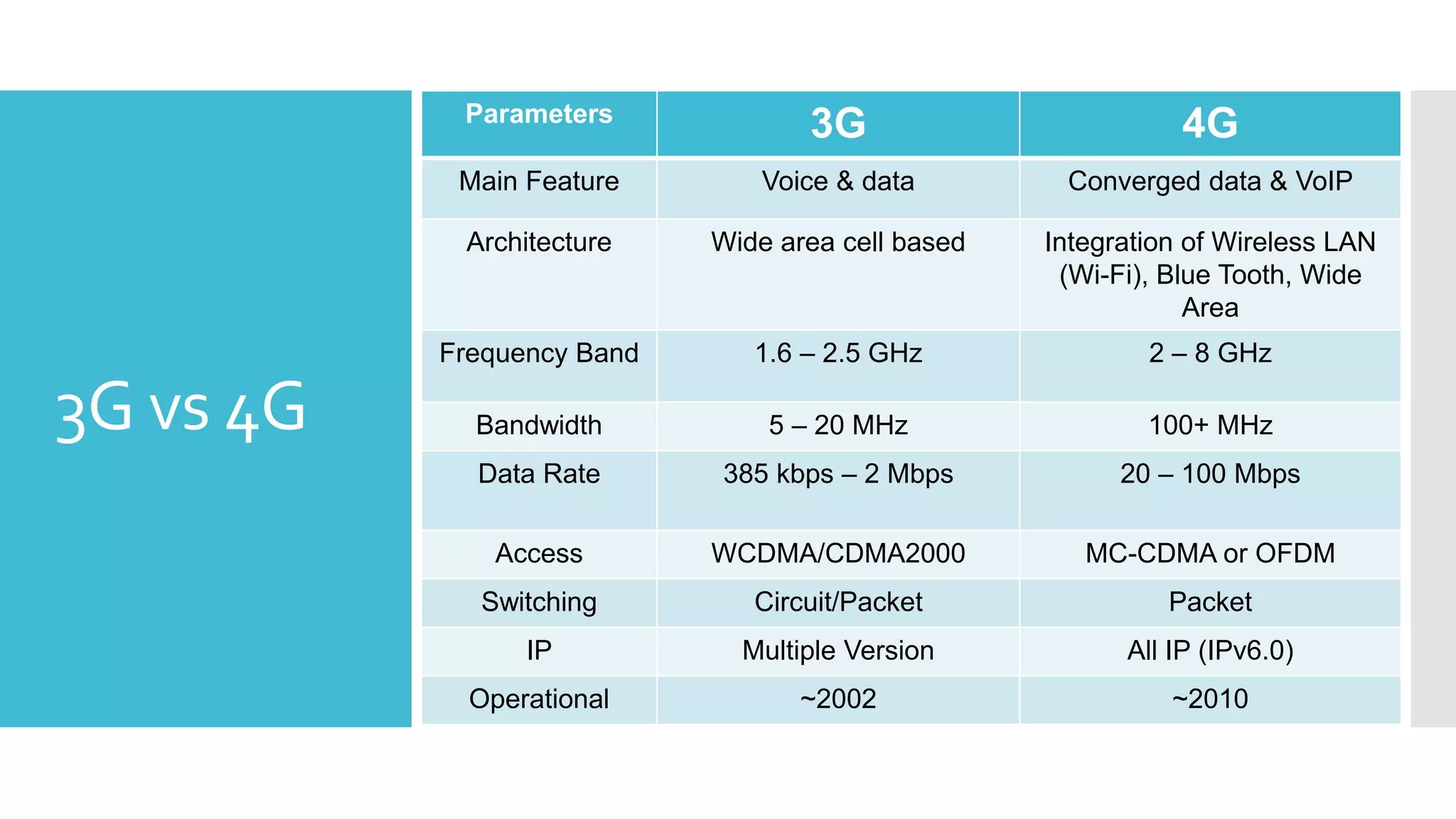
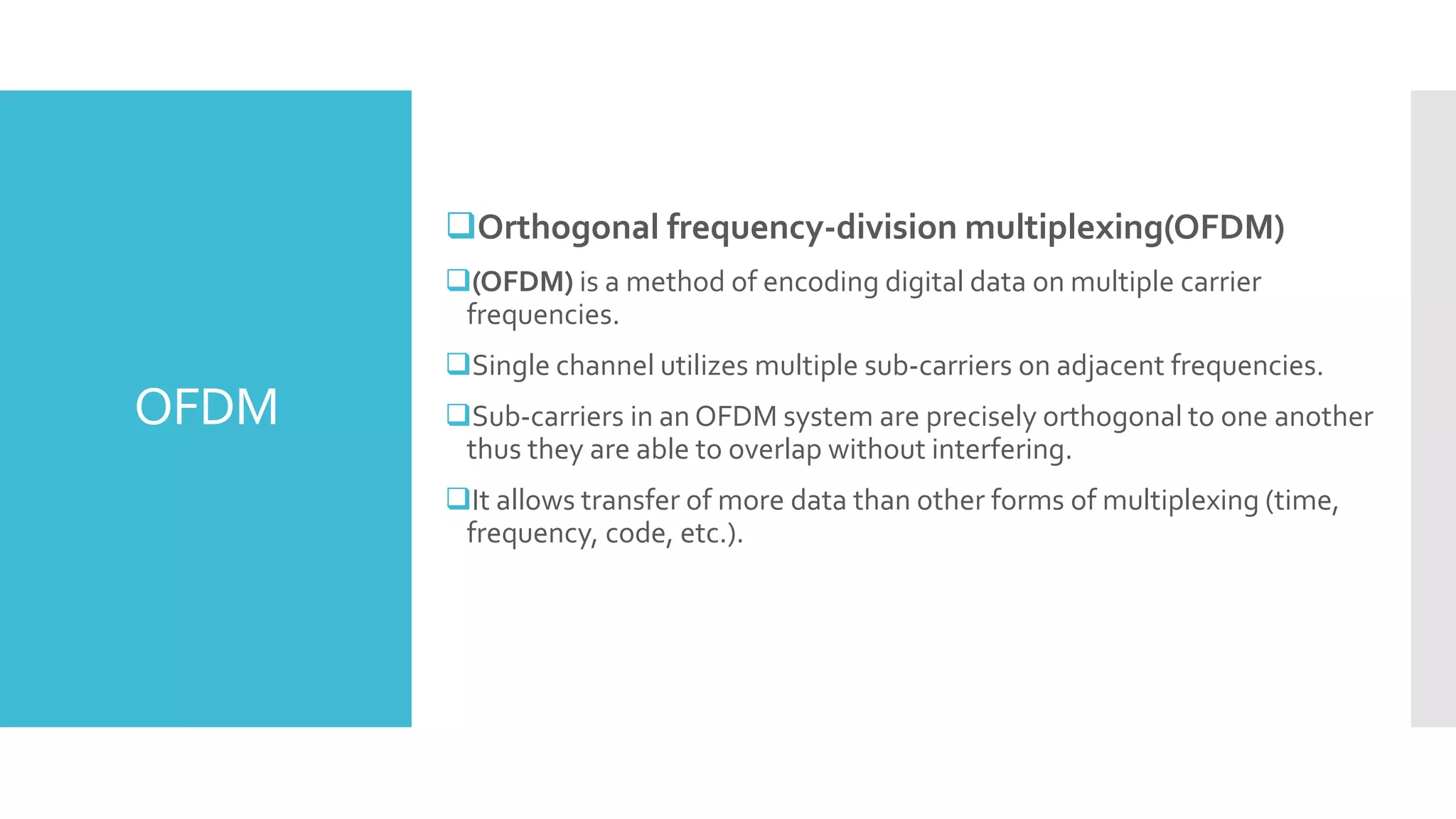
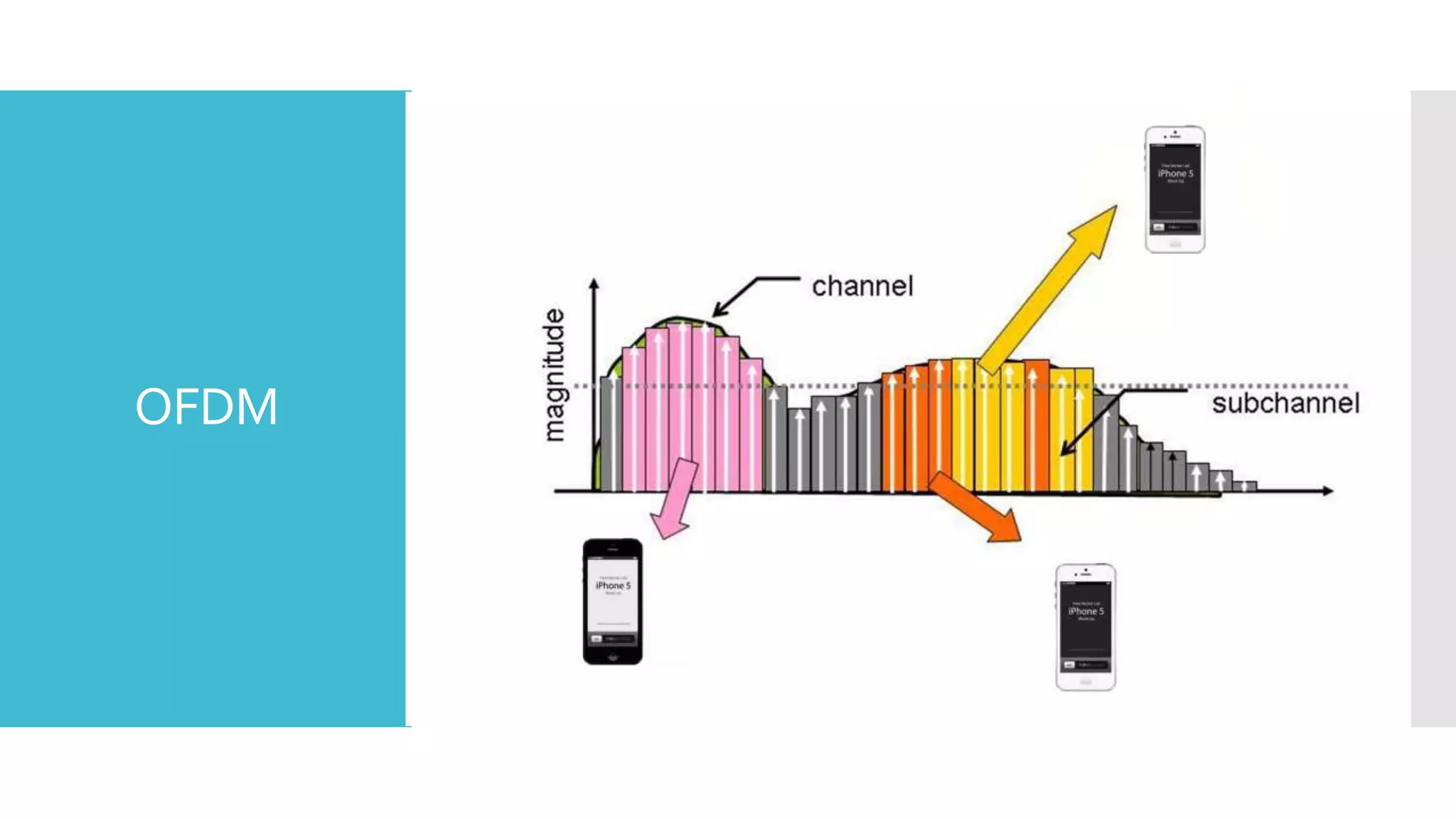
