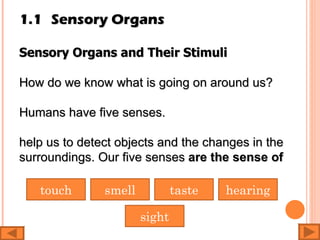
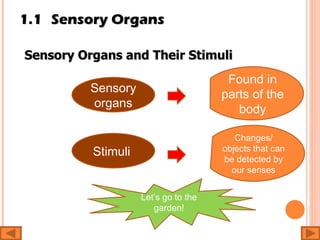
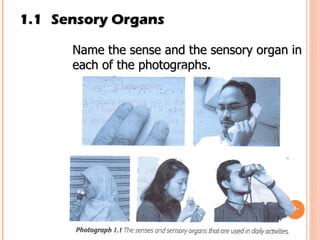
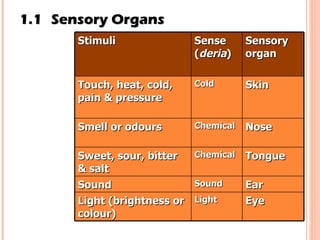
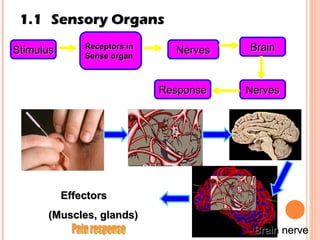
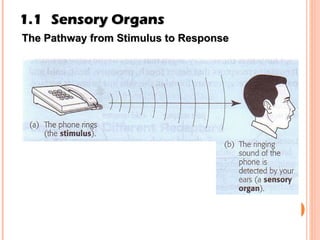
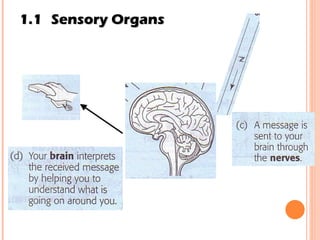
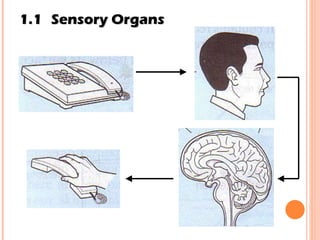
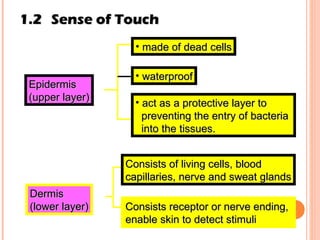
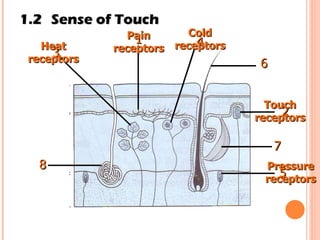
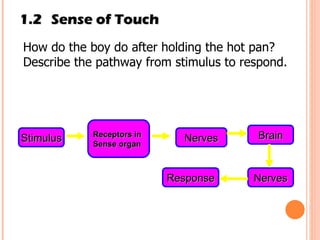
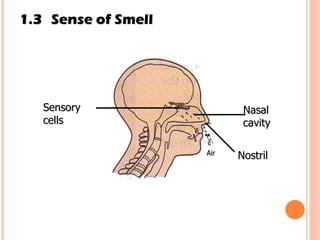
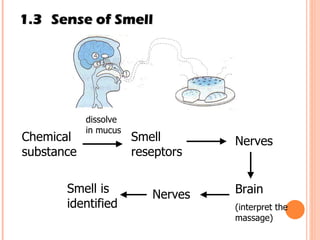
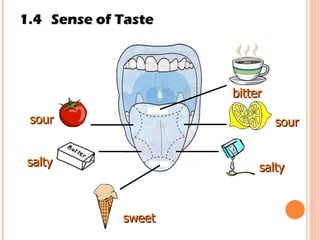
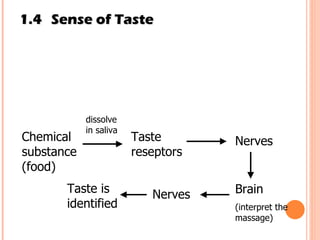
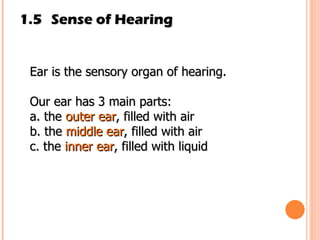
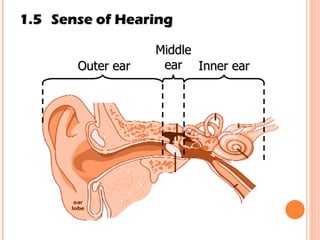
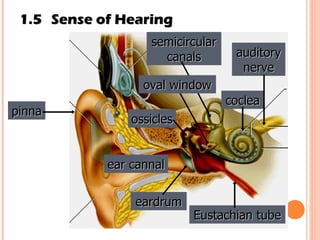
