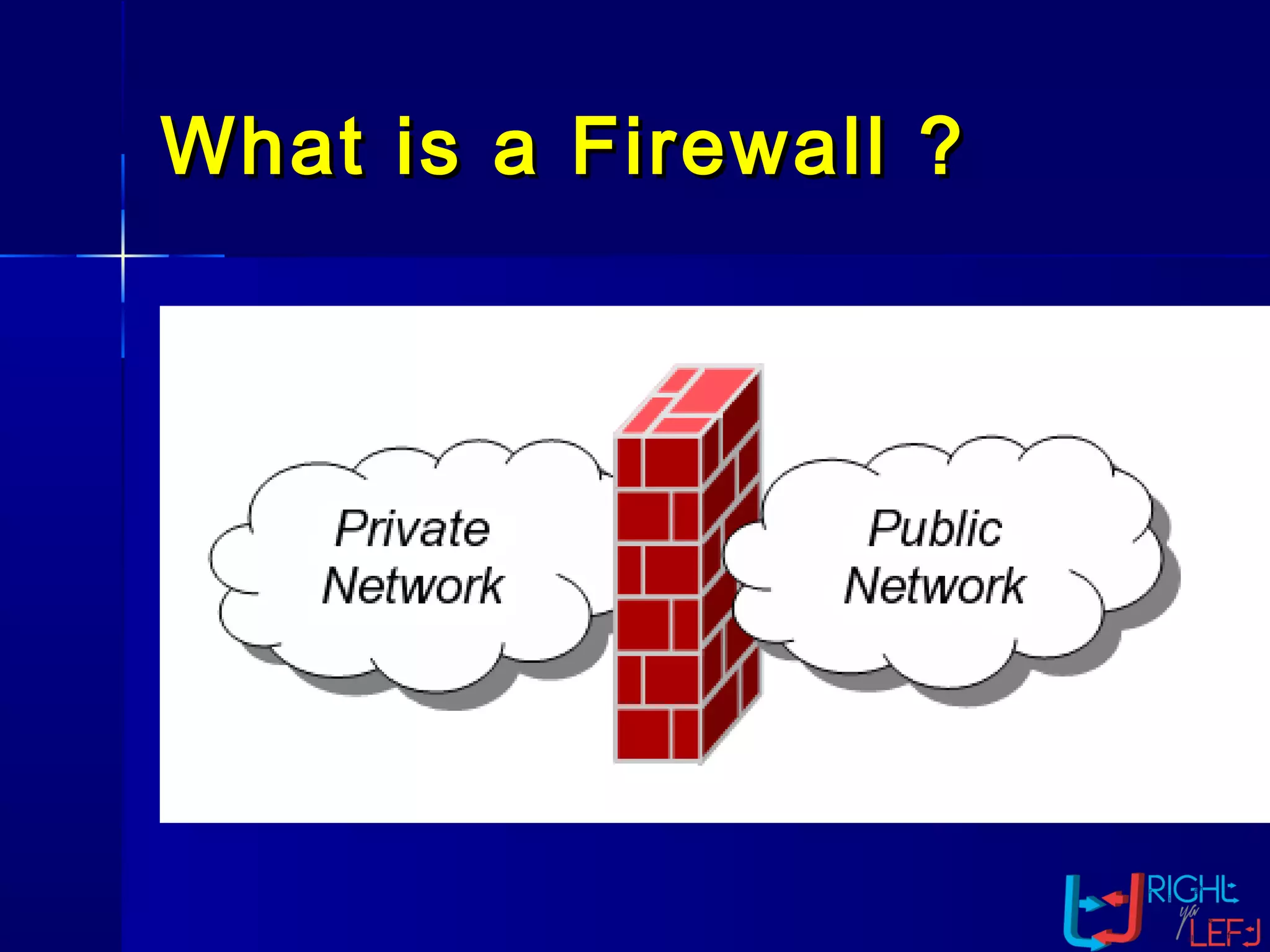
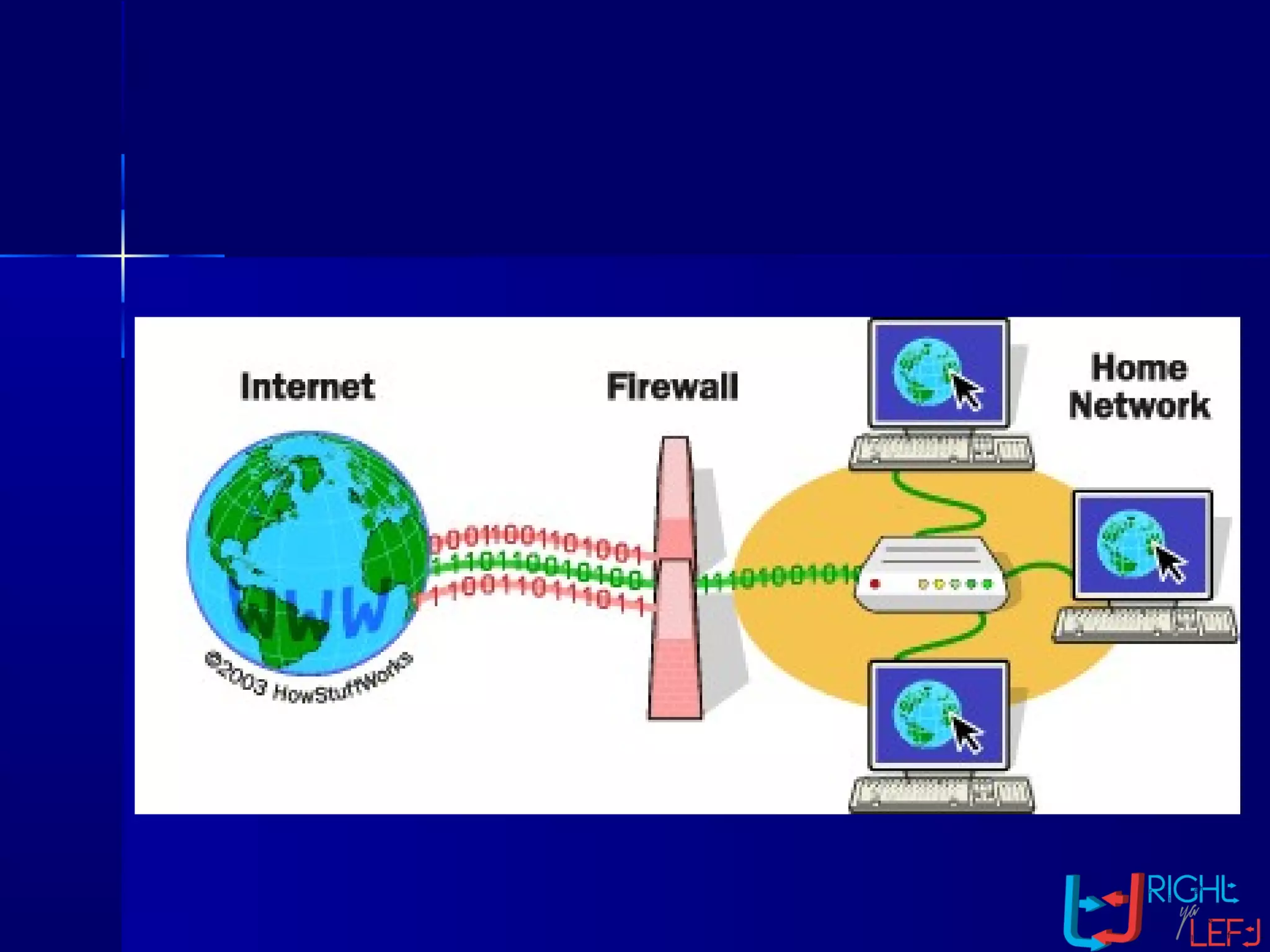
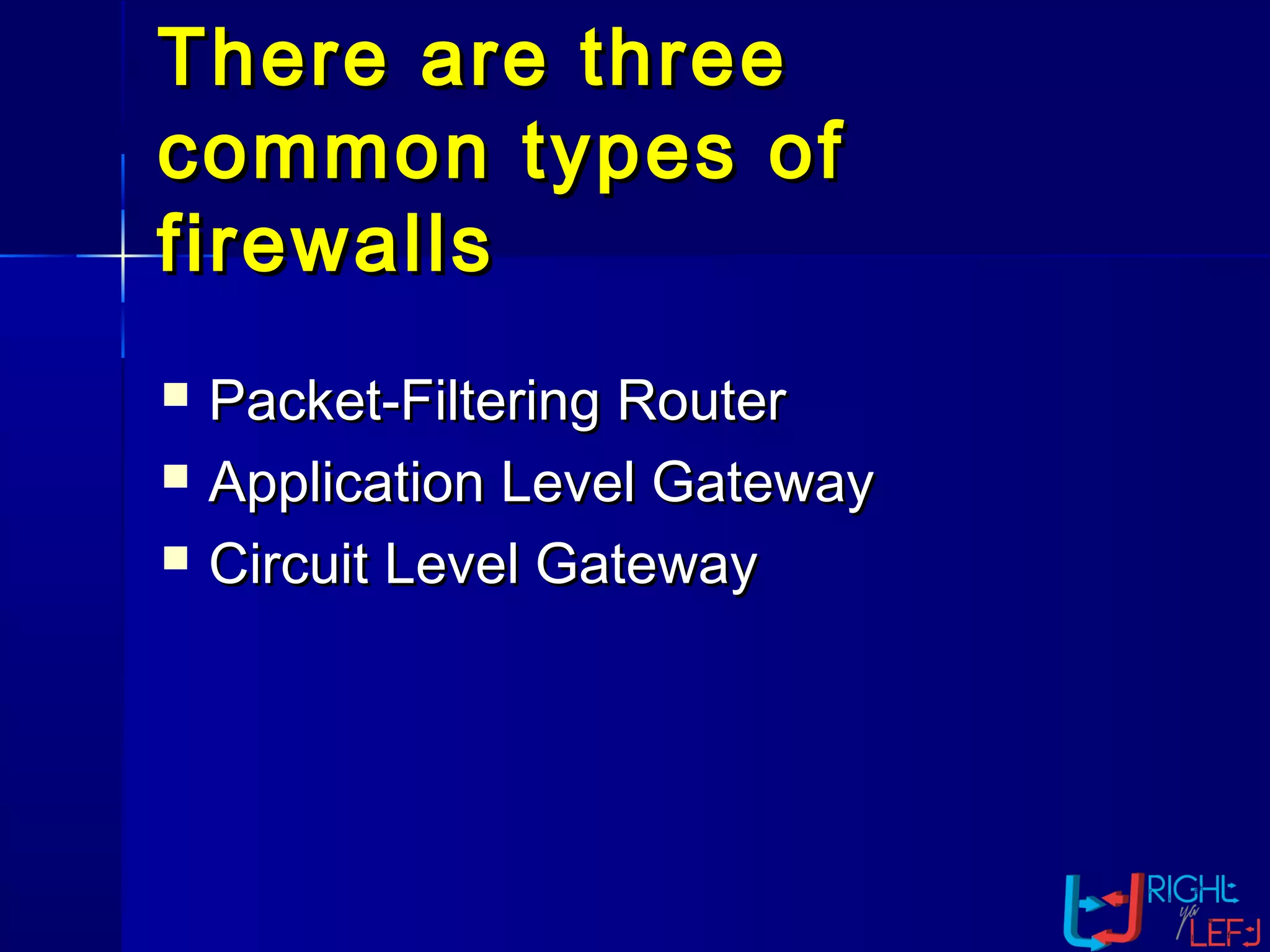