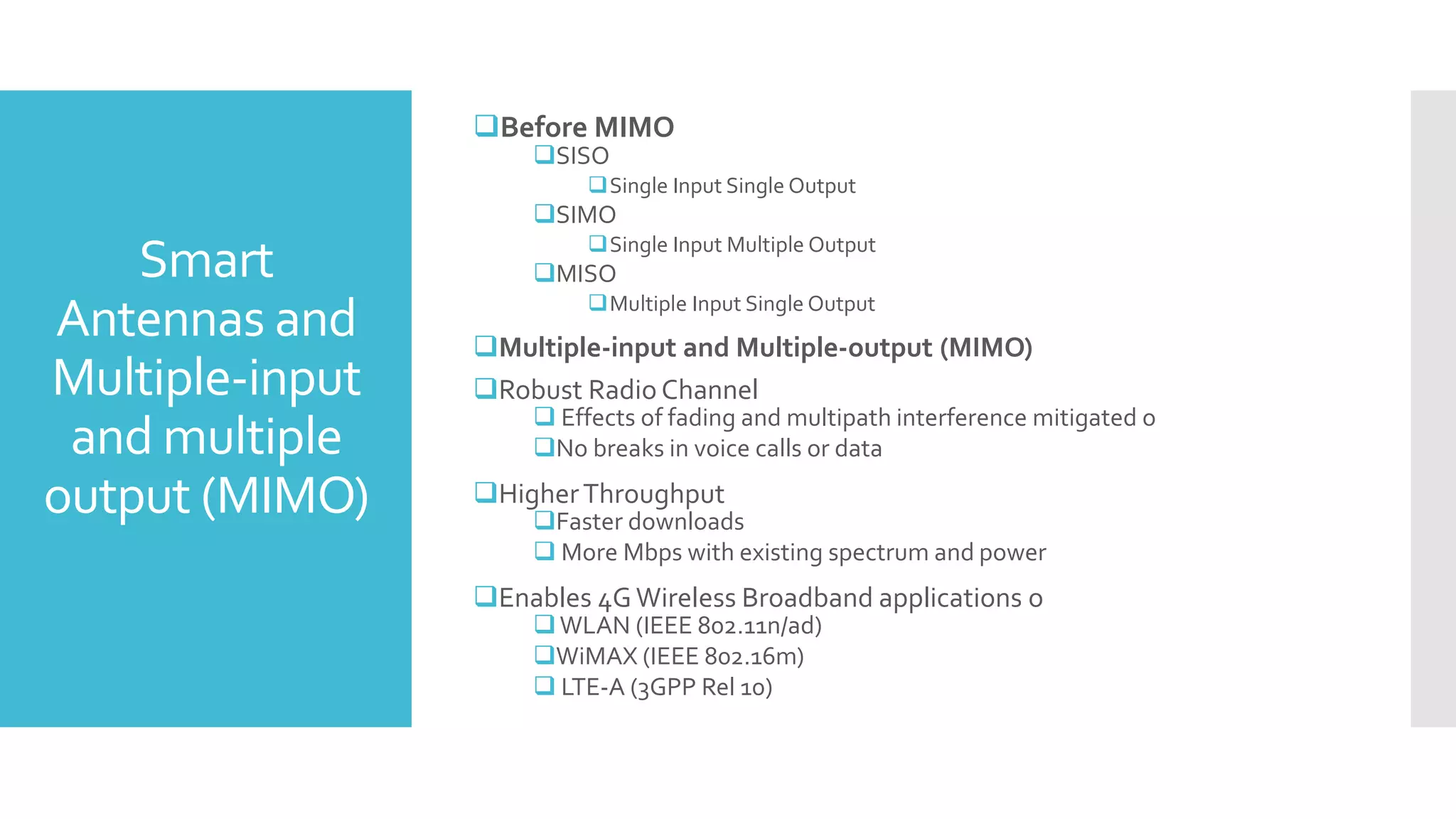
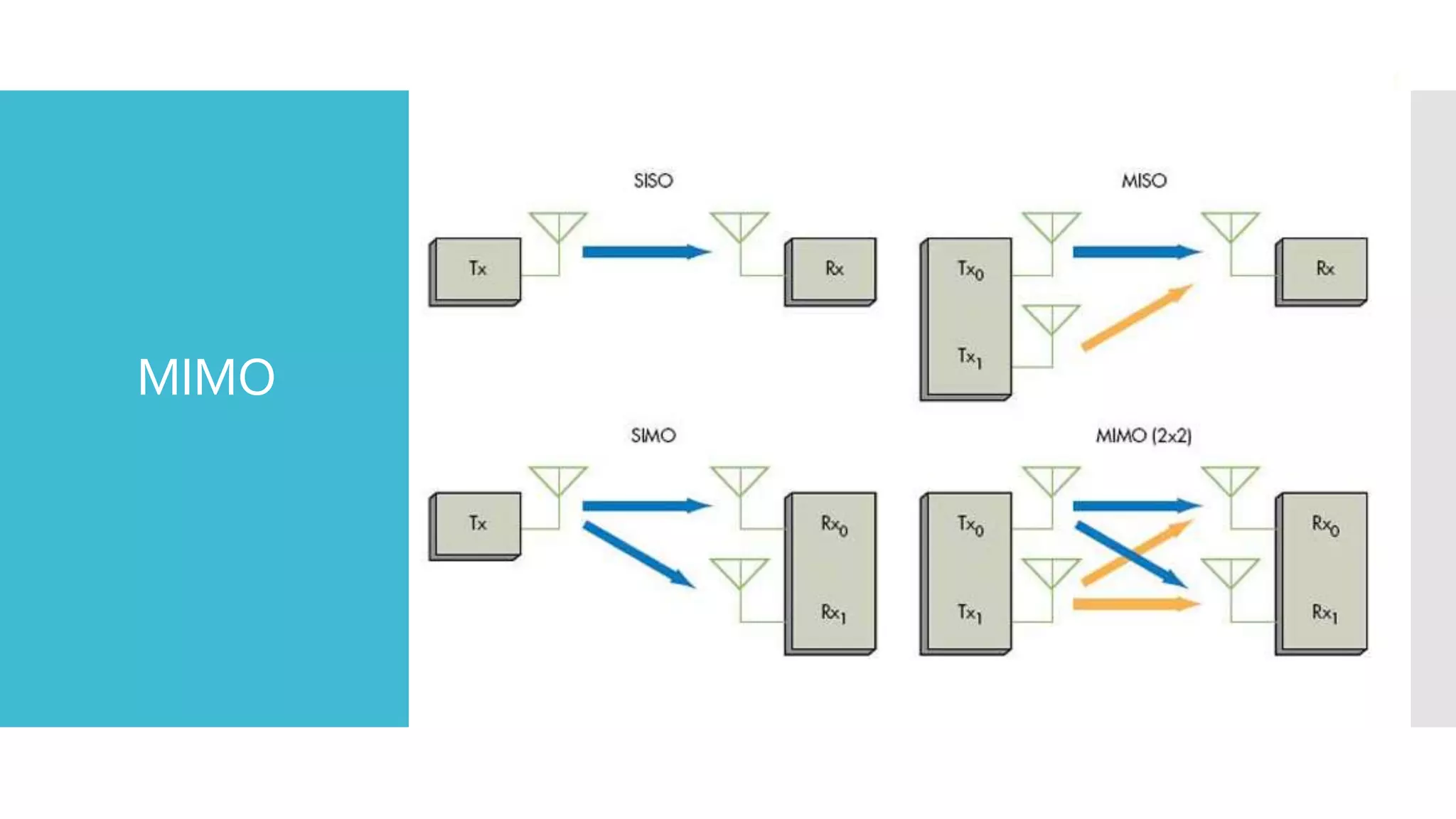
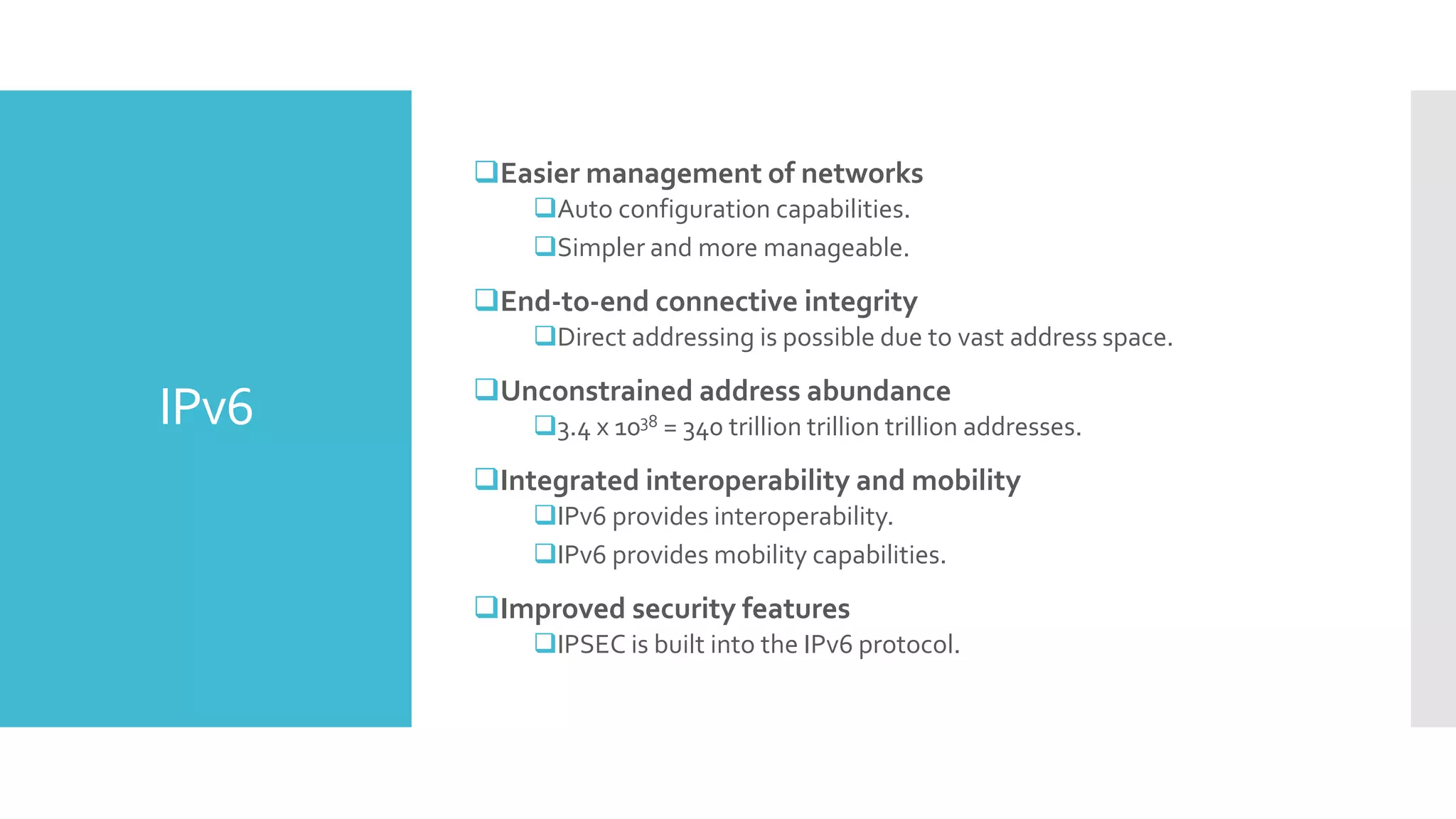