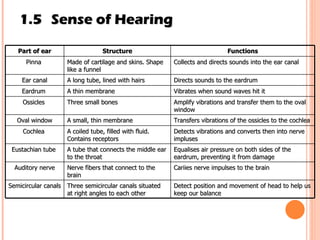
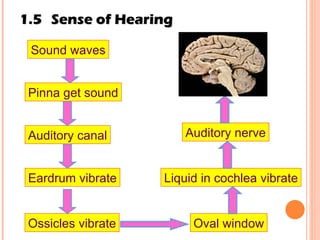
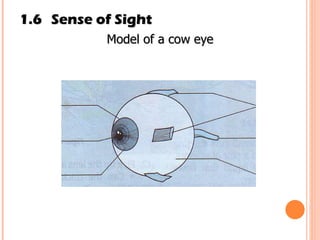
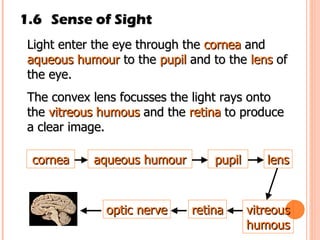
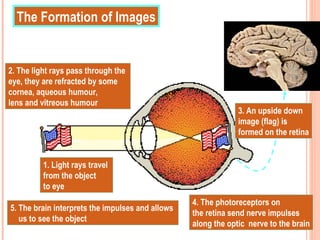
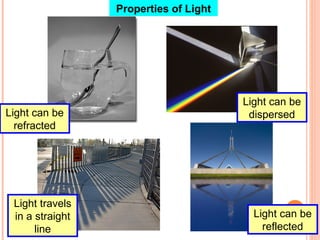
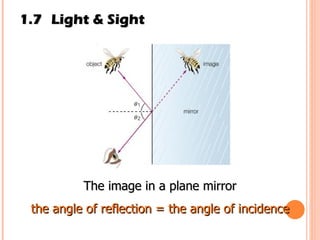
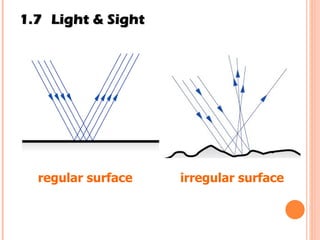
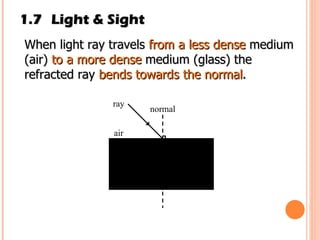
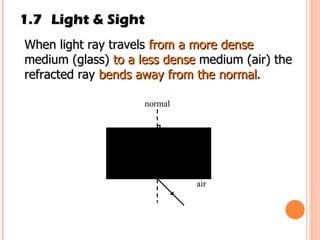
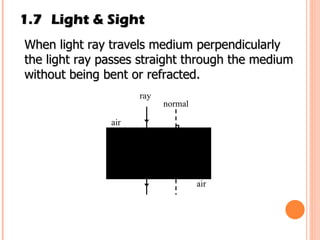
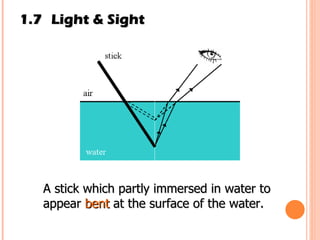
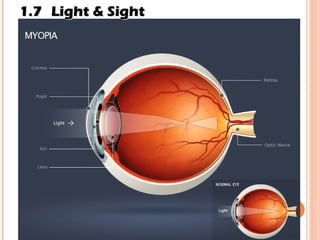
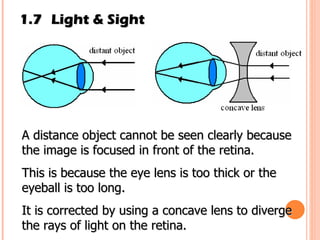
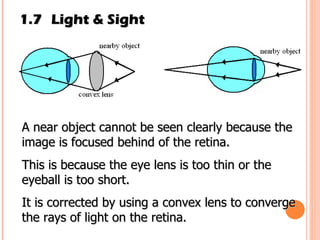
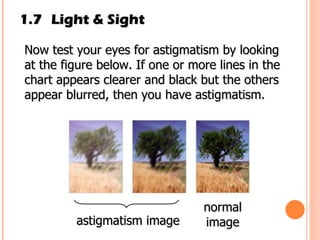
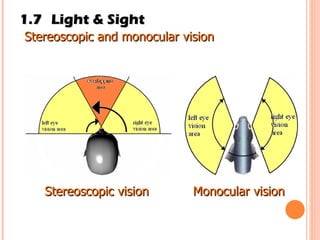
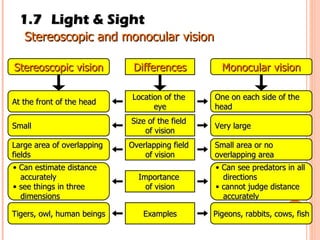
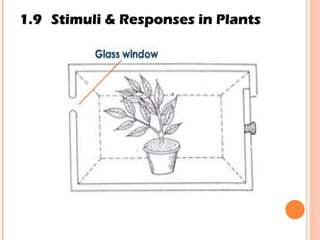