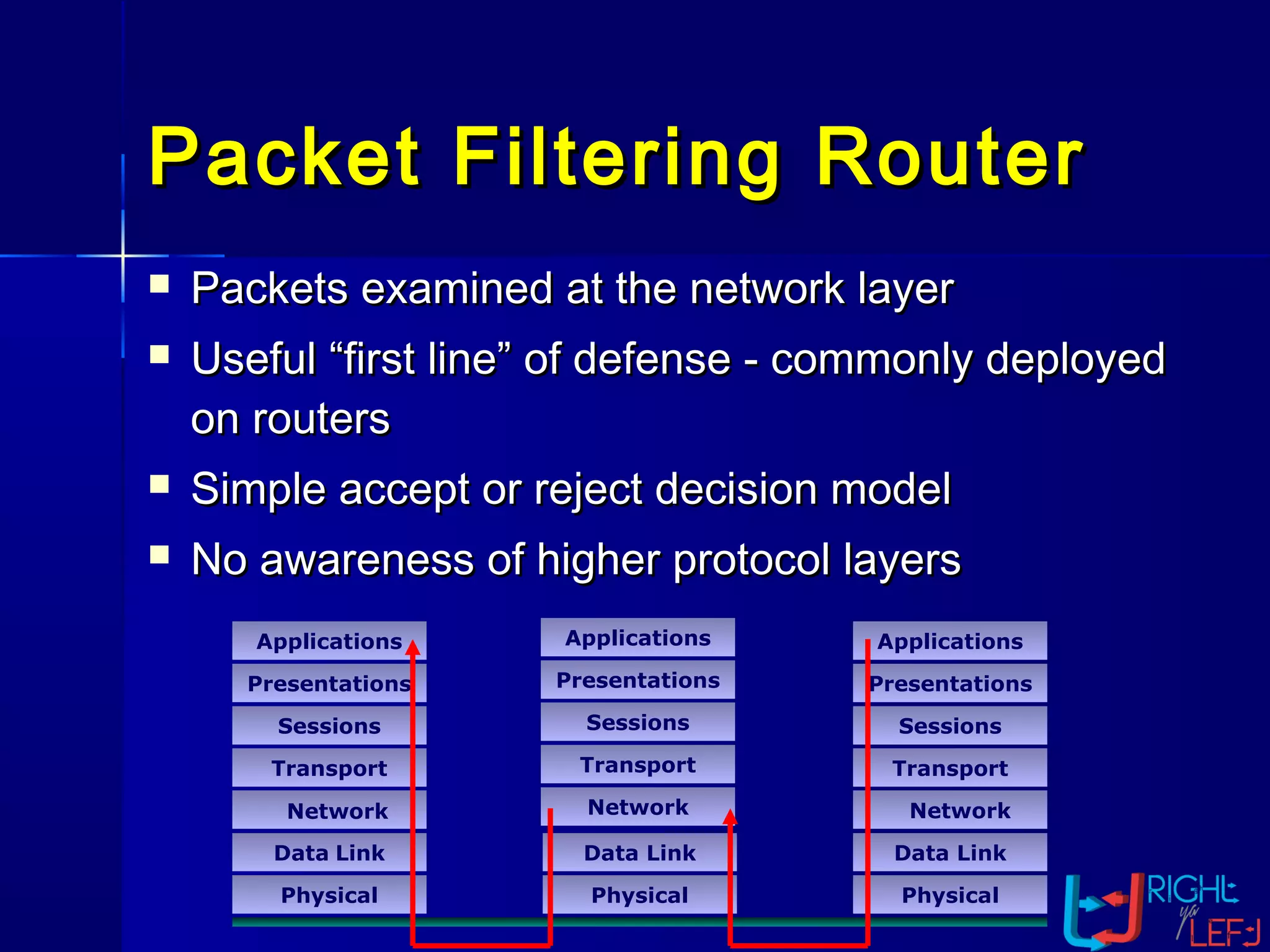
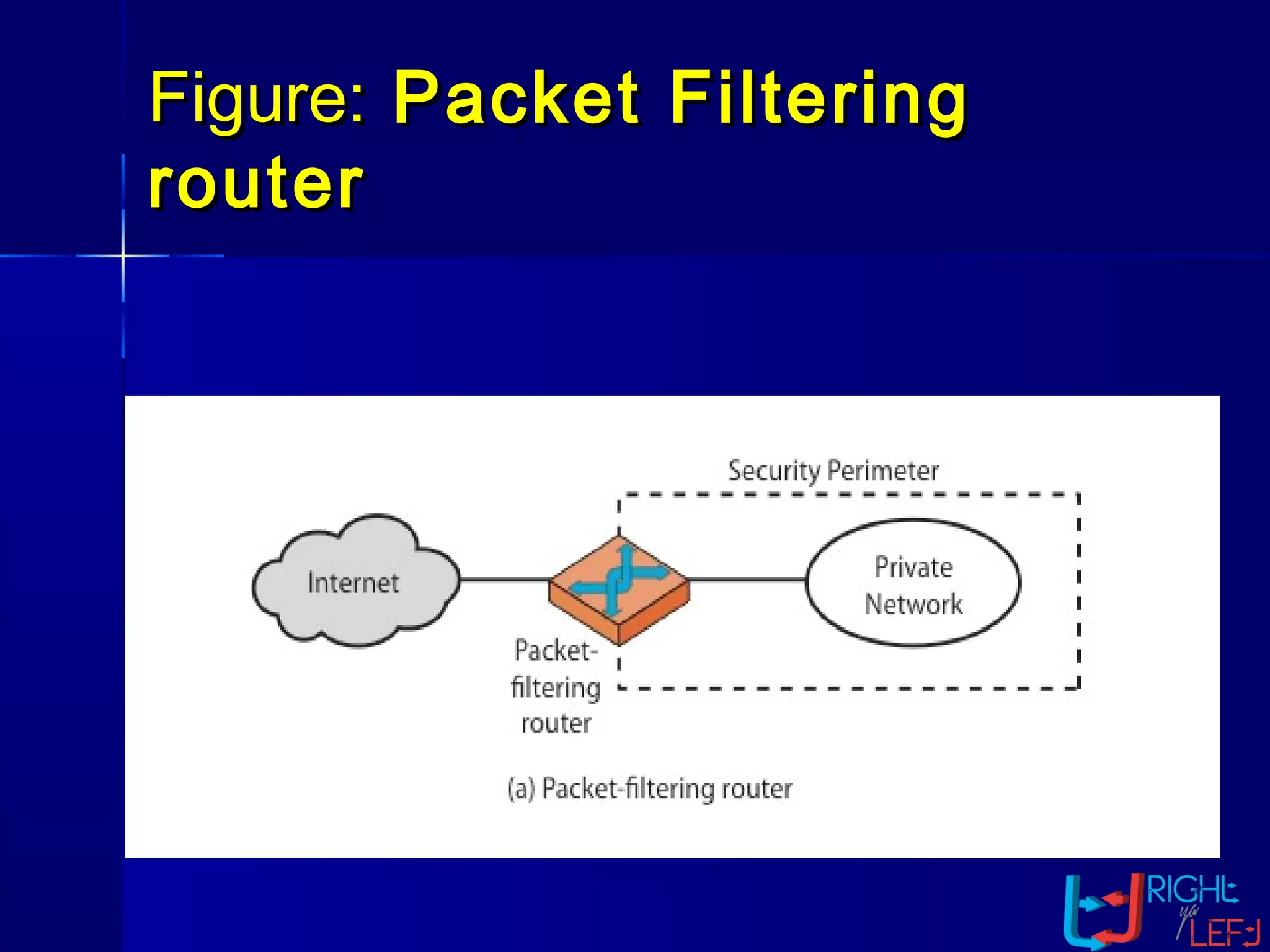
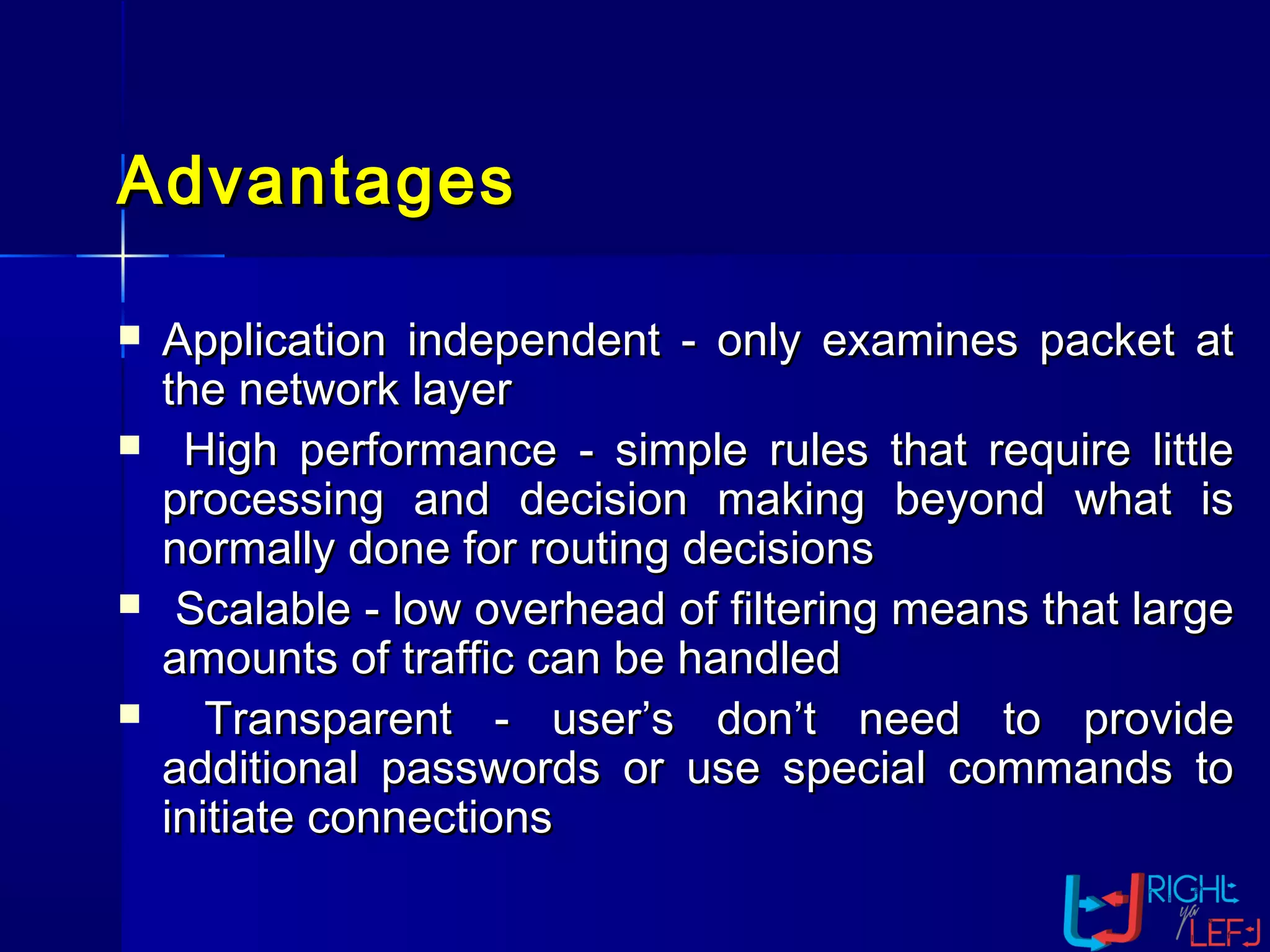
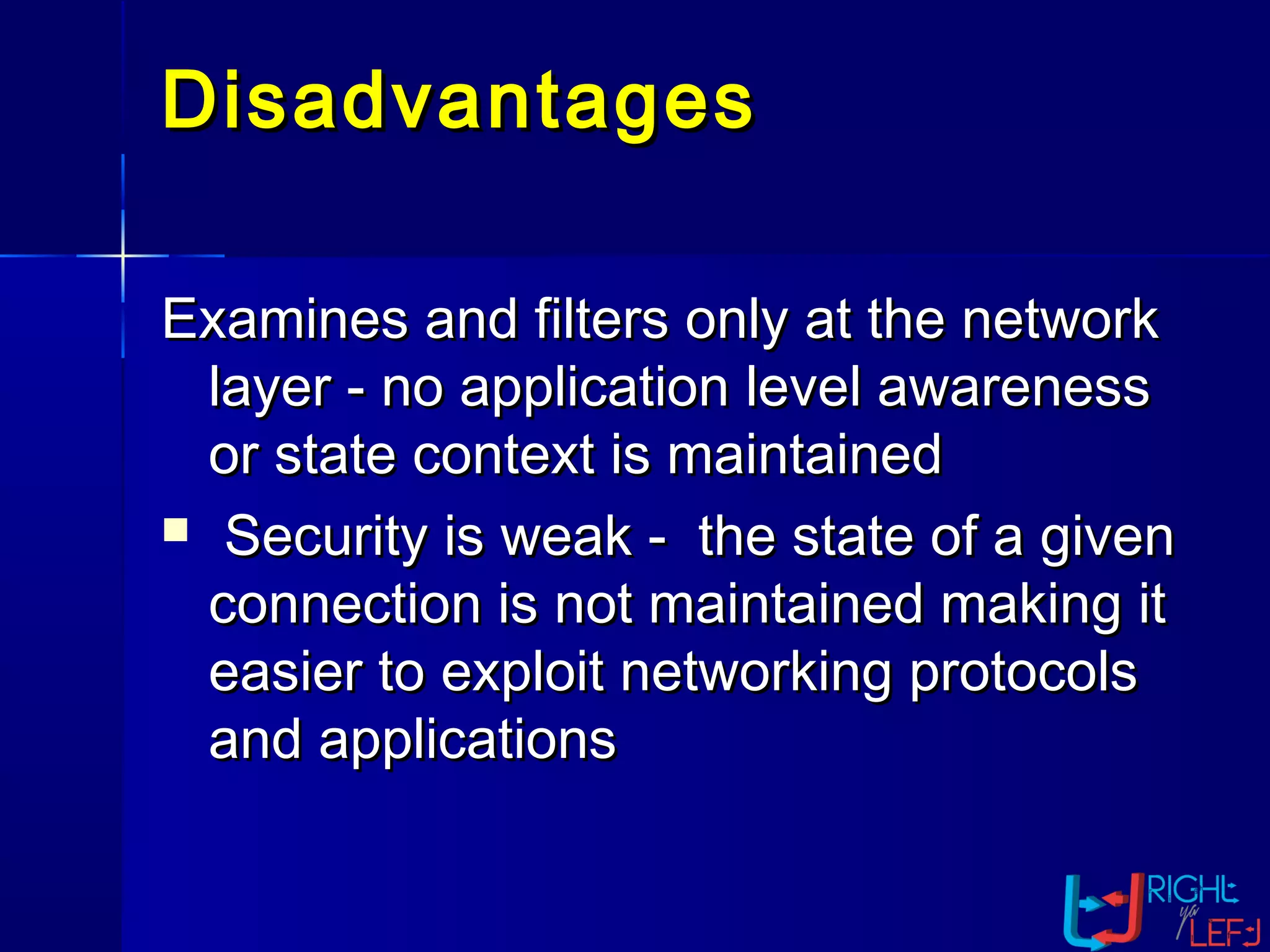
