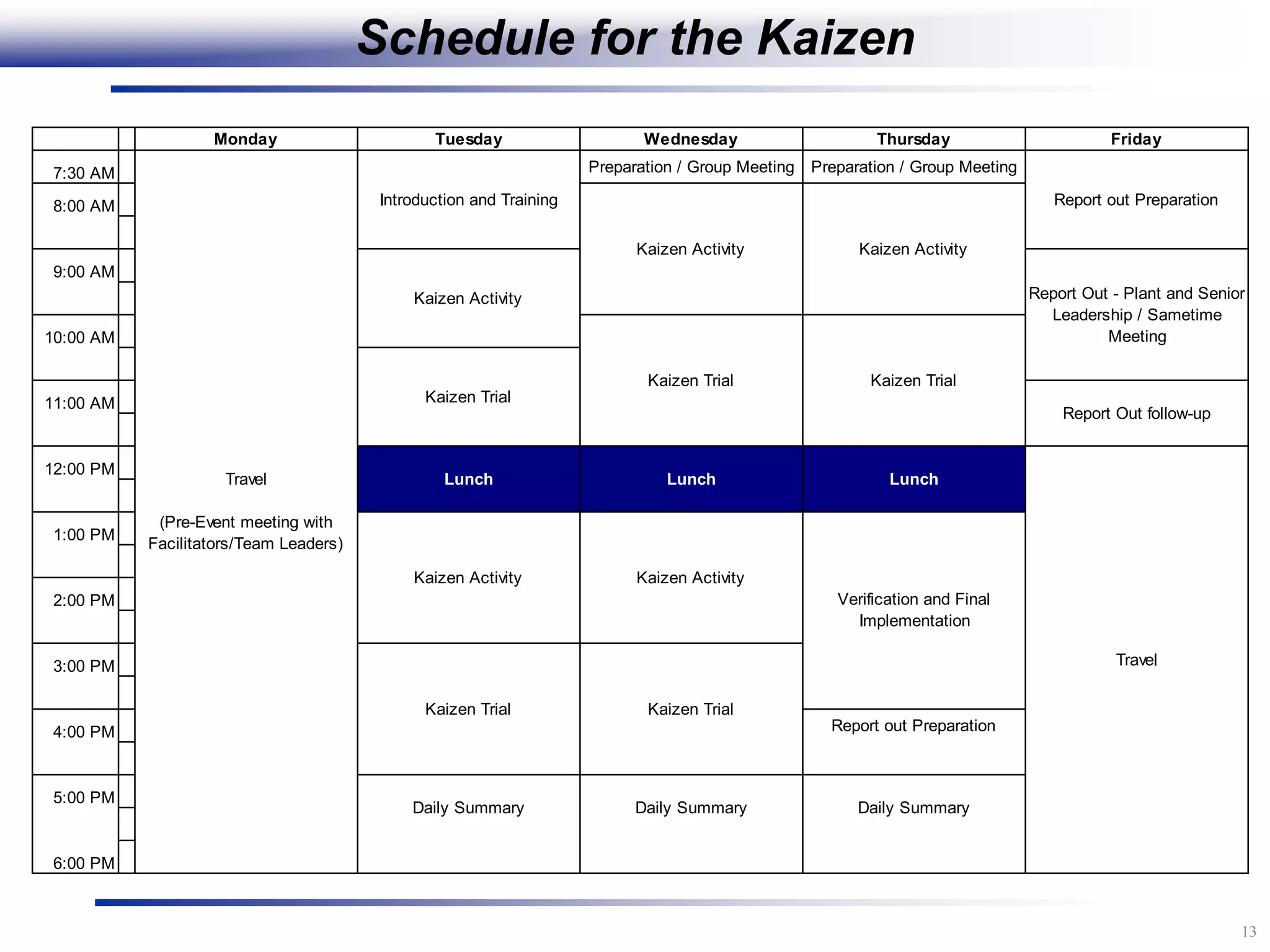
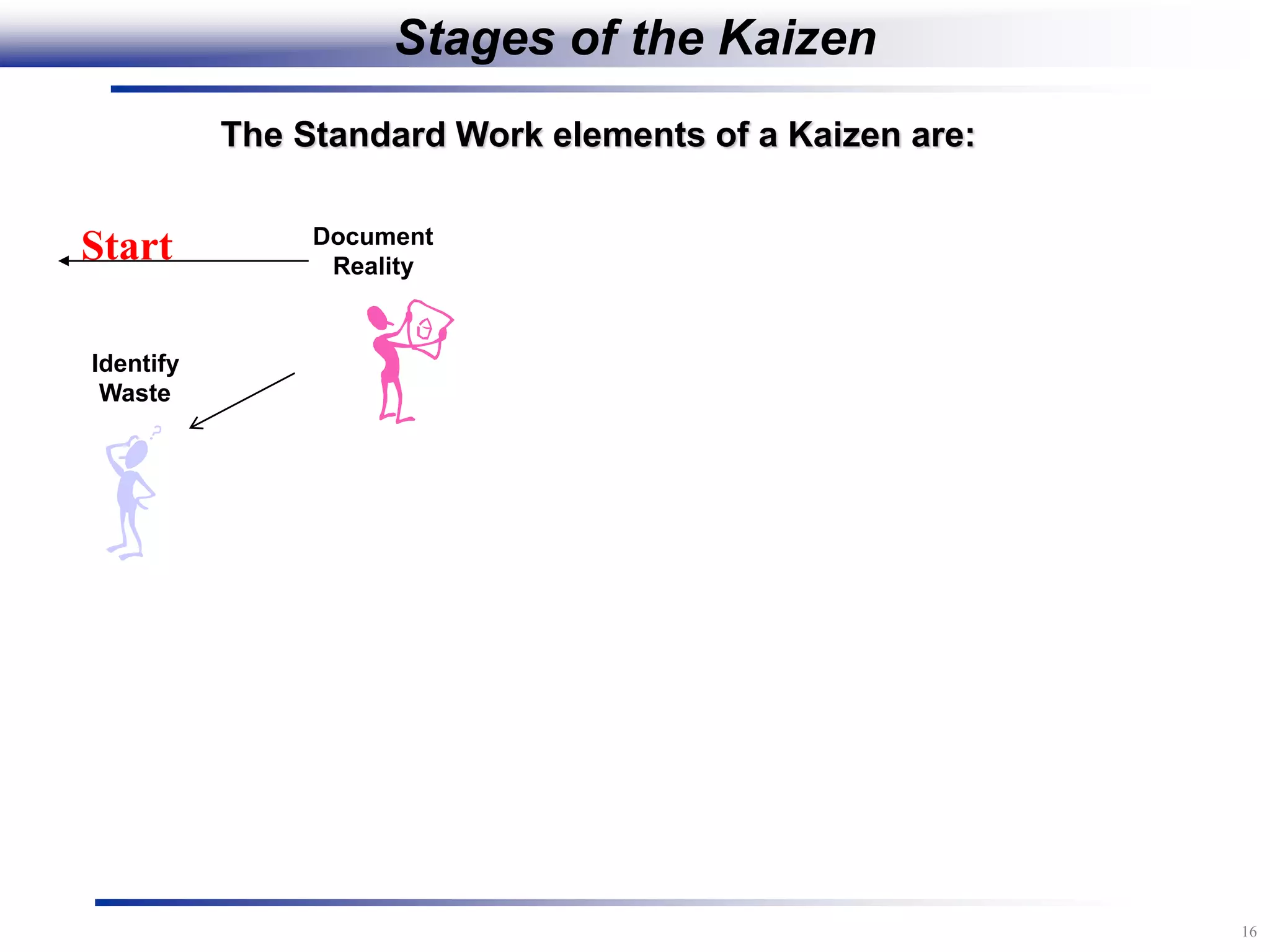
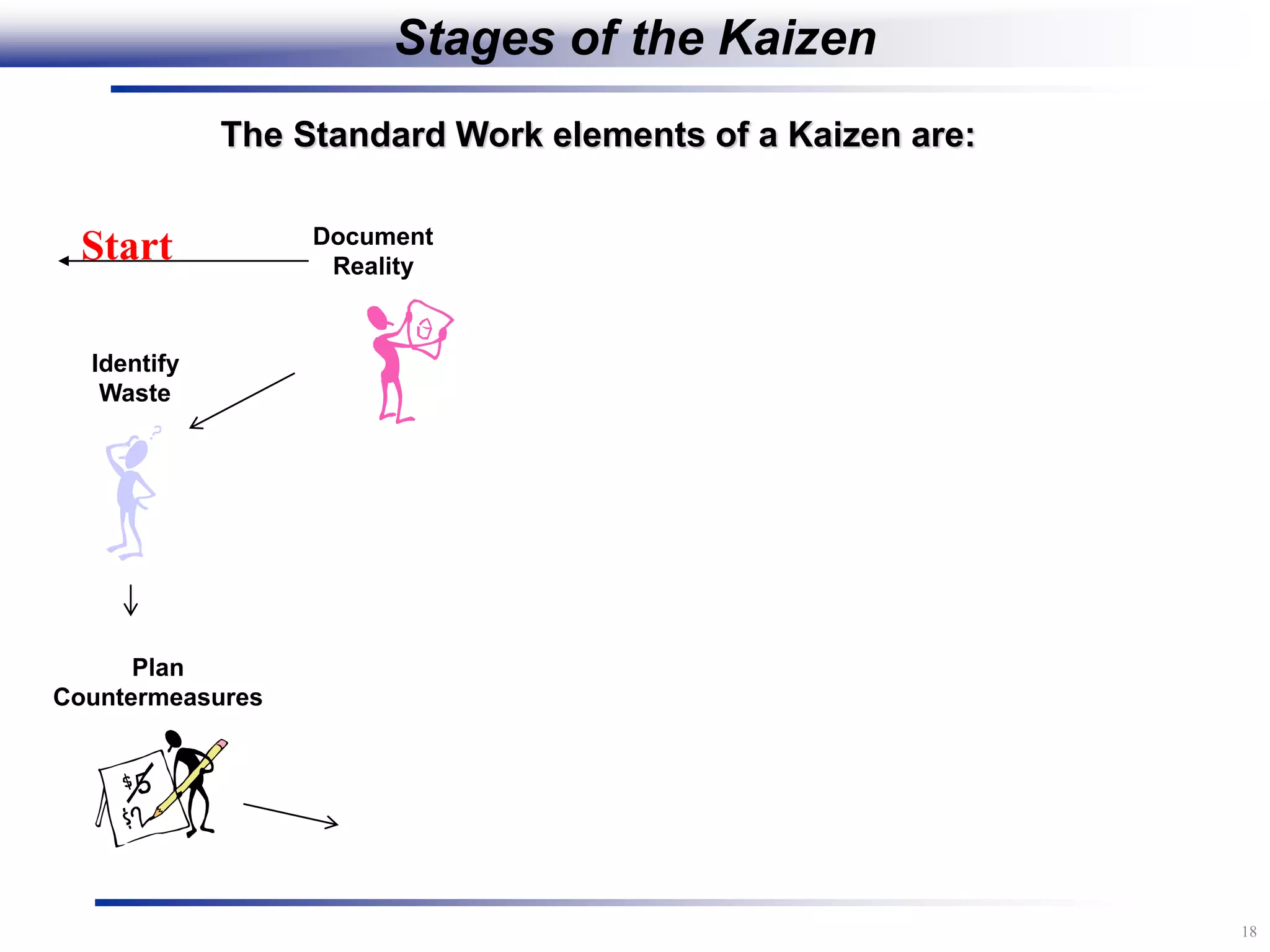
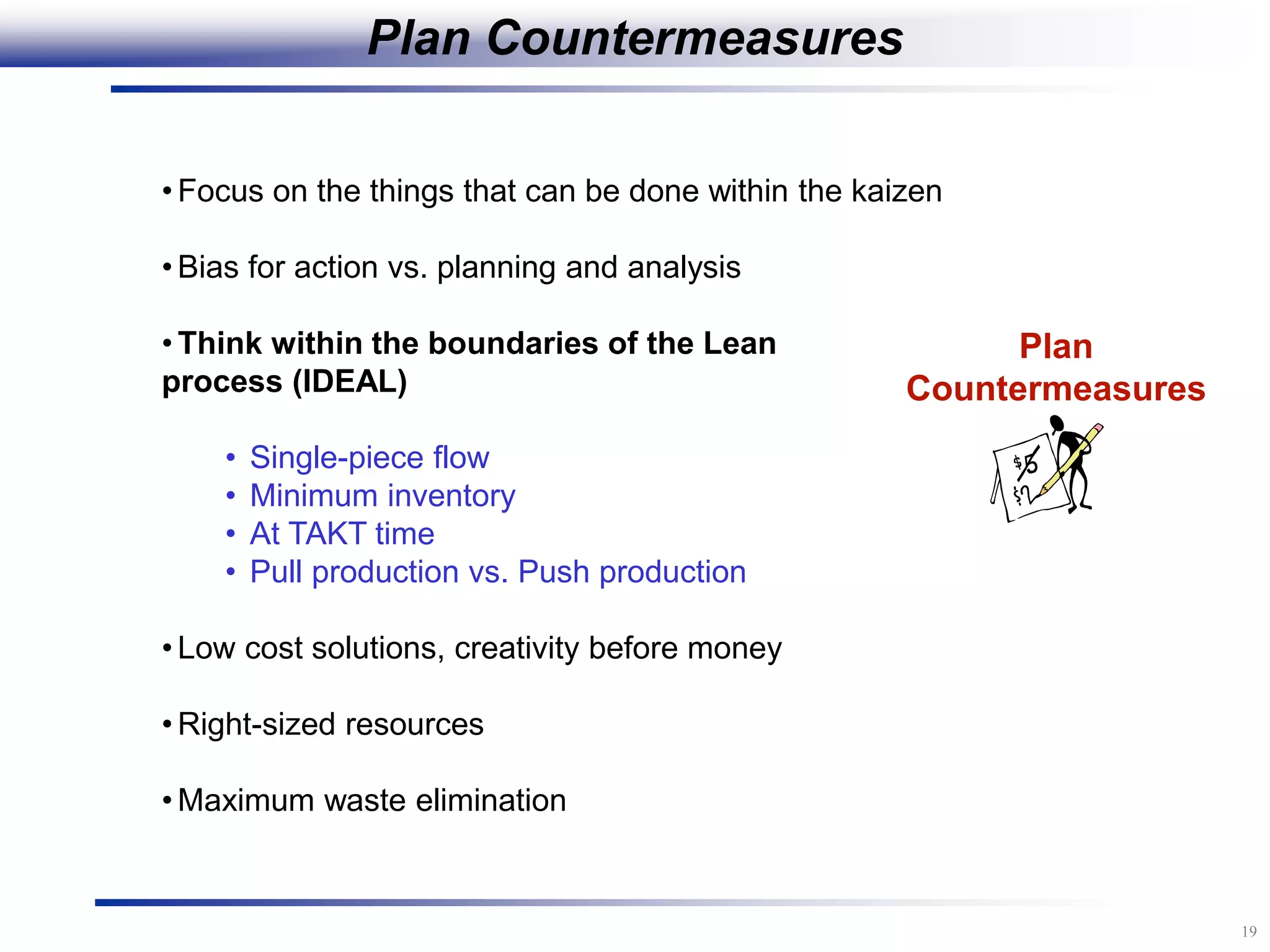
