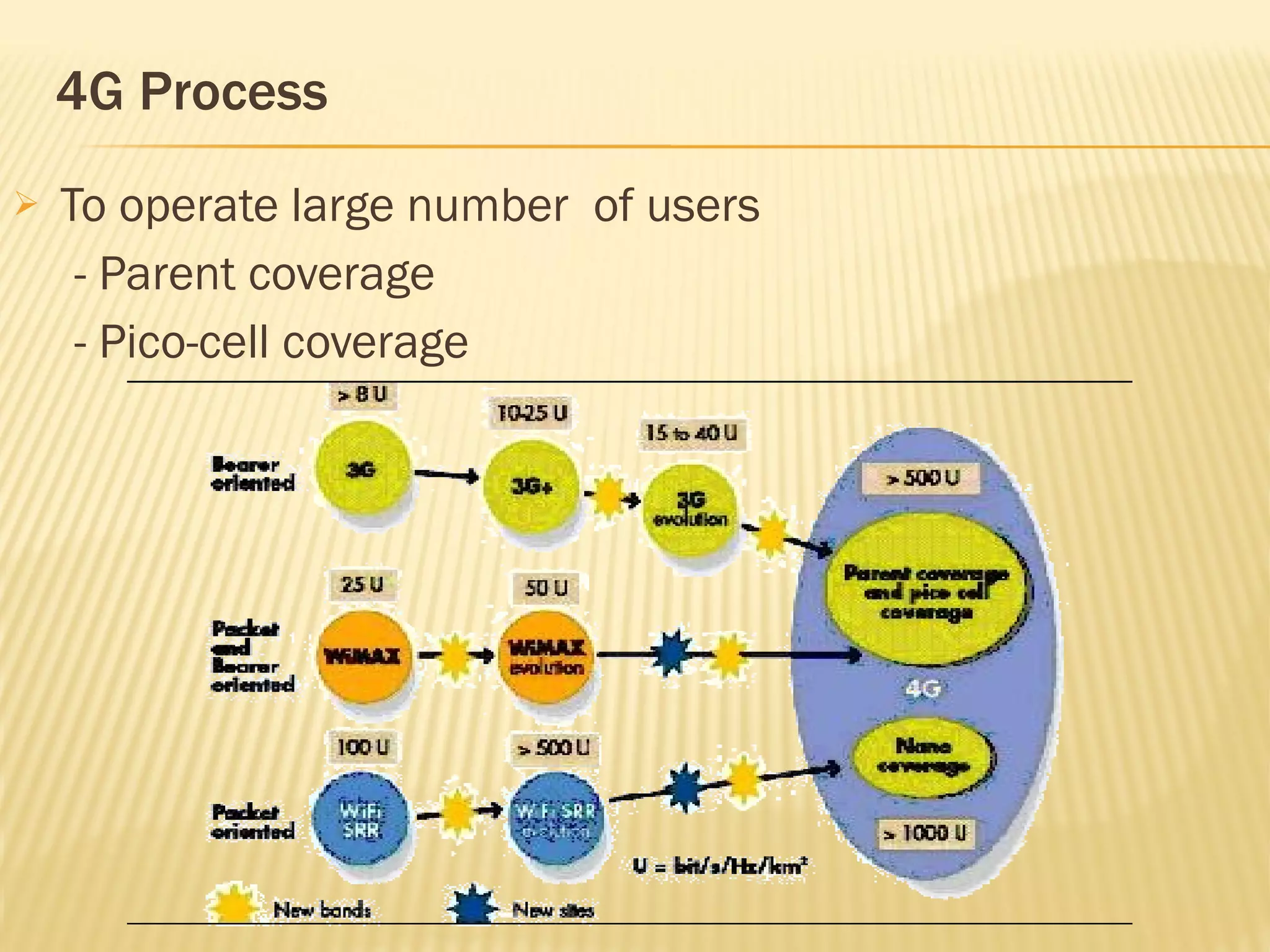
4G networks aim to provide higher data transfer rates, support more users, and enable new applications compared to 3G networks. Key technologies required for 4G include OFDMA, MIMO, wider bandwidth channels between 100-200 MHz, and hybrid network architectures. Challenges in developing 4G networks include securing sufficient licensed spectrum, providing seamless coverage between different radio access technologies, developing caching technologies, and establishing network selection mechanisms. 4G aims to support applications like mobile TV with high resolution, telemedicine, location-based services, and seamless IP connectivity for users on the move.