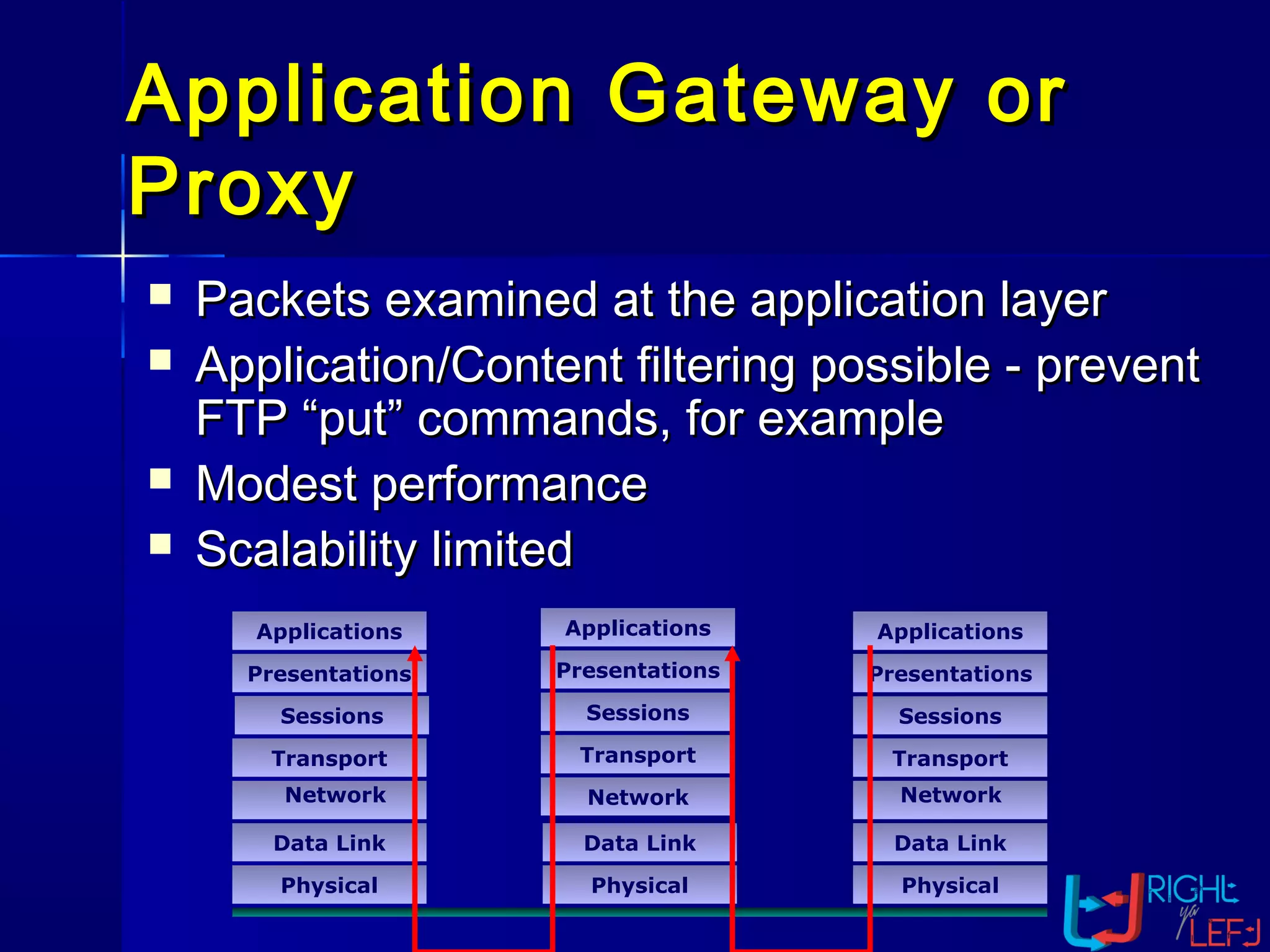
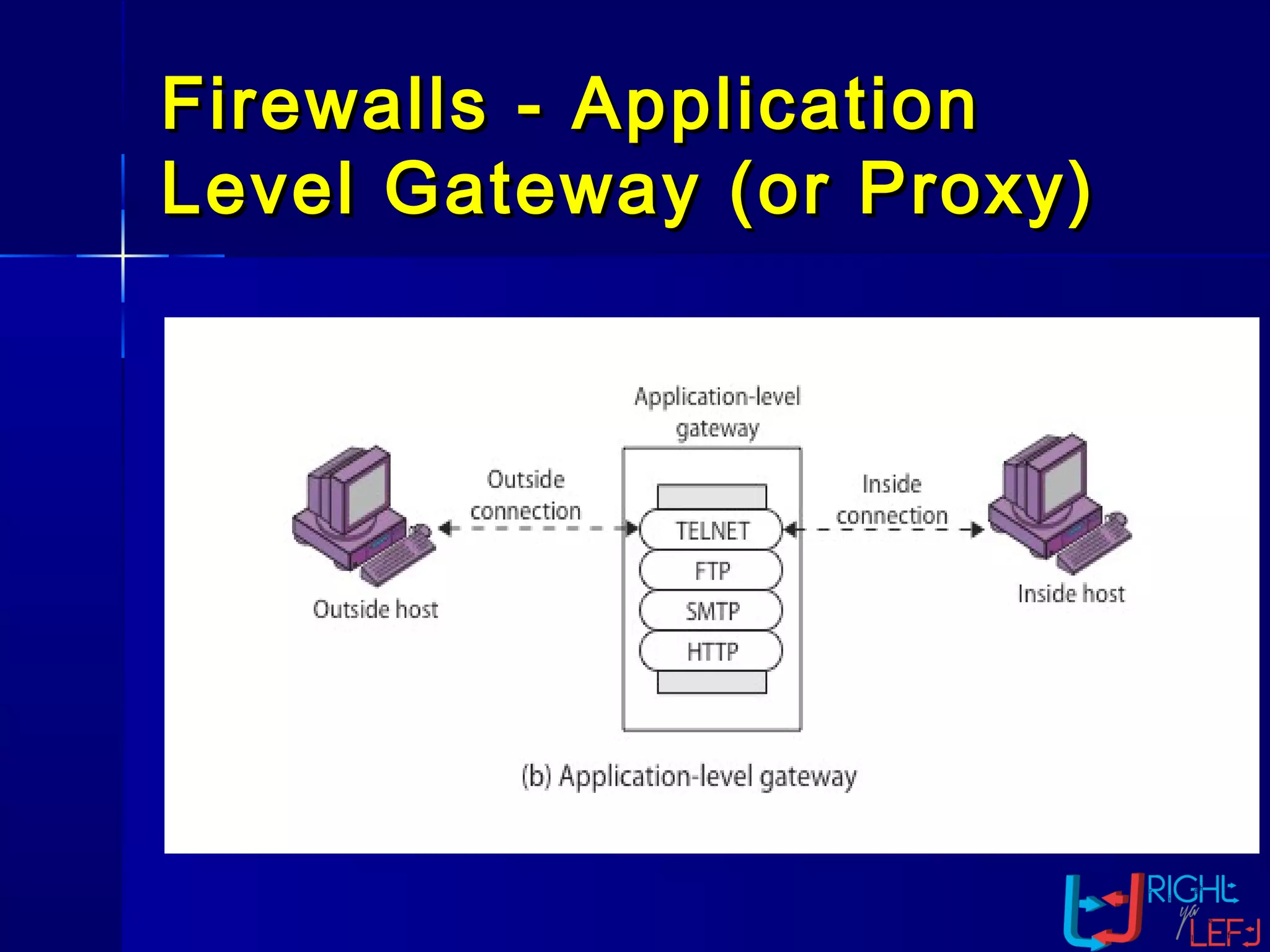
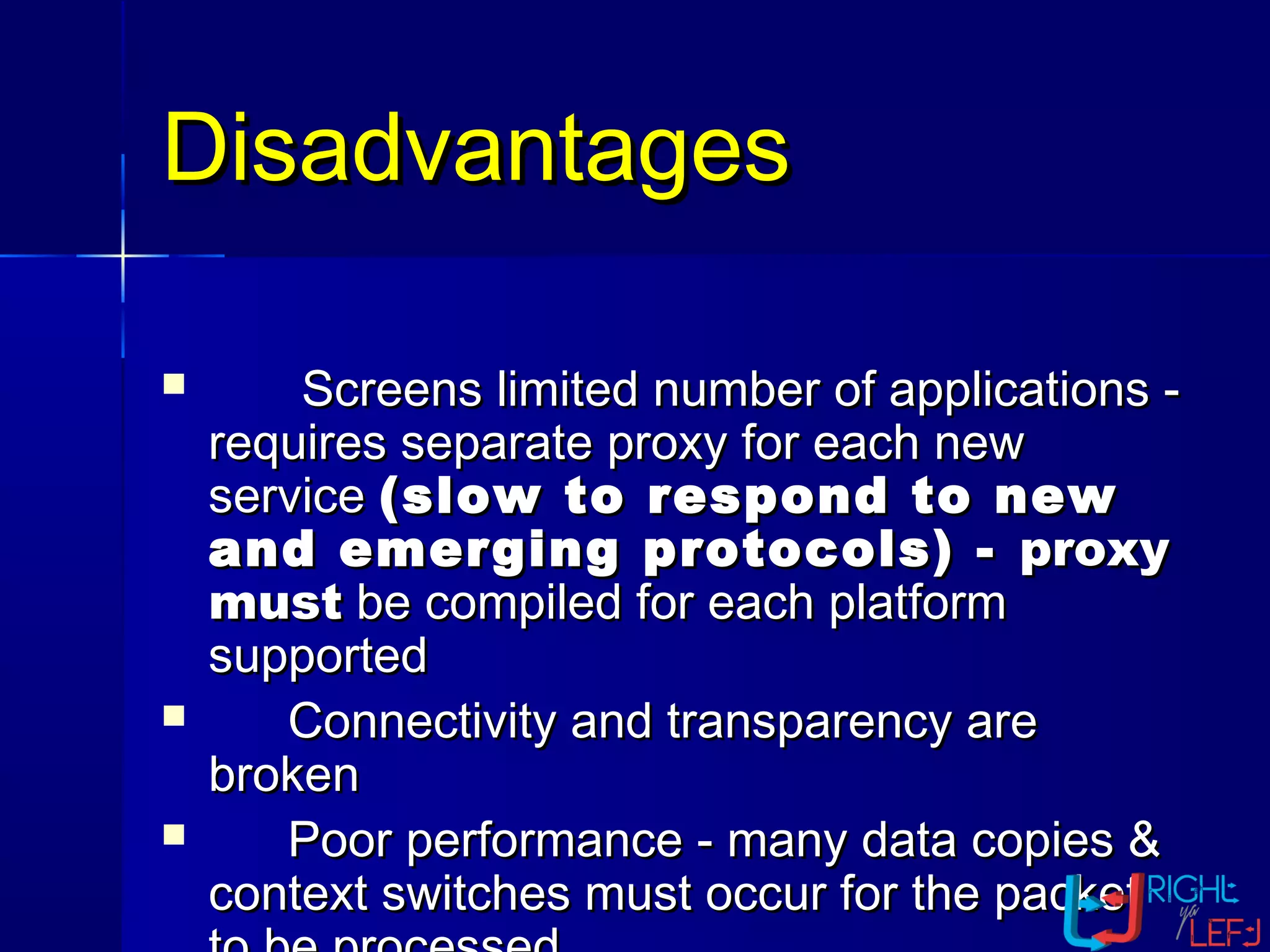