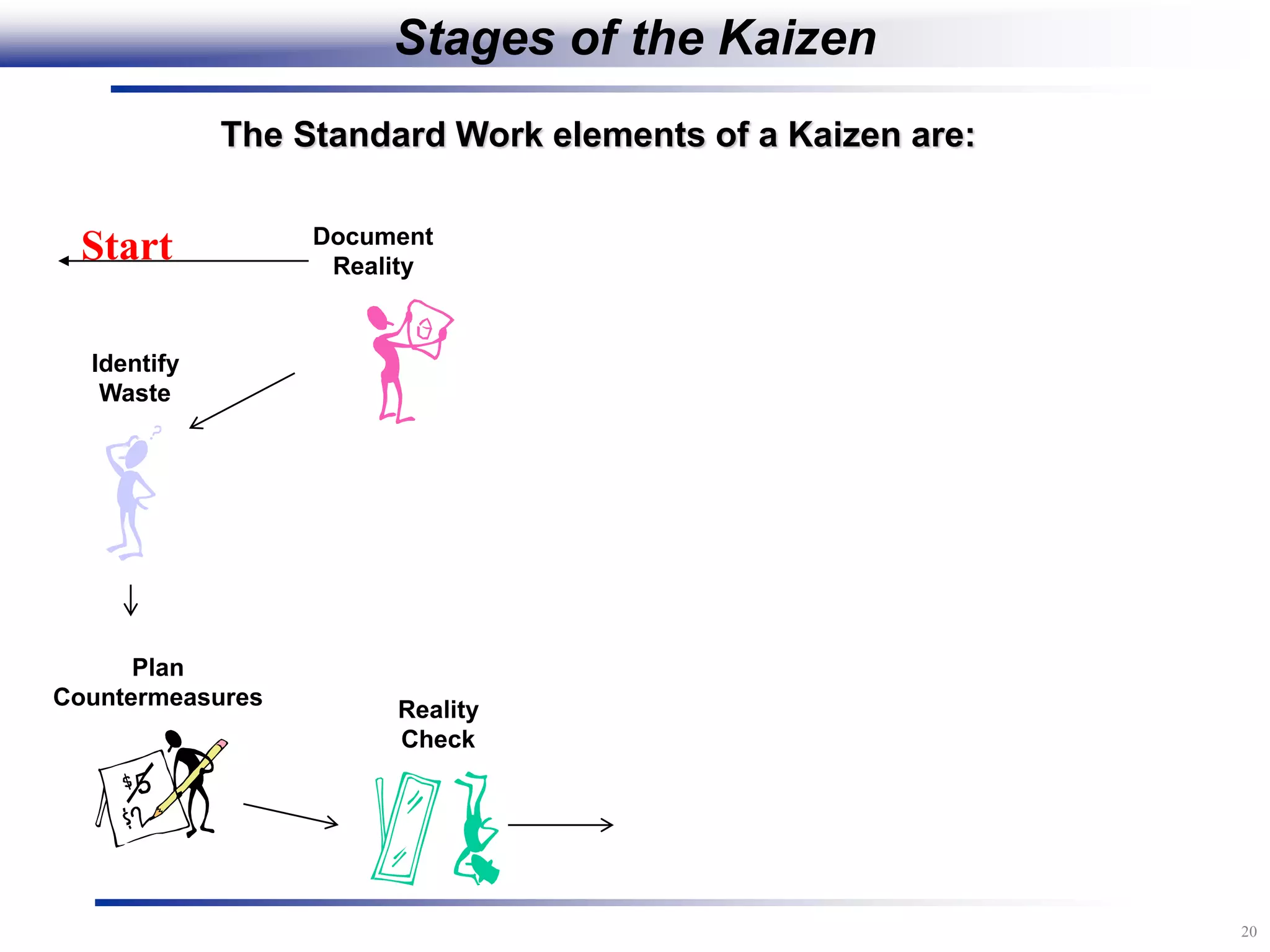
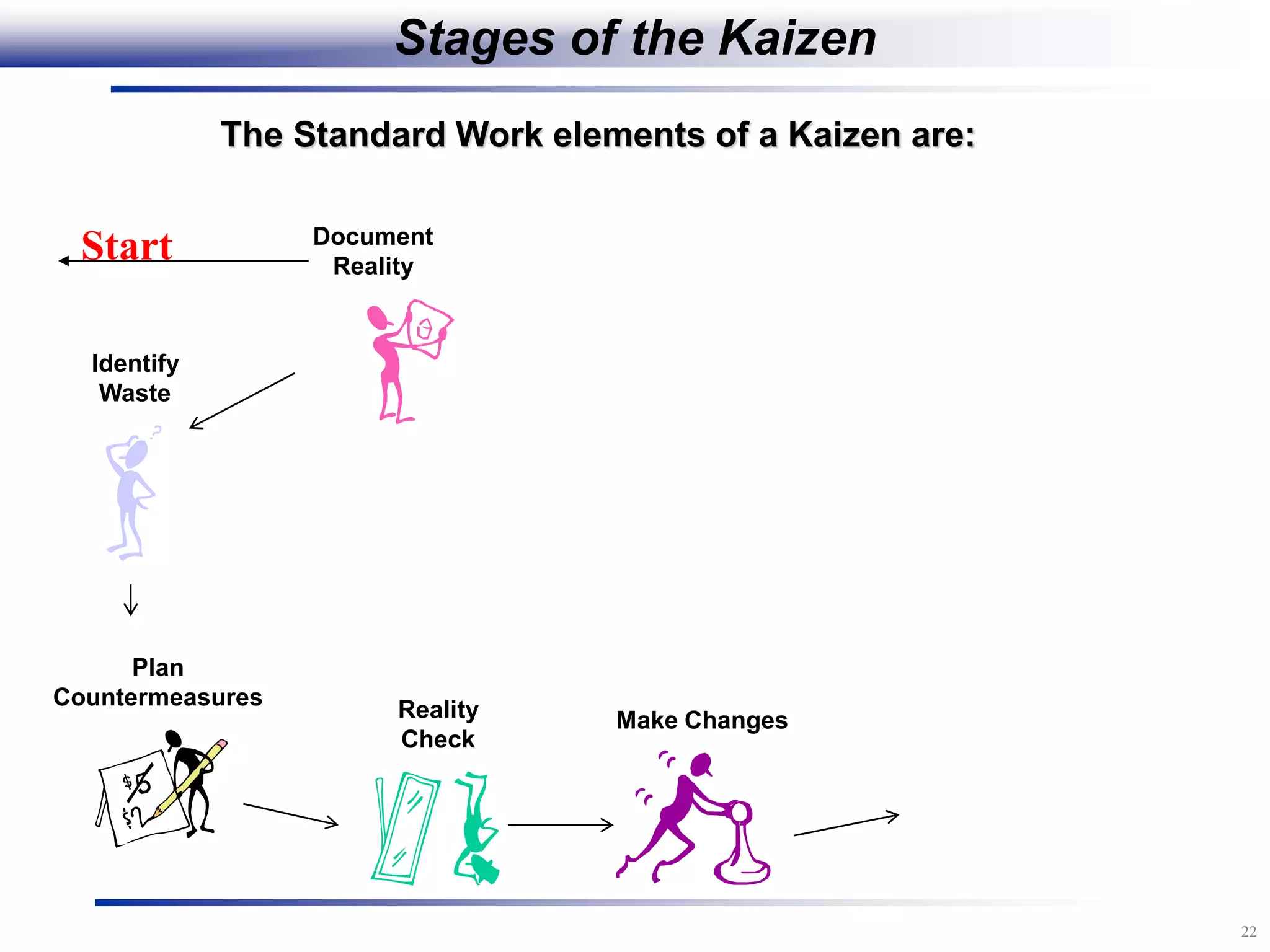
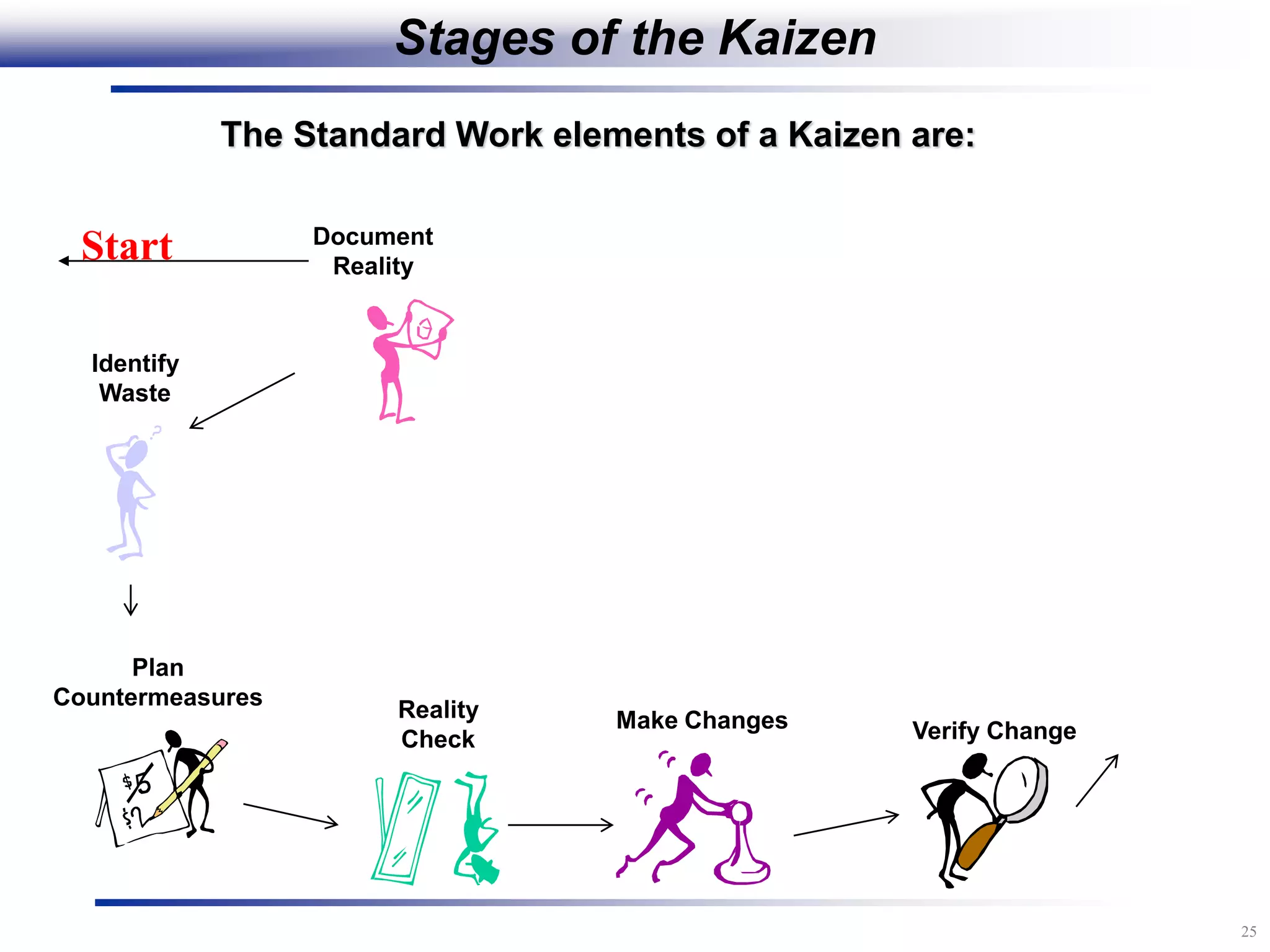
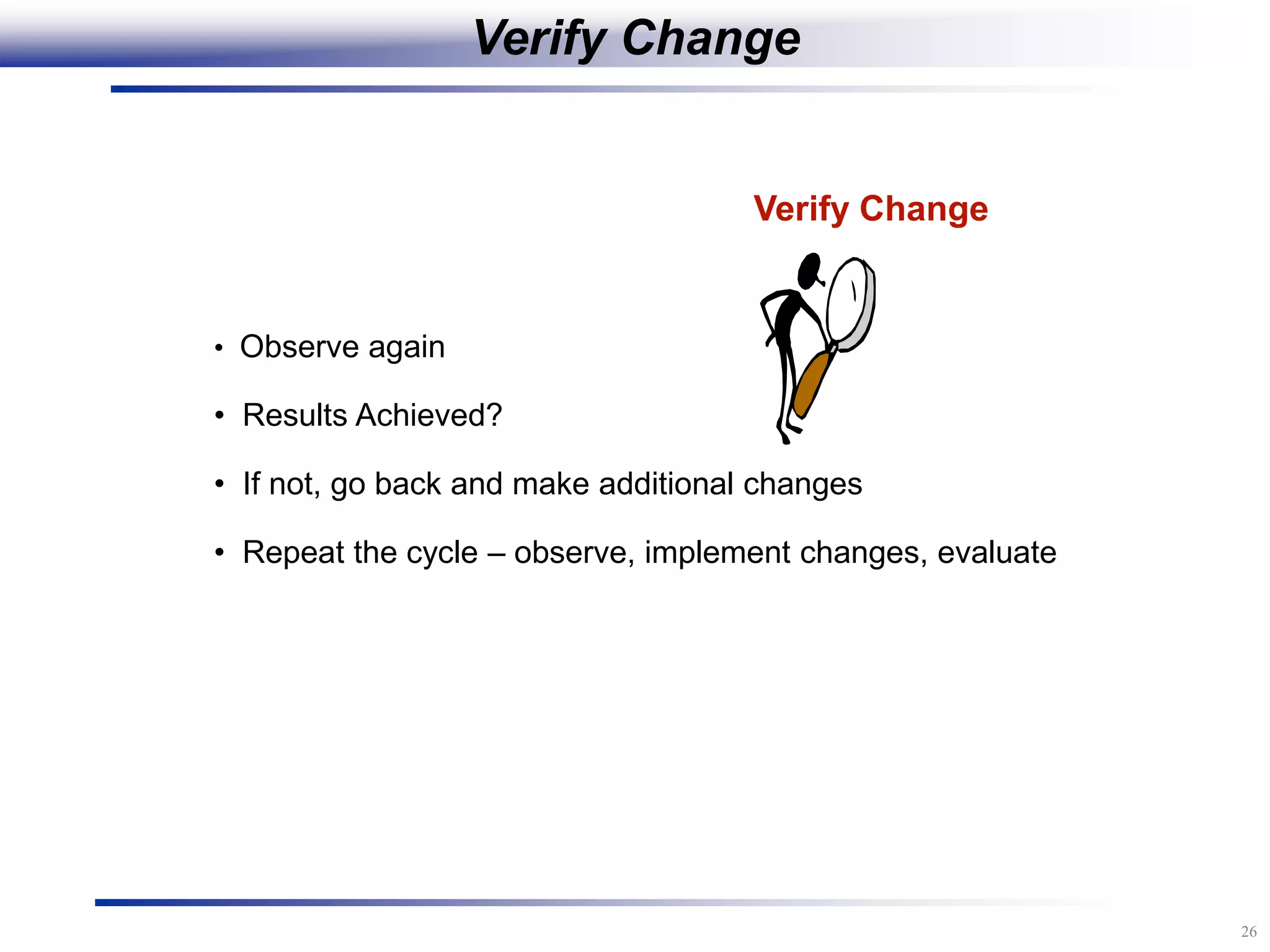