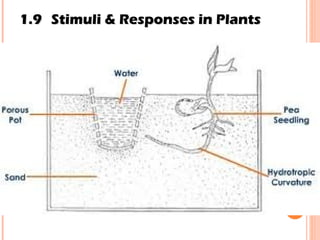
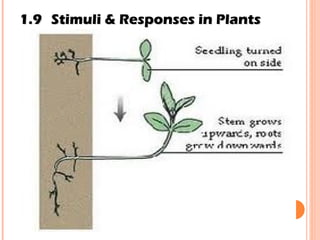
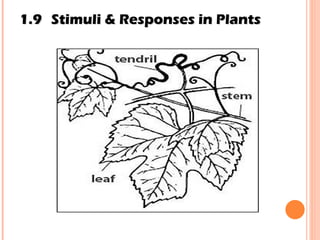
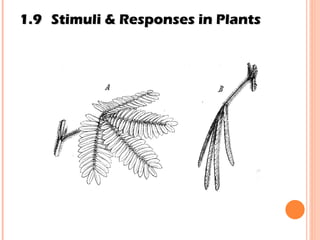
The document discusses the five human senses - touch, smell, taste, hearing, and sight. It describes the sensory organs associated with each sense, how stimuli are detected by sensory receptors, and how nerve signals are transmitted to the brain. For each sense, it provides details on the sensory pathways, common stimuli, and examples of sensory responses. The roles of light and sound in vision and hearing are also examined. In under 3 sentences, the document provides an overview of the human sensory systems and how they detect external stimuli and transmit nerve signals to the brain.