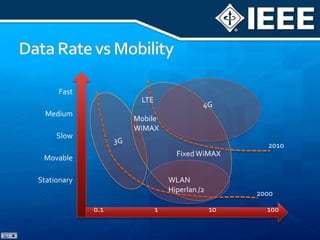
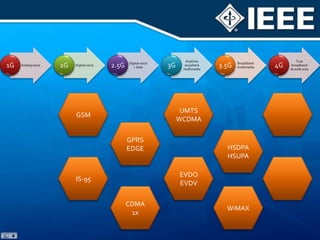
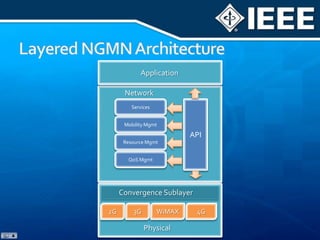
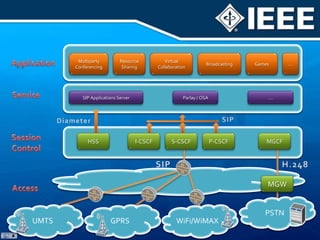
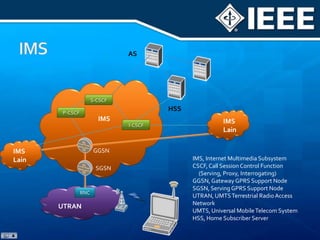
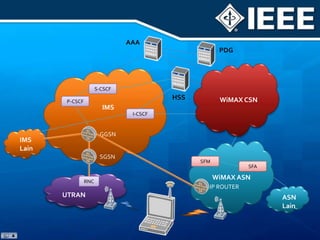
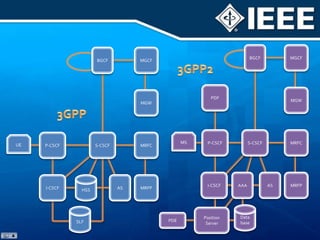
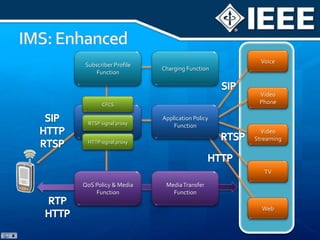
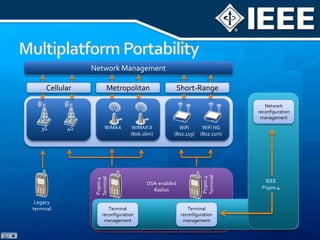
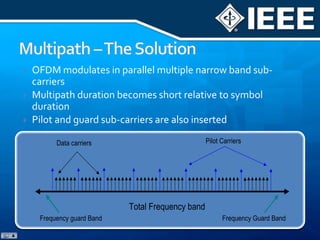
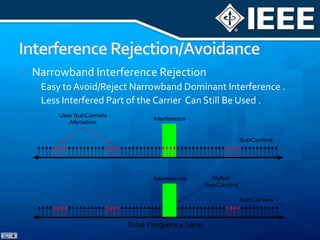
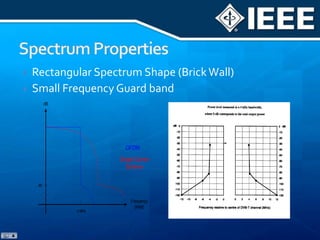
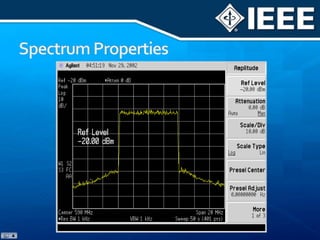
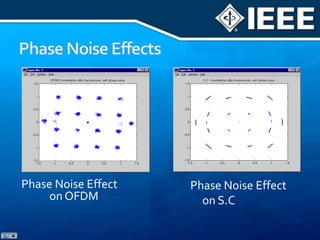
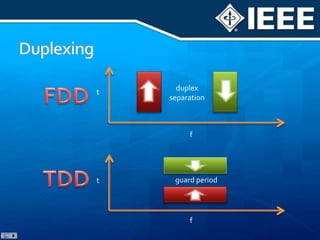
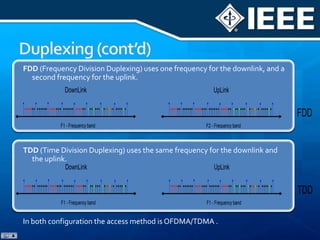
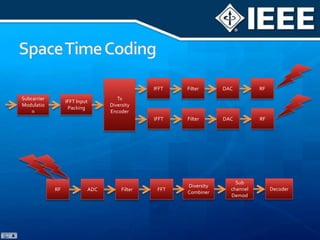
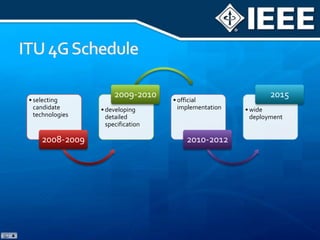
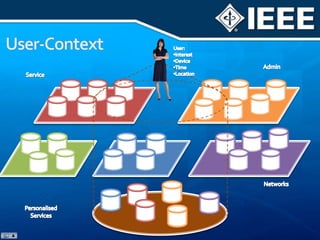
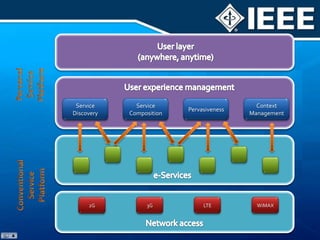
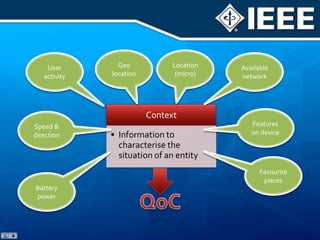
The document discusses 4G mobile technologies, emphasizing the significance of mobile data rates, interactivity, and various standards and methods such as OFDMA and MIMO in enhancing communication systems. It also addresses cognitive radio and dynamic spectrum access, detailing their roles in resource management and coexistence in wireless networks. Key advancements in mobile applications and network access methodologies are highlighted, showcasing the evolution from 2G to 4G systems.