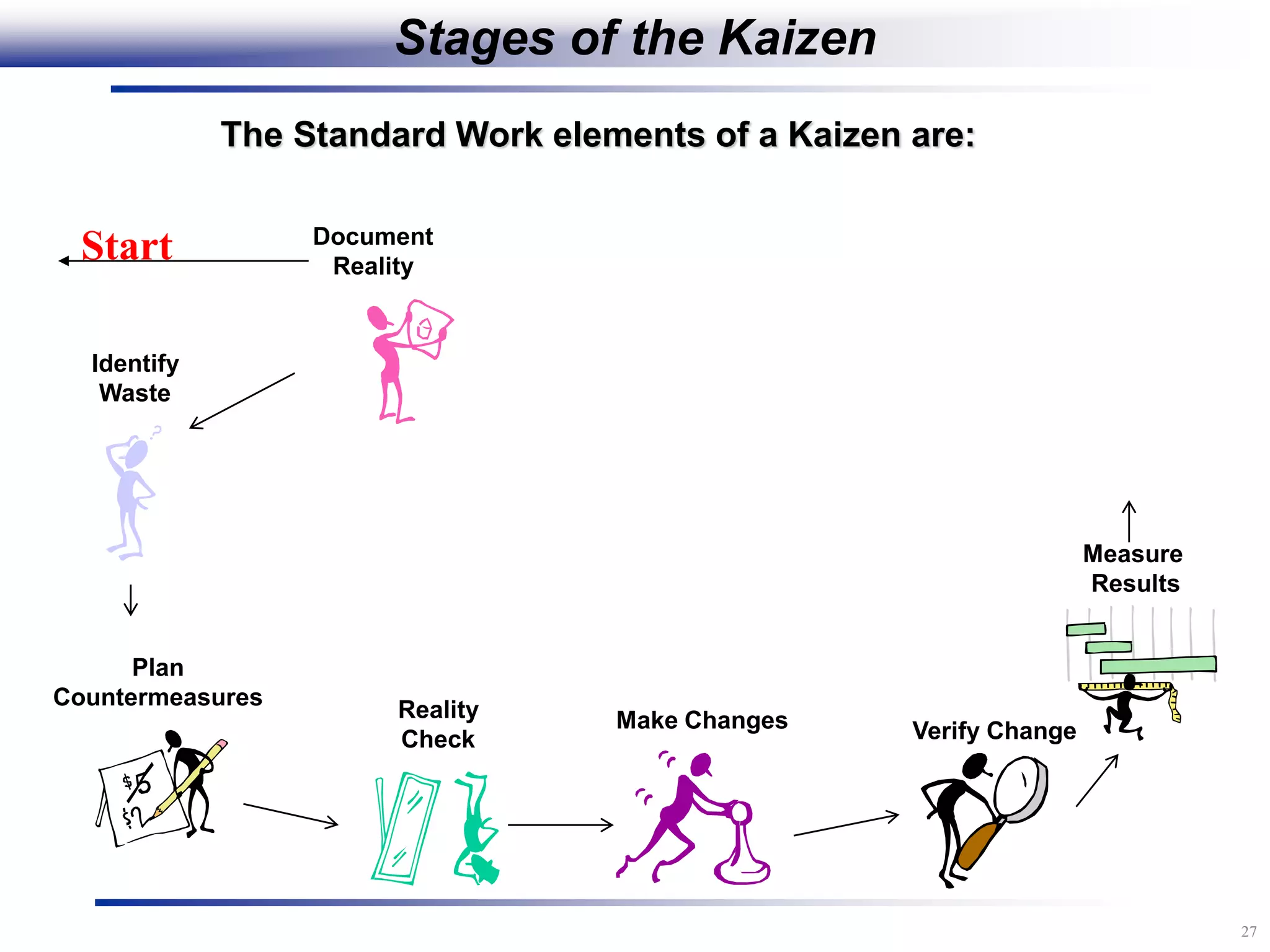
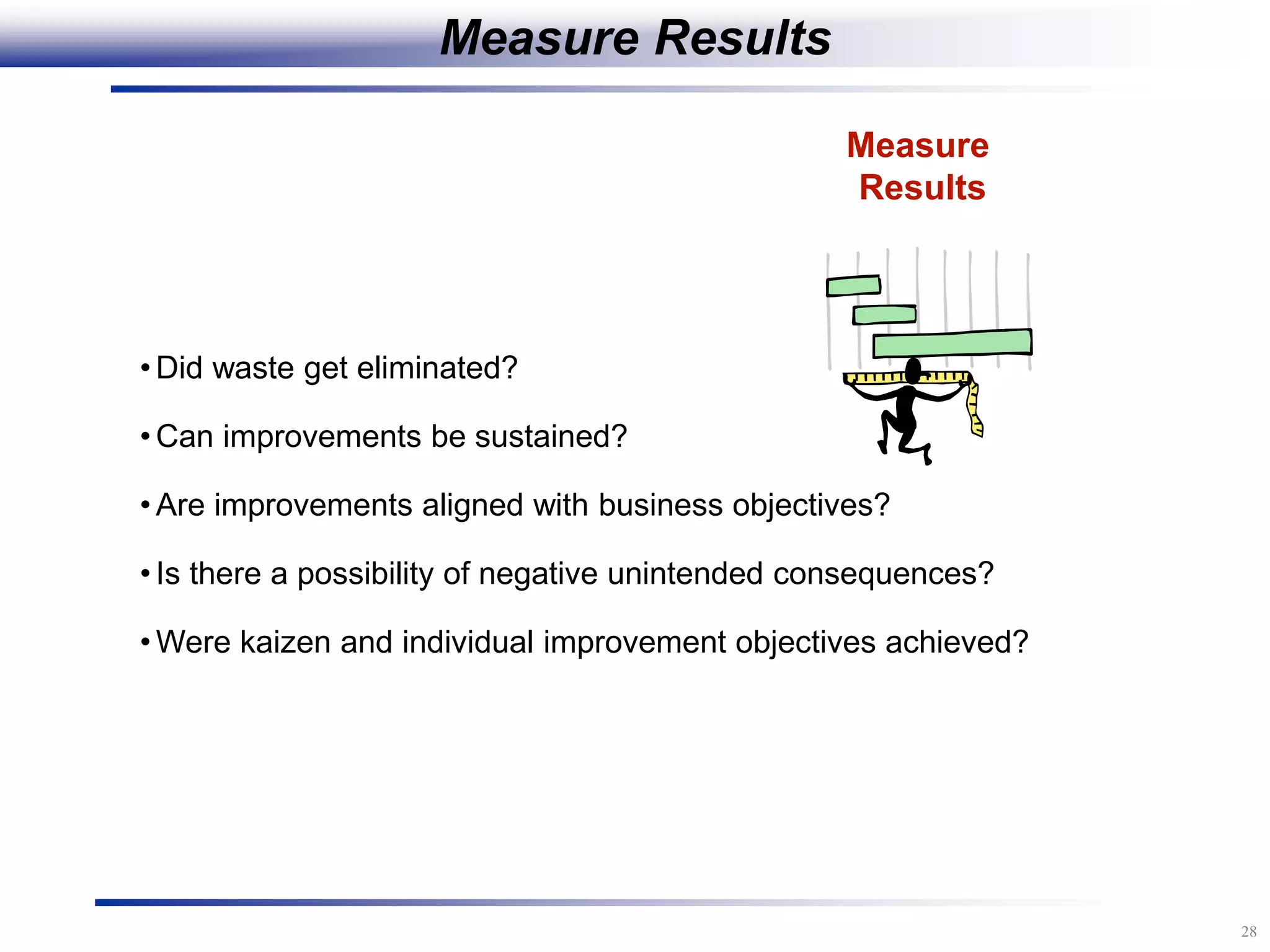
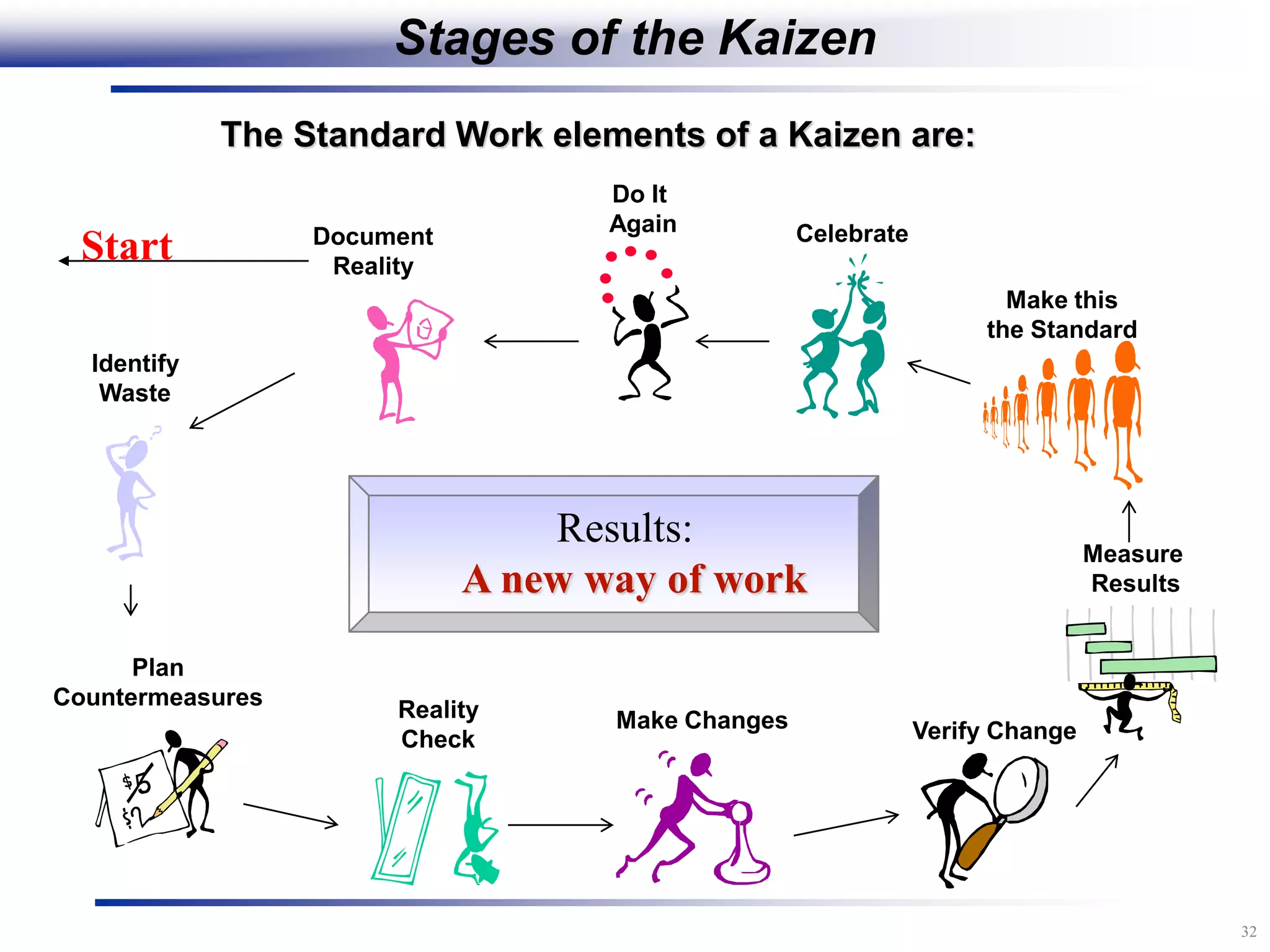
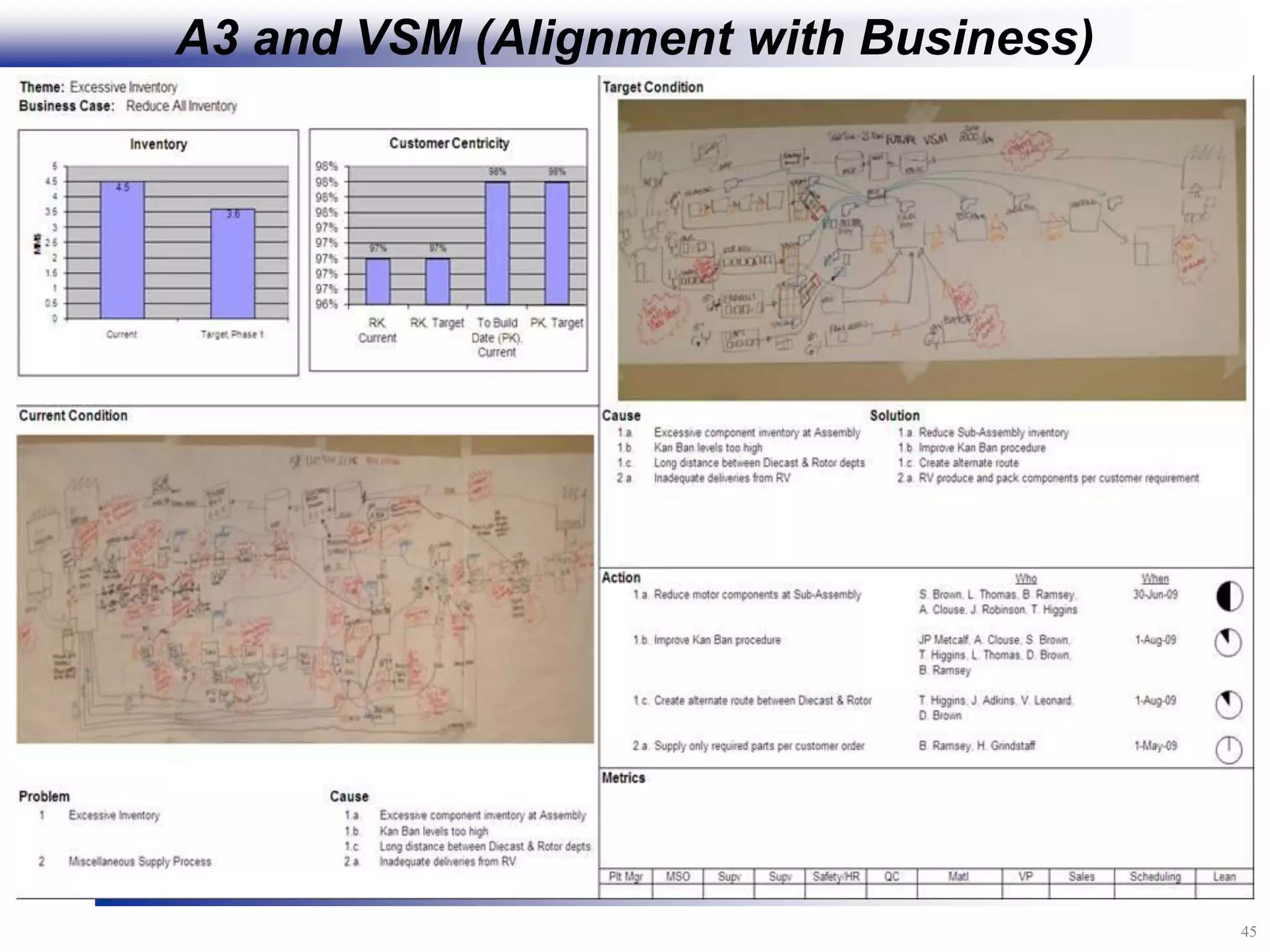
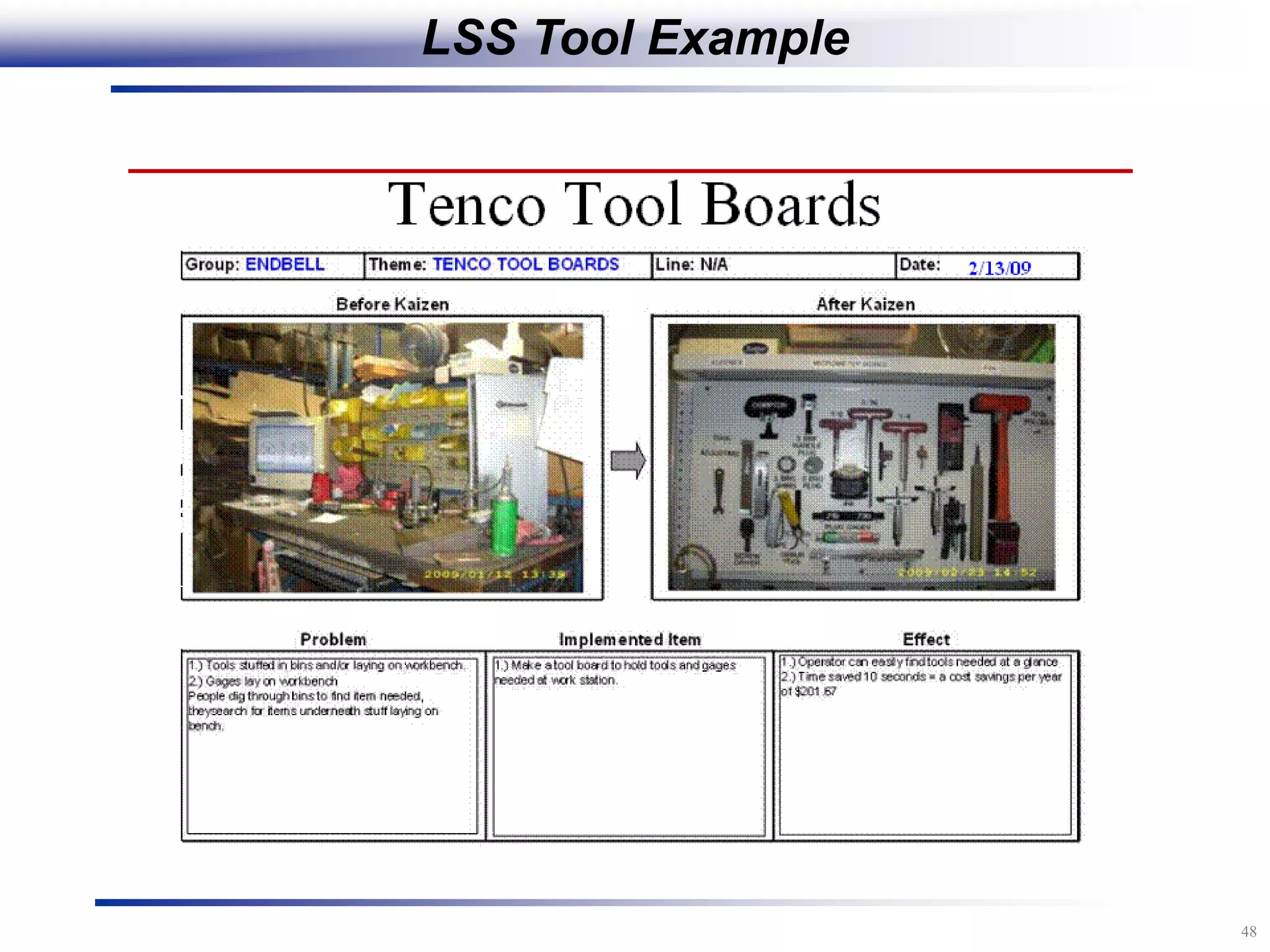
