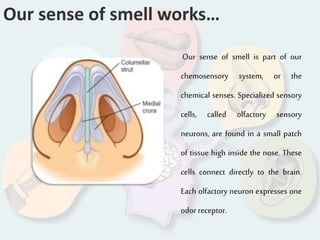
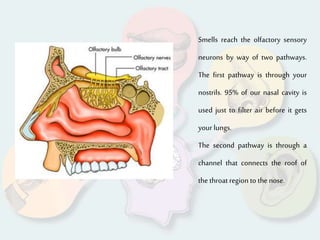
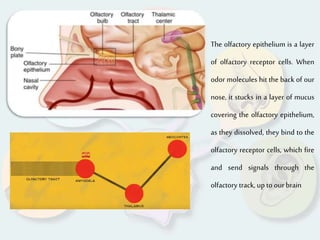
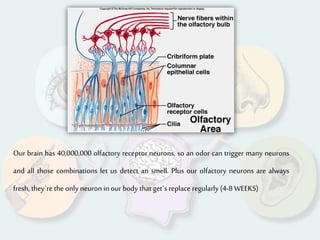
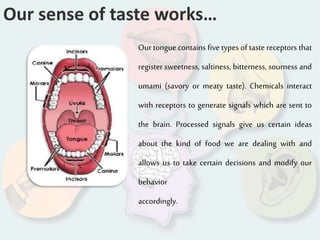
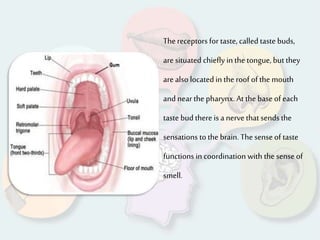
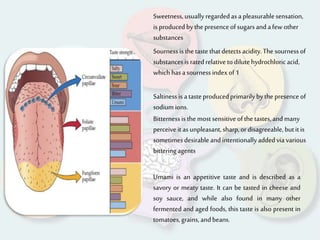
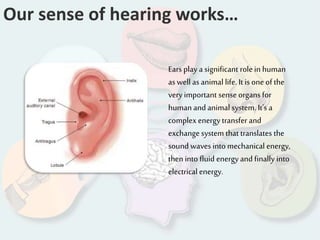
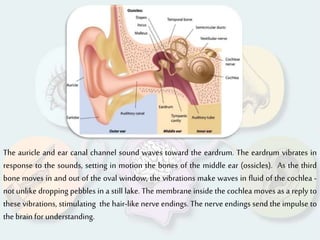
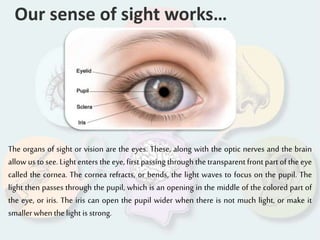
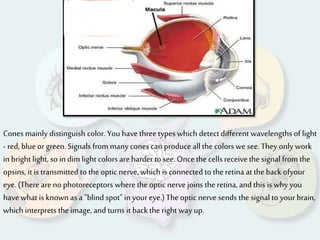
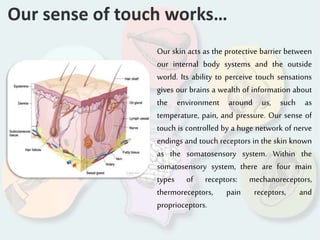
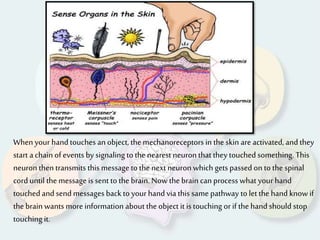
The document summarizes how each of the 5 human senses (smell, taste, hearing, sight, touch) works. Each sense consists of specialized sensory organs and cells that detect stimuli and transmit signals to the brain. For smell, odor molecules bind to receptors in the nose. For taste, receptors on the tongue detect sweet, salty, bitter, sour, and umami flavors. Hearing involves sound waves vibrating the eardrum and bones to stimulate hair cells in the cochlea. Sight relies on light stimulating photoreceptor cells in the retina to form images. Touch is mediated by mechanoreceptors, thermoreceptors and other receptors in the skin that detect pressure, temperature and pain.