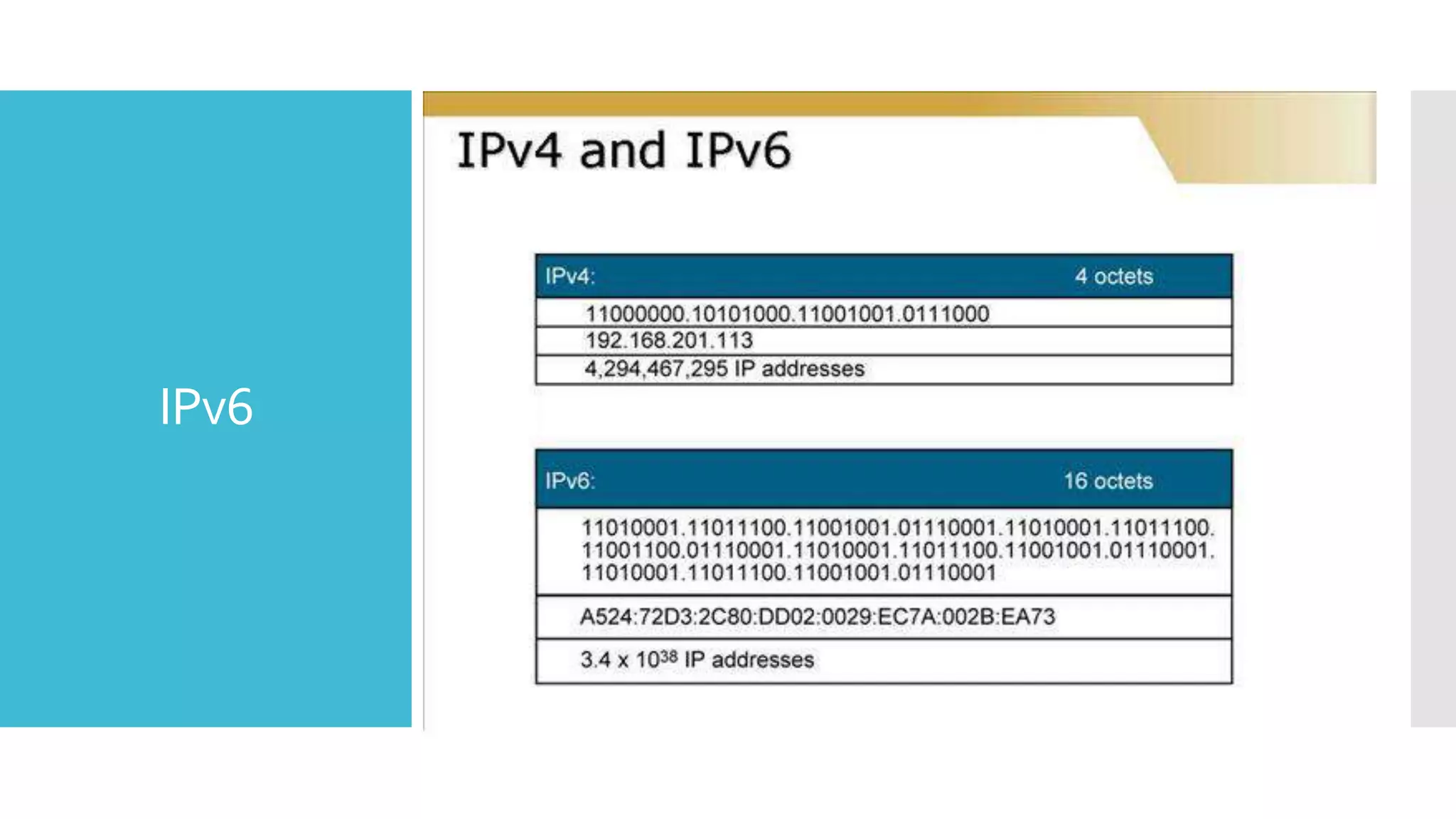
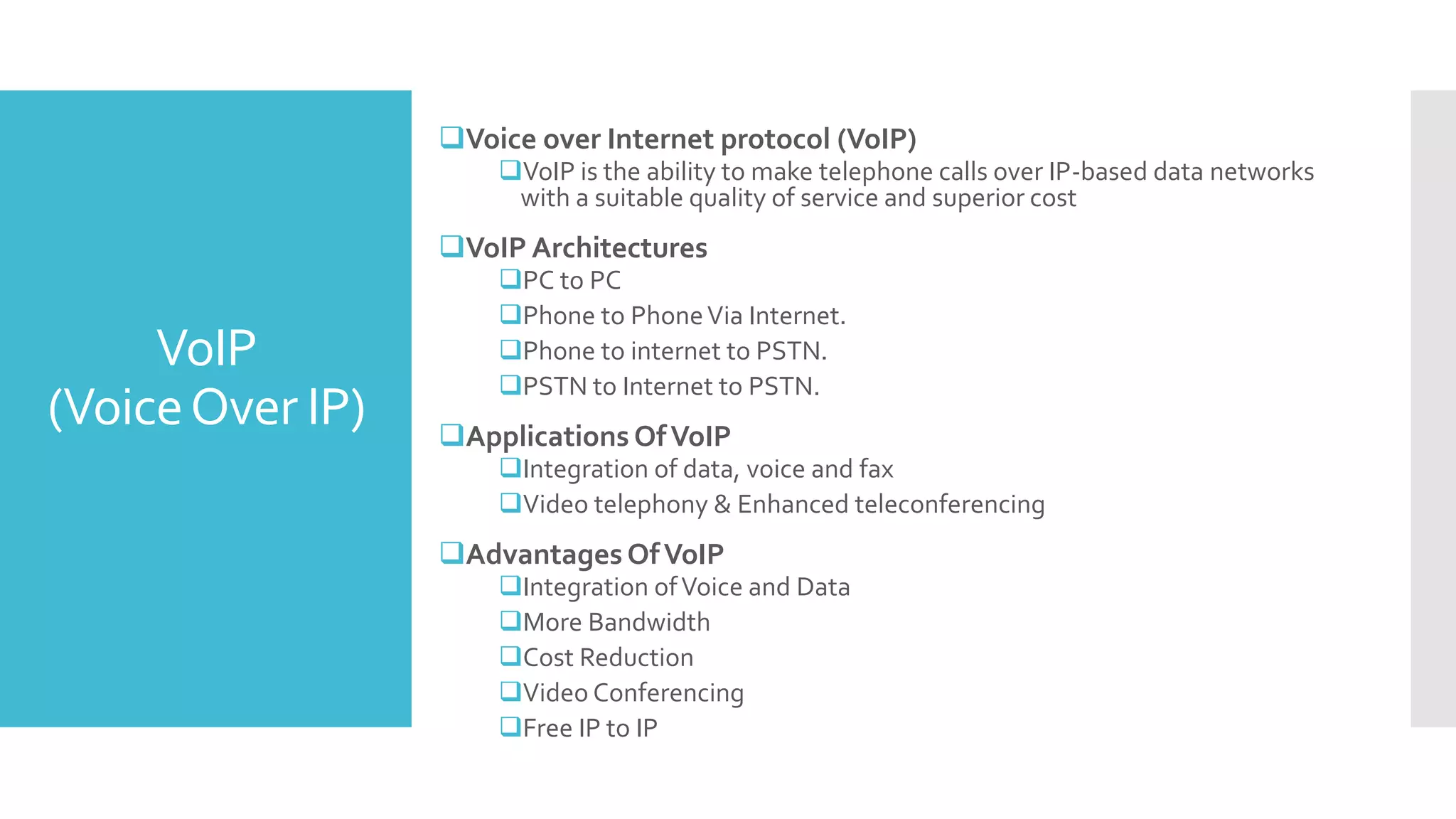
