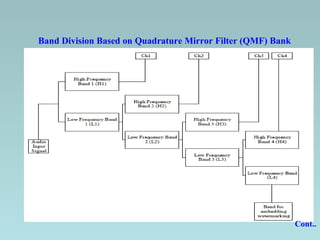
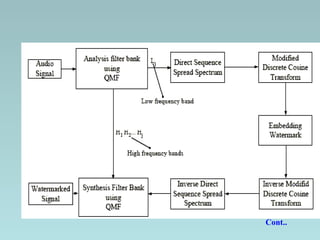
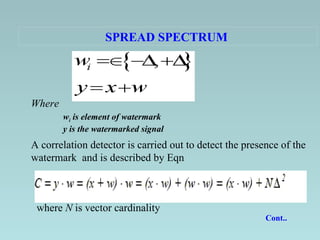
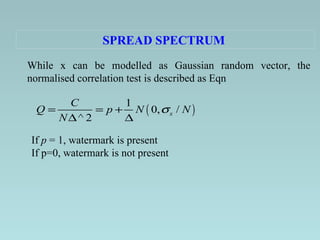
This document discusses different techniques for digital audio watermarking. It introduces audio watermarking and its aims of copy control, ownership identification, and enforcing usage policies. It then describes four main techniques - DC level shifting, frequency masking, spread spectrum, and band division based on QMF bank. It analyzes the robustness and limitations of each technique, finding that spread spectrum and band division based on QMF bank are more robust to attacks like compression but spread spectrum has better detection rates. The document concludes that audio watermarks can be embedded invisibly while still allowing extraction without the original signal.