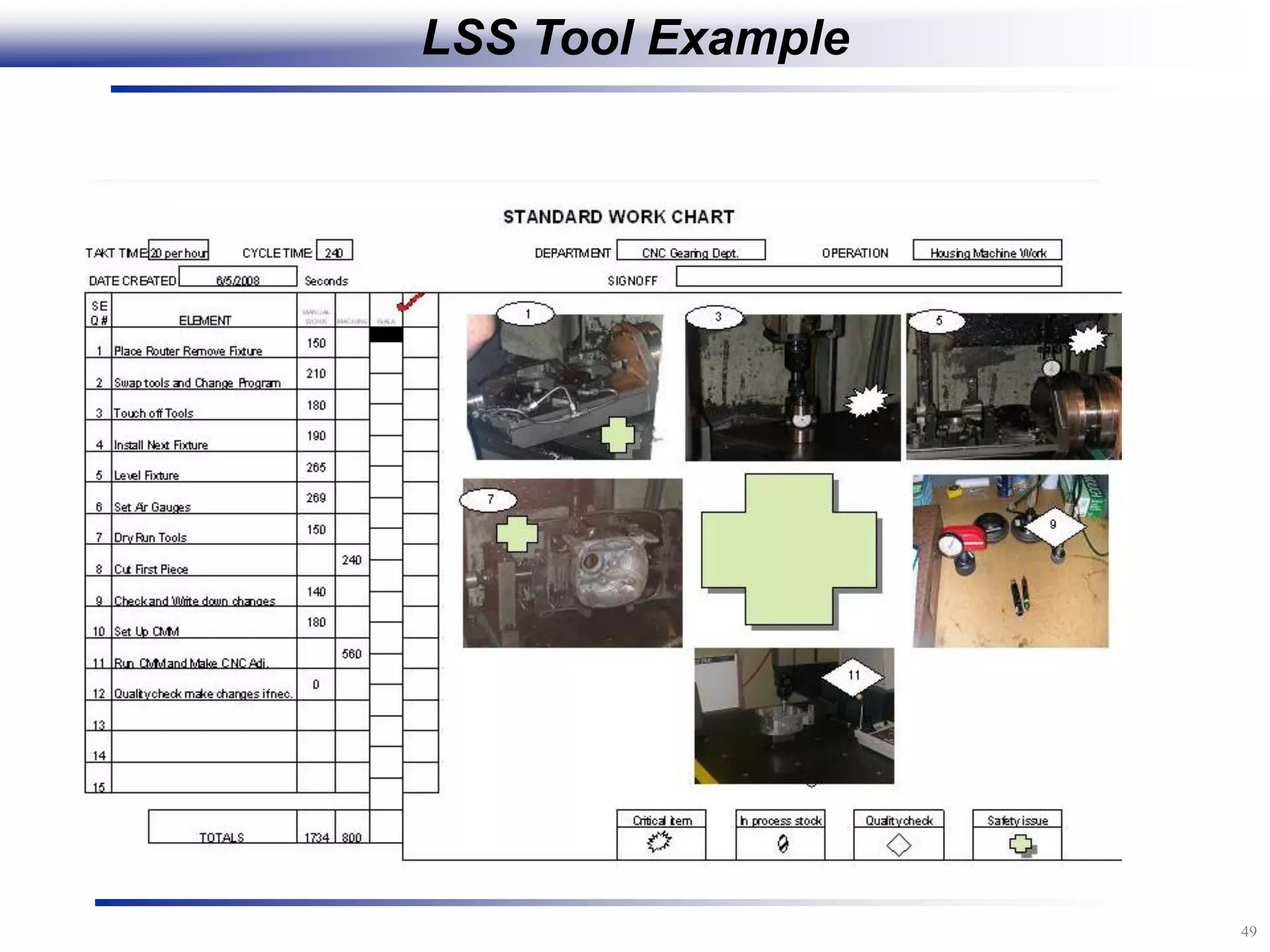
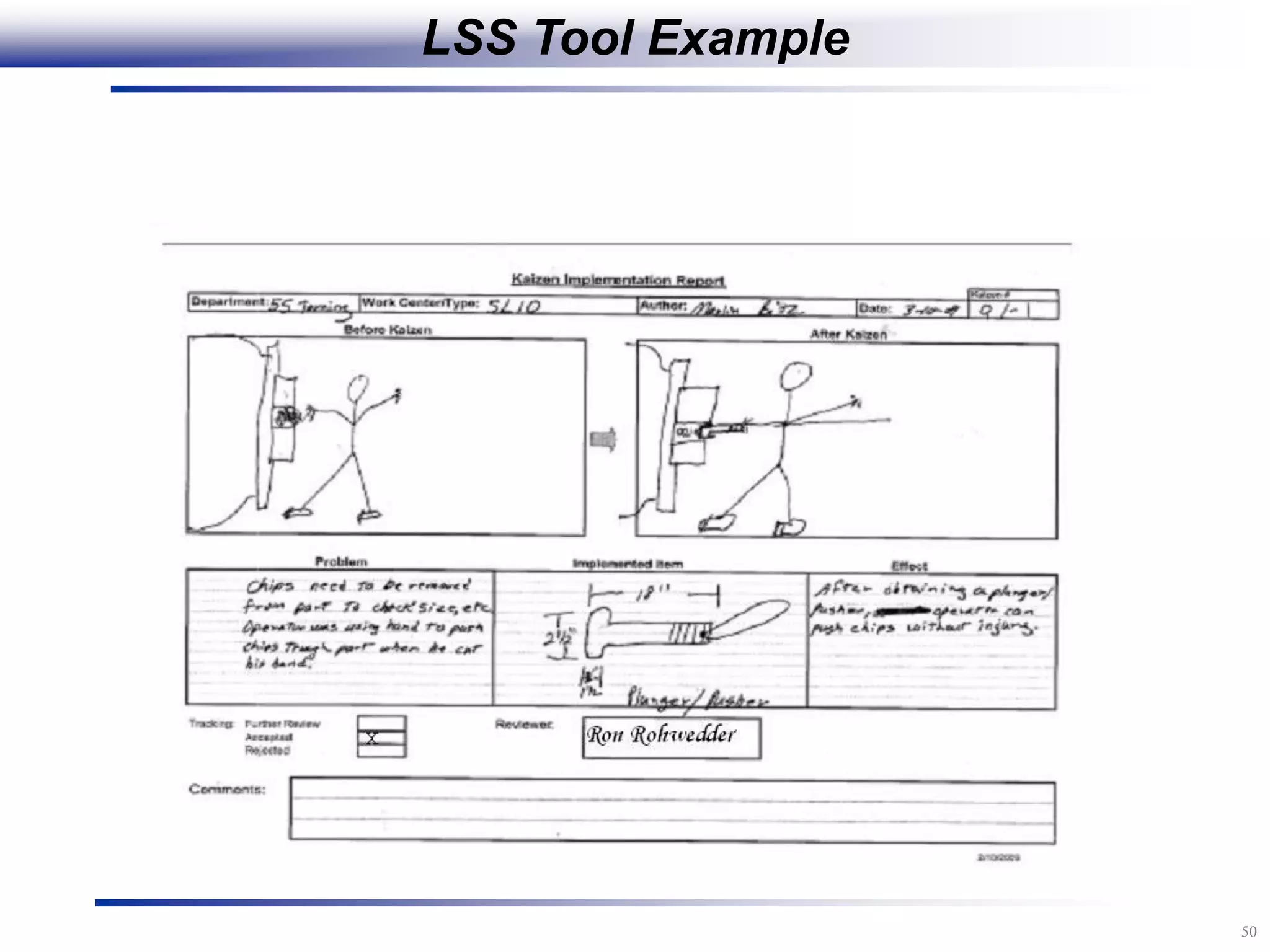
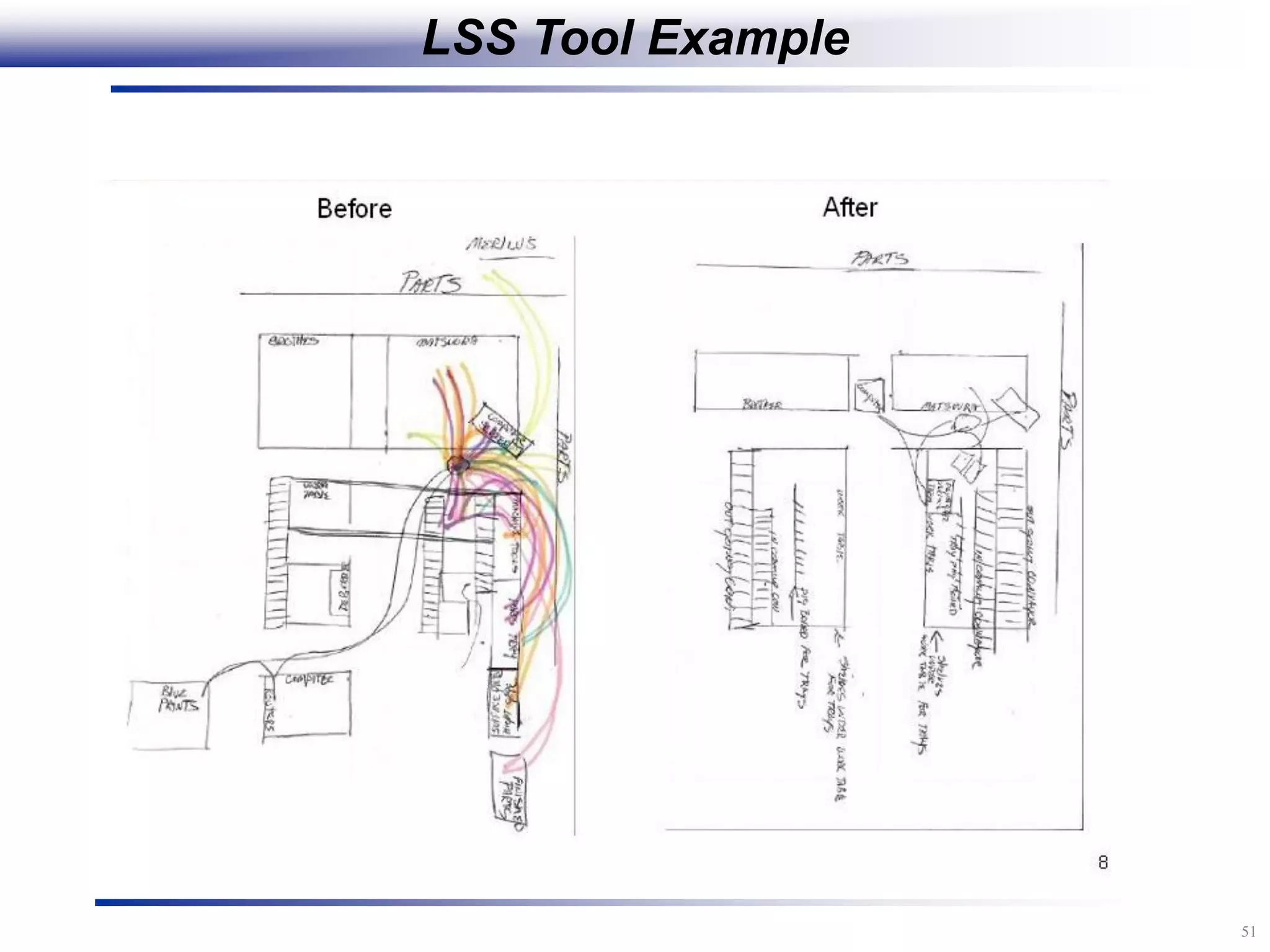
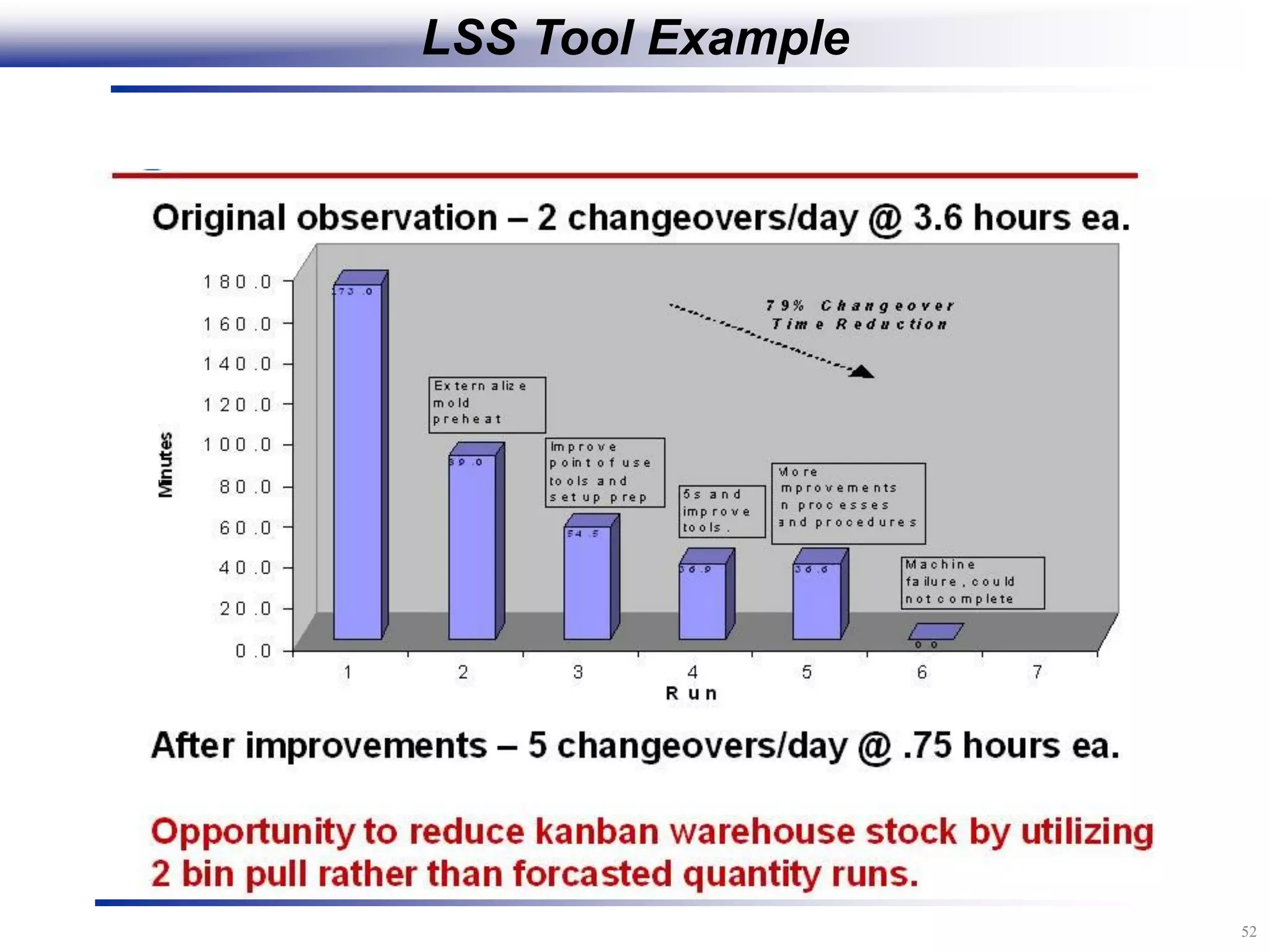