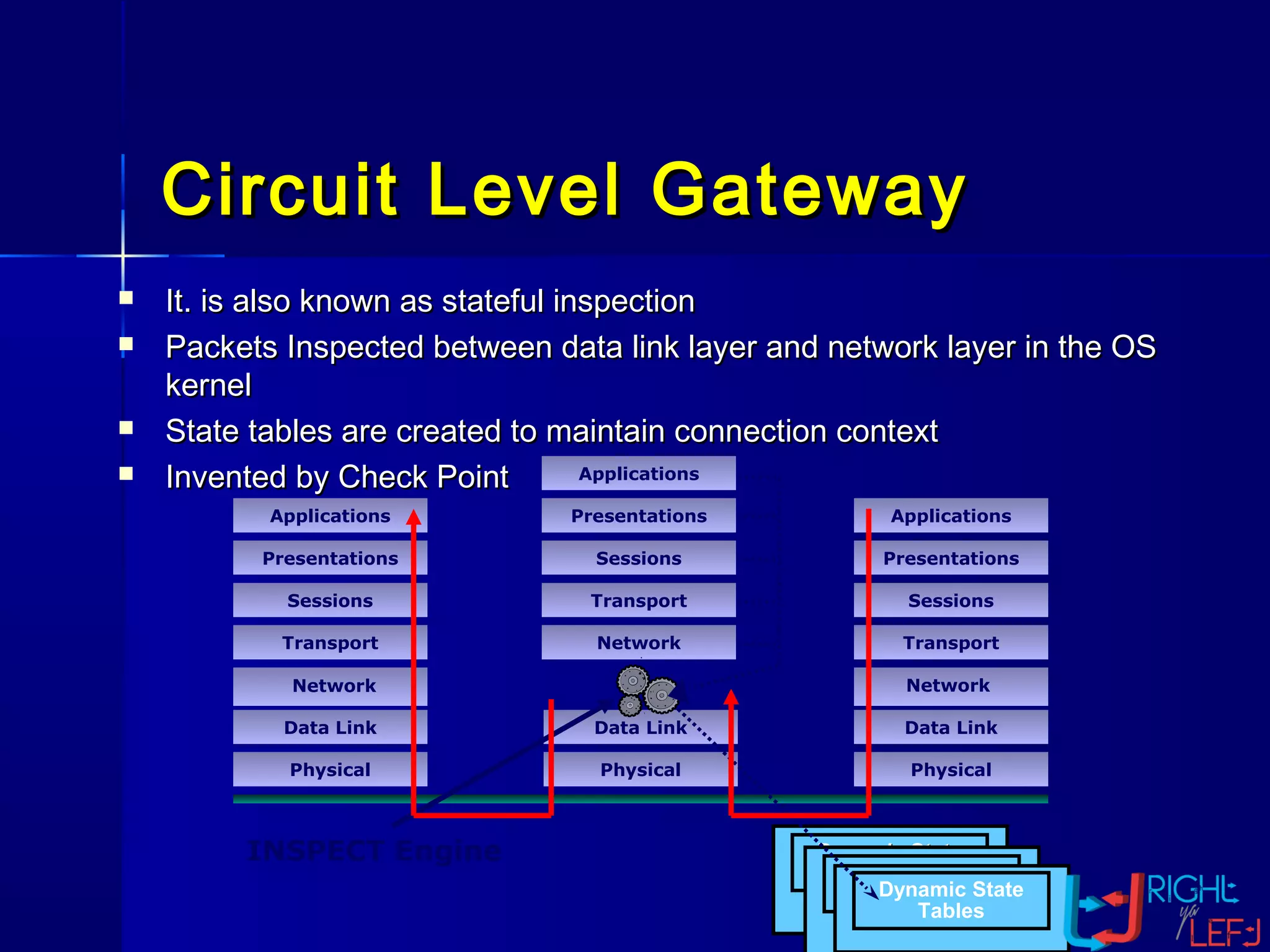
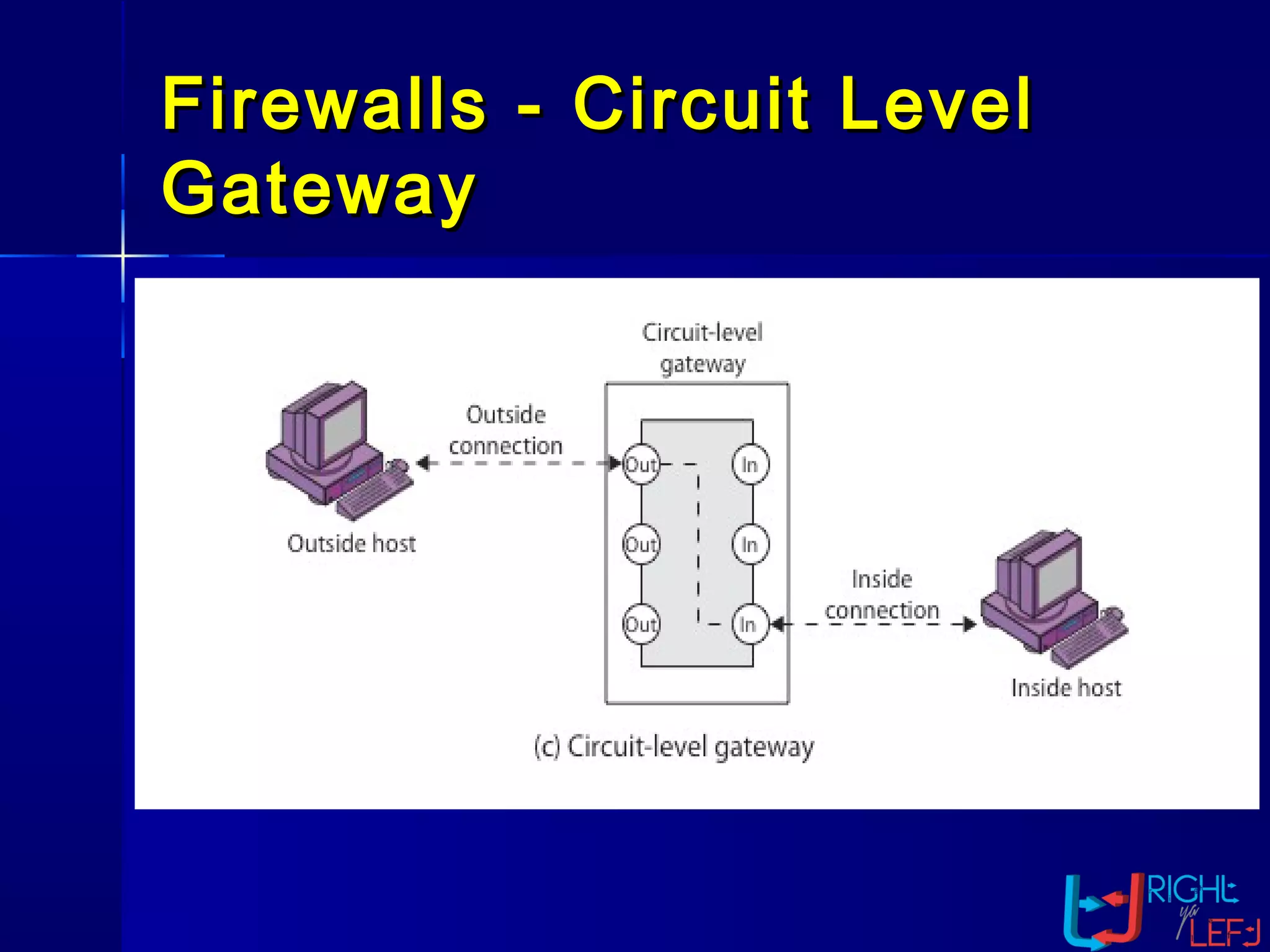
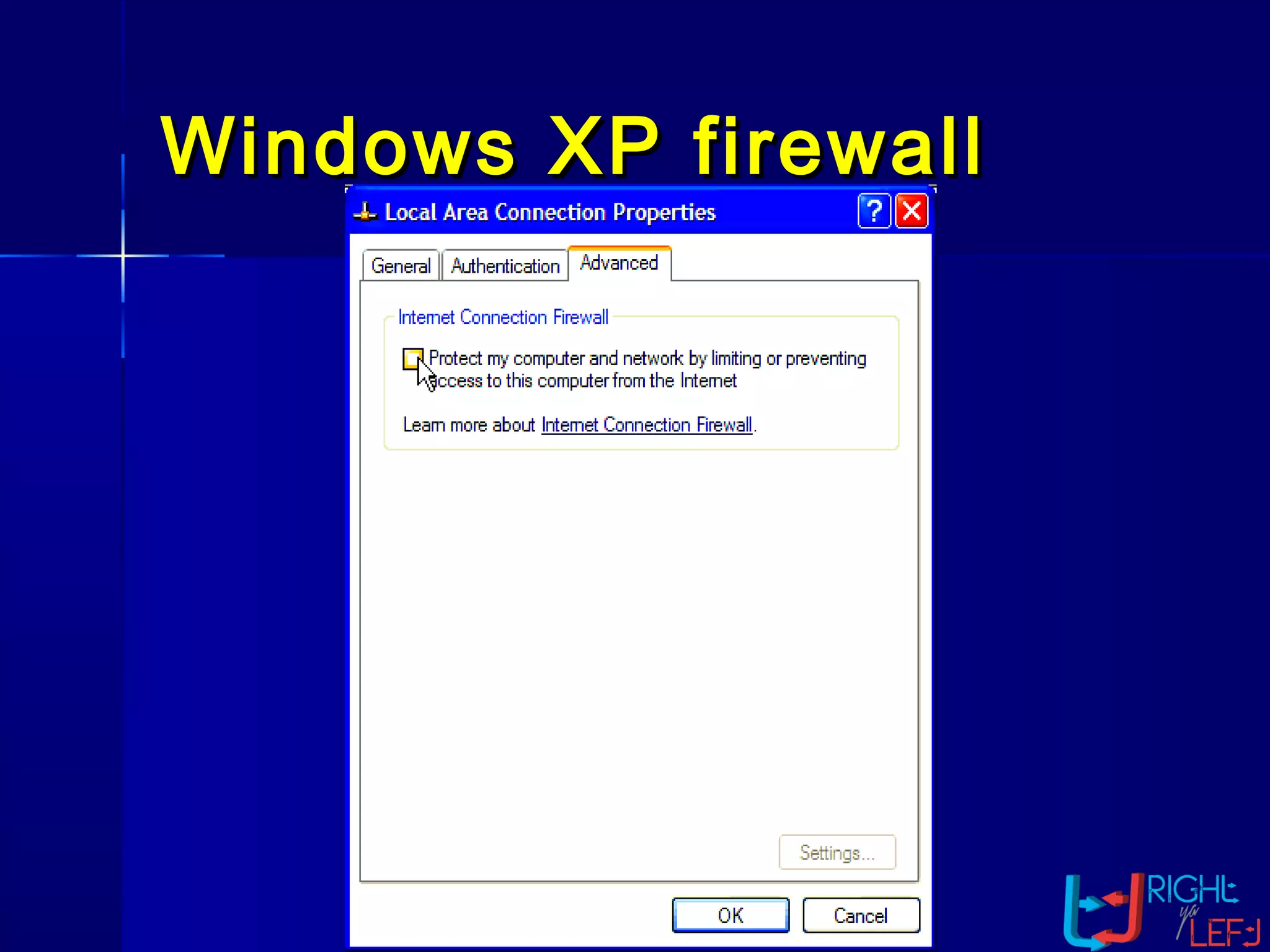
The document outlines the concept of firewalls, importance, types (including packet-filtering, application-level, and circuit-level gateways), and their distinctions between hardware and software firewalls. It discusses their protective roles against various cyber threats, appropriate uses, and personal firewalls’ capabilities and limitations. Additionally, it highlights security policy characteristics, issues with firewalls, and concludes with the need for advancements in firewall technology to improve virus scanning capabilities.