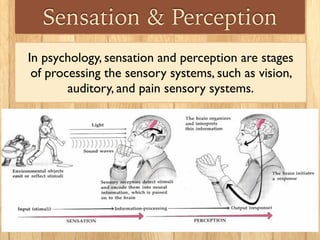
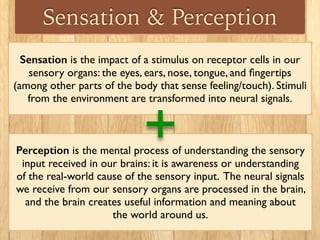
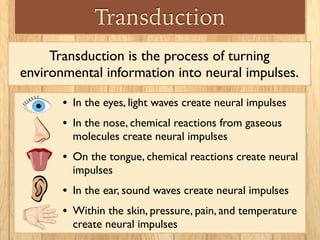
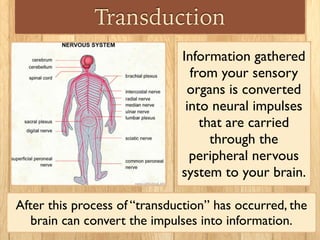
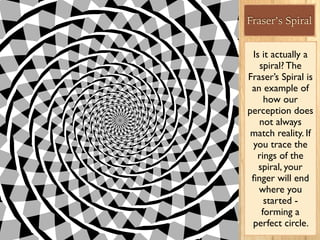
Sensation is the impact of external stimuli on our sensory receptors, while perception is our brain's interpretation of these sensory inputs. Transduction is the process where environmental stimuli are converted into neural impulses that are transmitted to the brain. The brain then processes these impulses to create useful information and meaning about the world. Key concepts in sensation and perception include absolute and difference thresholds, signal detection theory, and sensory adaptation in which we become less sensitive to unchanging stimuli over time.