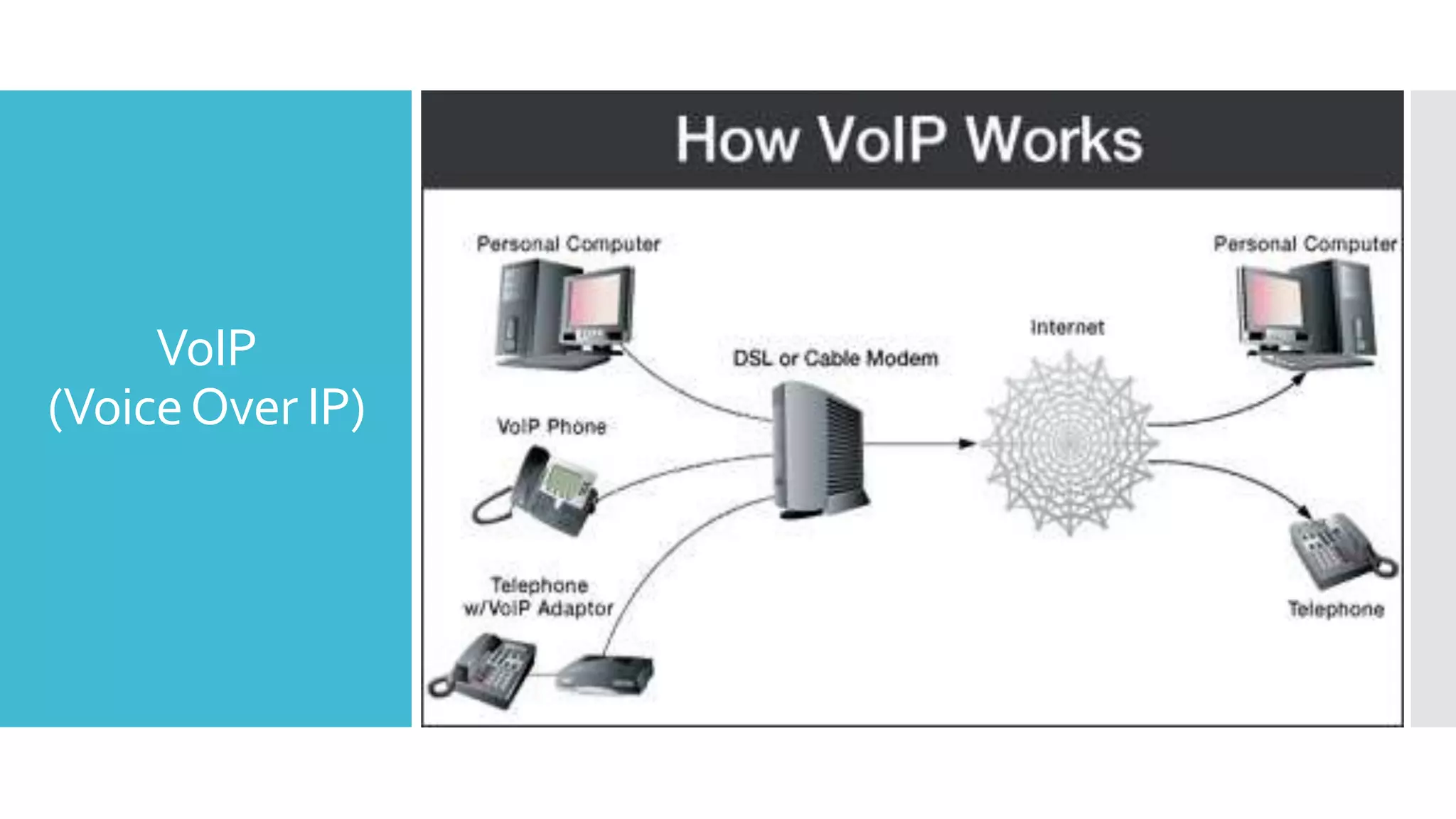
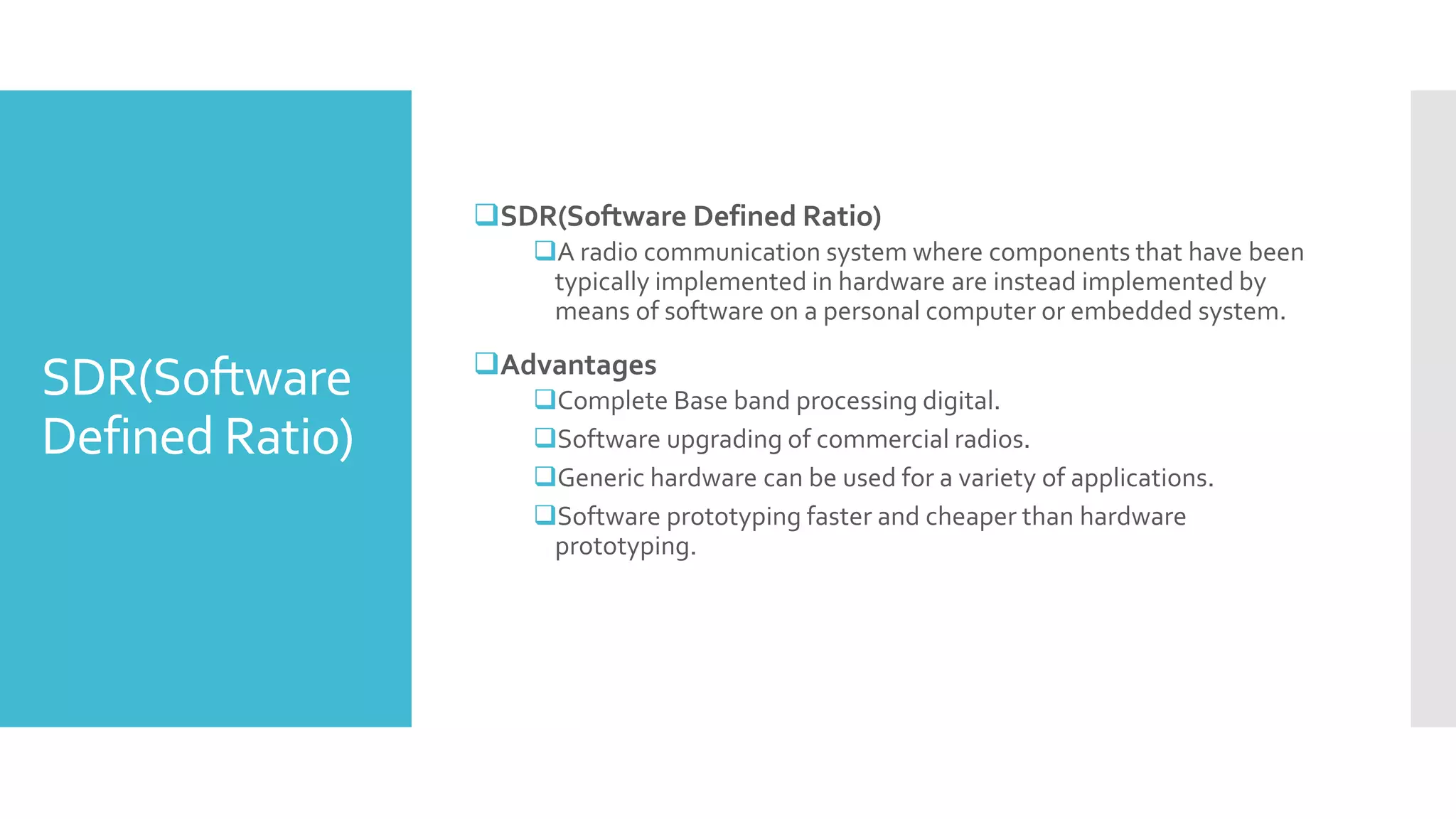
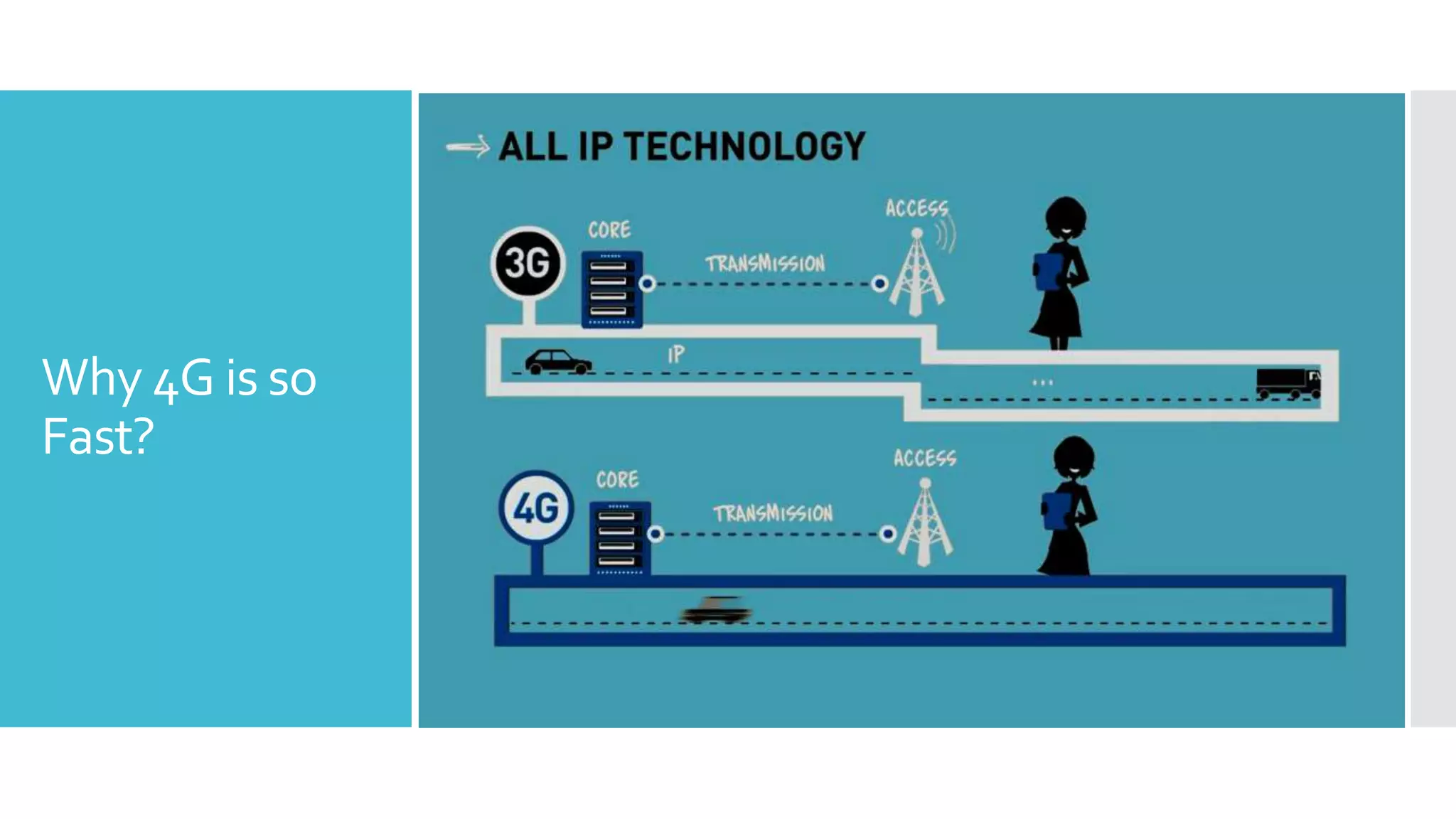
The document provides a comprehensive overview of mobile communication systems across generations, focusing primarily on the transition from 3G to 4G technology. It highlights key features, technologies, advantages, and disadvantages of 4G, as well as applications and future prospects of mobile communications. The discussion includes technical specifications, speed comparisons, and the impact of technologies like VoIP and IPv6 in enhancing mobile services.