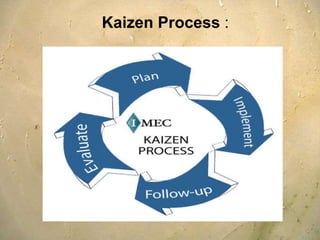
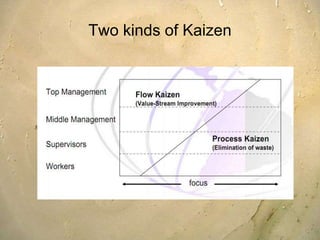
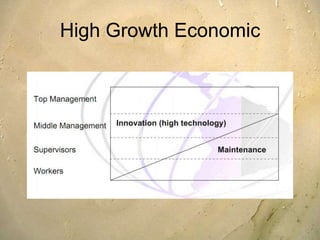
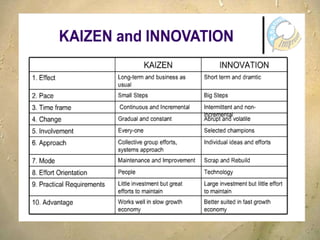
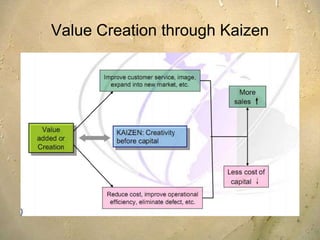
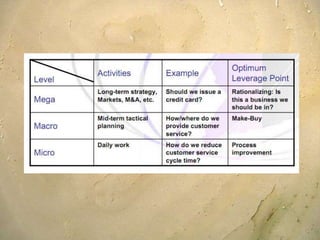
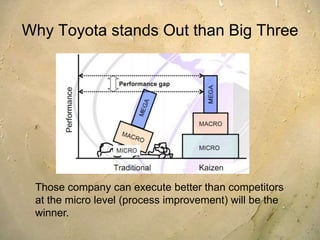
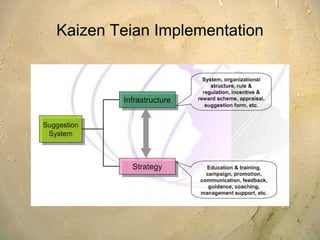
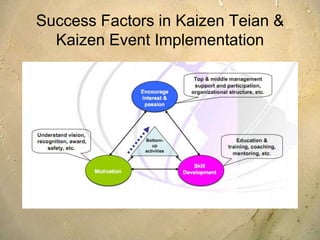
Kaizen is a Japanese philosophy that focuses on continuous improvement involving all employees. It aims to eliminate waste and improve processes through small, incremental changes. The key elements of kaizen include teamwork, personal discipline, improved morale, quality circles, and suggestions for improvement. It has helped Japanese companies like Toyota become industry leaders through minimal costs and efforts. The kaizen process involves planning, doing, checking, and acting to standardize, measure, analyze for improvements and standardize new processes in repetitive cycles. Common kaizen tools used are the kaizen teian (suggestion system) and kaizen events to drive process improvements.