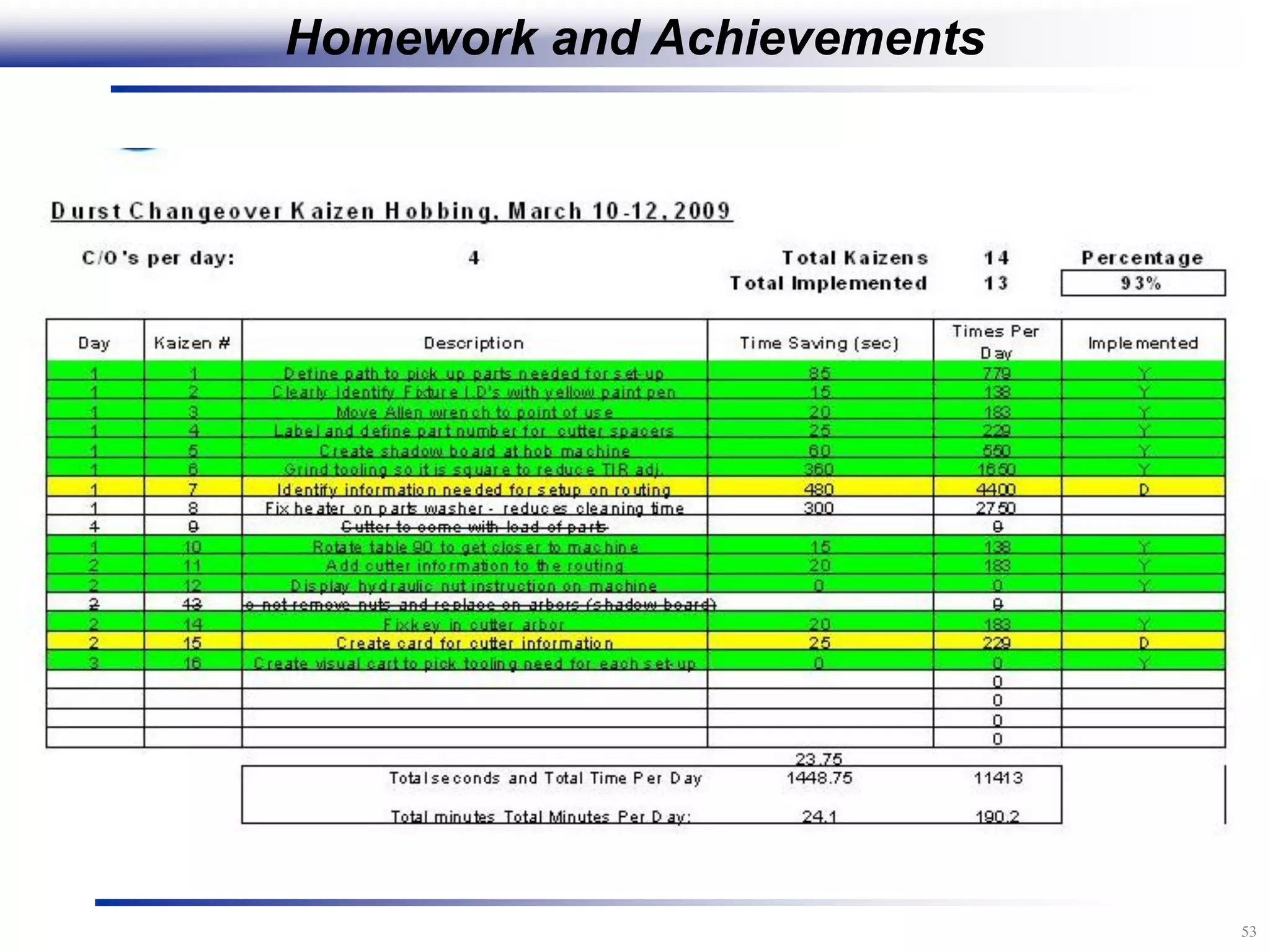
The document outlines the stages of conducting a Kaizen, which is a tool used to rapidly improve work processes. It involves documenting the current process, identifying waste, planning countermeasures, making changes to eliminate waste, verifying the changes work, measuring results, and making the new process the standard. The stages include planning and preparation, a multi-day event to implement changes, reporting out results, and following up to ensure improvements are sustained long-term. The goal is to continuously improve processes to better meet customer needs through engaging employees in identifying and eliminating waste.