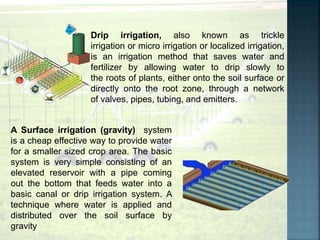
Water resource management involves planning, developing, distributing, and managing water resources to satisfy competing demands. It aims to allocate water equitably across all uses. Cultivation is sensitive to water shortages, so good water management practices are needed to maintain optimal usage and maximize production. These practices include proper field channels, land leveling, tilling, drip irrigation, and treadle pumps.