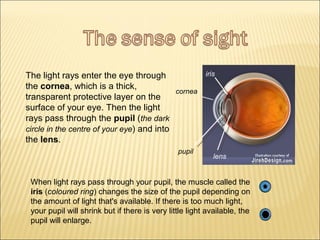
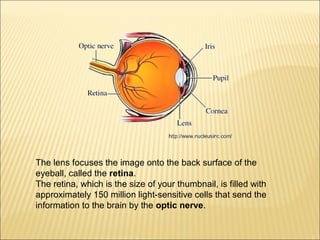
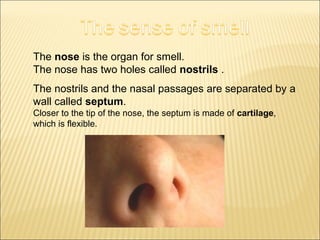
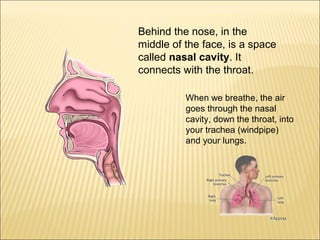
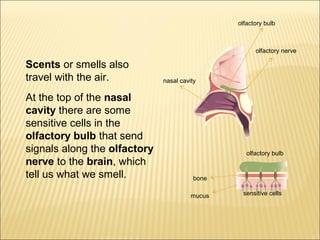
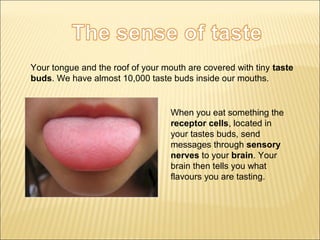
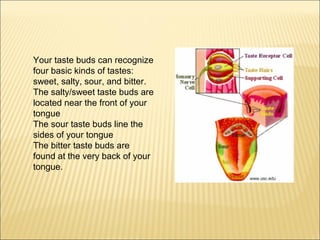
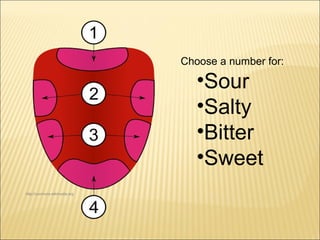
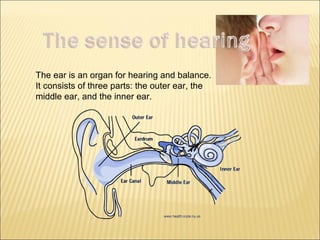
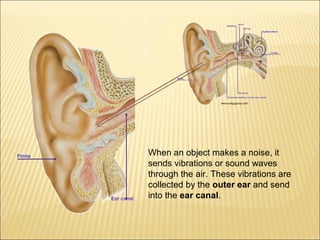
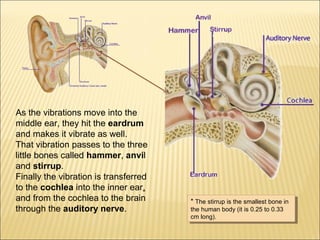
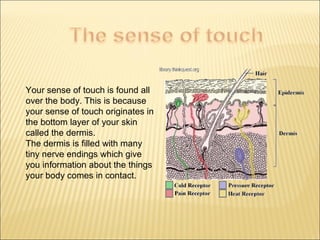
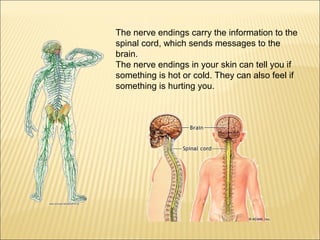
The five main human senses are sight, taste, smell, hearing, and touch. Each sense has specialized sensory organs that contain receptors which detect stimuli and send signals along sensory nerves to the brain. The brain then interprets these signals to inform us about our surroundings through our five senses.